Matrix Similarity After Cyclic Shifts
EasyUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given an m x n integer matrix mat and an integer k. The matrix rows are 0-indexed.
The following proccess happens k times:
- Even-indexed rows (0, 2, 4, ...) are cyclically shifted to the left.
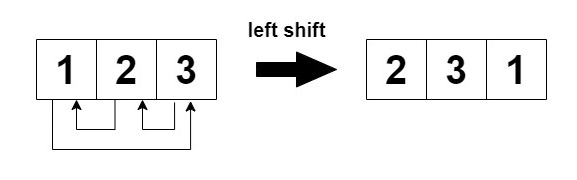
- Odd-indexed rows (1, 3, 5, ...) are cyclically shifted to the right.
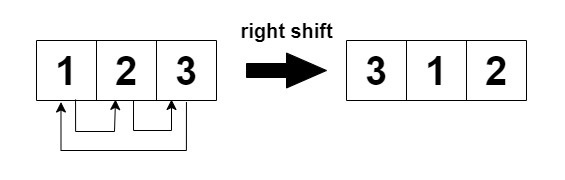
Return true if the final modified matrix after k steps is identical to the original matrix, and false otherwise.
Examples
Example 1
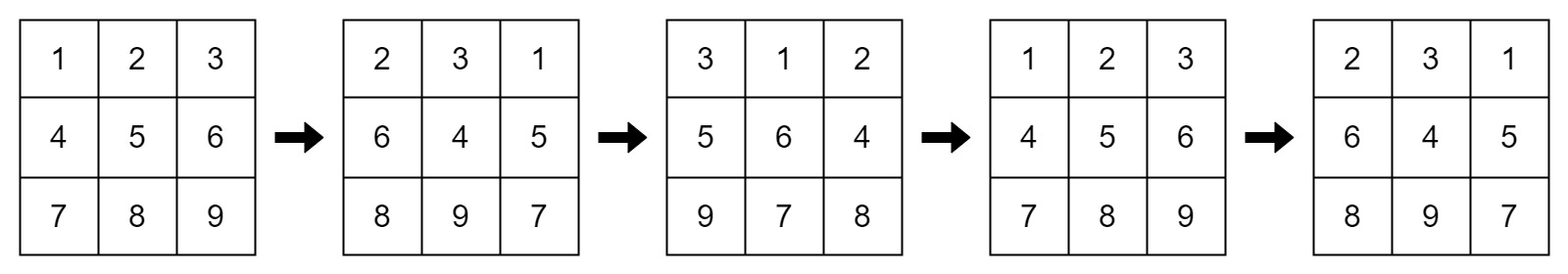
Input: mat = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 4
Output: false
Explanation:
In each step left shift is applied to rows 0 and 2 (even indices), and right
shift to row 1 (odd index).
Example 2
Input: mat = [[1,2,1,2],[5,5,5,5],[6,3,6,3]], k = 2
Output: true
Explanation:
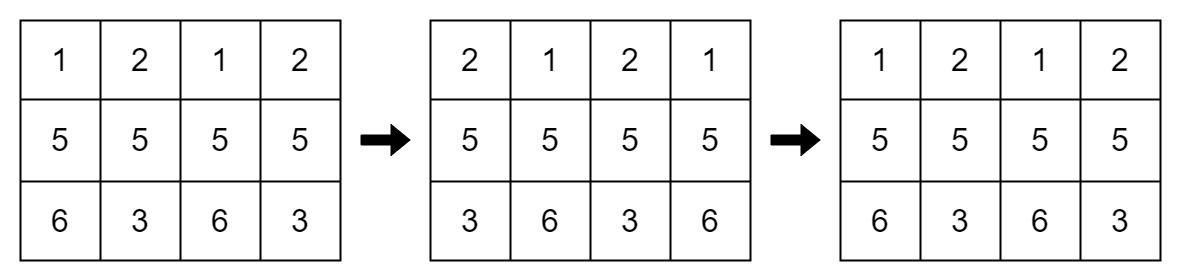
Example 3
Input: mat = [[2,2],[2,2]], k = 3
Output: true
Explanation:
As all the values are equal in the matrix, even after performing cyclic shifts
the matrix will remain the same.
Constraints
1 <= mat.length <= 251 <= mat[i].length <= 251 <= mat[i][j] <= 251 <= k <= 50
Solution
Method 1 – Simulation with Modulo Shifts
Intuition
Each row is shifted left or right cyclically, depending on its index parity, for k times. After all shifts, we compare the resulting matrix to the original. Since shifting by the row length is a full cycle, we use modulo to optimize the number of shifts.
Approach
- For each row in the matrix:
- If the row index is even, shift left by
k % npositions. - If the row index is odd, shift right by
k % npositions.
- If the row index is even, shift left by
- After all shifts, compare the resulting matrix to the original.
- Return
trueif they are identical, elsefalse.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool areSimilar(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int k) {
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
vector<int> row(n);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int idx = (i % 2 == 0) ? (j + k) % n : (j - k + n) % n;
row[j] = mat[i][idx];
}
if (row != mat[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
Go
func areSimilar(mat [][]int, k int) bool {
m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0])
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
row := make([]int, n)
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
var idx int
if i%2 == 0 {
idx = (j + k) % n
} else {
idx = (j - k + n) % n
}
row[j] = mat[i][idx]
}
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if row[j] != mat[i][j] {
return false
}
}
}
return true
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean areSimilar(int[][] mat, int k) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int[] row = new int[n];
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int idx = (i % 2 == 0) ? (j + k) % n : (j - k + n) % n;
row[j] = mat[i][idx];
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (row[j] != mat[i][j]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun areSimilar(mat: Array<IntArray>, k: Int): Boolean {
val m = mat.size
val n = mat[0].size
for (i in 0 until m) {
val row = IntArray(n)
for (j in 0 until n) {
val idx = if (i % 2 == 0) (j + k) % n else (j - k + n) % n
row[j] = mat[i][idx]
}
if (!row.contentEquals(mat[i])) return false
}
return true
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def areSimilar(self, mat: list[list[int]], k: int) -> bool:
m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0])
for i in range(m):
row = [(mat[i][(j + k) % n] if i % 2 == 0 else mat[i][(j - k) % n]) for j in range(n)]
if row != mat[i]:
return False
return True
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn are_similar(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>, k: i32) -> bool {
let m = mat.len();
let n = mat[0].len();
for i in 0..m {
let mut row = vec![0; n];
for j in 0..n {
let idx = if i % 2 == 0 {
(j + k as usize) % n
} else {
(j + n - (k as usize % n)) % n
};
row[j] = mat[i][idx];
}
if row != mat[i] {
return false;
}
}
true
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
areSimilar(mat: number[][], k: number): boolean {
const m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
const row = new Array(n);
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
const idx = i % 2 === 0 ? (j + k) % n : (j - k + n) % n;
row[j] = mat[i][idx];
}
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (row[j] !== mat[i][j]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(mn), wheremandnare the matrix dimensions, as we process each cell once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the temporary row array.