Max Sum of Rectangle No Larger Than K
HardUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Max Sum of Rectangle No Larger Than K Problem
Problem
Given an m x n matrix matrix and an integer k, return the max sum of a rectangle in the matrix such that its sum is no larger than k.
It is guaranteed that there will be a rectangle with a sum no larger than k.
Examples
Example 1:
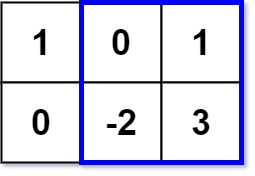
Input:
matrix = [[1,0,1],[0,-2,3]], k = 2
Output:
2
Explanation: Because the sum of the blue rectangle [[0, 1], [-2, 3]] is 2, and 2 is the max number no larger than k (k = 2).
Example 2:
Input:
matrix = [[2,2,-1]], k = 3
Output:
3
Solution
Method 1 – Prefix Sum + Binary Search
Intuition
We reduce the 2D problem to a series of 1D subarray sum problems by fixing two rows and compressing the columns between them. For each compressed array, we use prefix sums and binary search to find the max subarray sum no larger than k.
Approach
- For each pair of rows (top and bottom):
- Compress the matrix between these rows into a 1D array of column sums.
- For the compressed array:
- Use prefix sums and a sorted list to find the max subarray sum no larger than k.
- For each prefix sum, use binary search to find the smallest prefix so that current_sum - prefix <= k.
- Track the maximum found for all row pairs.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxSumSubmatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int k) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size(), ans = INT_MIN;
for (int top = 0; top < m; ++top) {
vector<int> colSum(n);
for (int bottom = top; bottom < m; ++bottom) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) colSum[j] += matrix[bottom][j];
set<int> s = {0};
int sum = 0;
for (int x : colSum) {
sum += x;
auto it = s.lower_bound(sum - k);
if (it != s.end()) ans = max(ans, sum - *it);
s.insert(sum);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func maxSumSubmatrix(matrix [][]int, k int) int {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
ans := -1 << 31
for top := 0; top < m; top++ {
colSum := make([]int, n)
for bottom := top; bottom < m; bottom++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
colSum[j] += matrix[bottom][j]
}
s := []int{0}
sum := 0
for _, x := range colSum {
sum += x
idx := sort.SearchInts(s, sum-k)
if idx < len(s) {
if sum-s[idx] > ans {
ans = sum - s[idx]
}
}
s = append(s, sum)
sort.Ints(s)
}
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int maxSumSubmatrix(int[][] matrix, int k) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length, ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int top = 0; top < m; ++top) {
int[] colSum = new int[n];
for (int bottom = top; bottom < m; ++bottom) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) colSum[j] += matrix[bottom][j];
TreeSet<Integer> s = new TreeSet<>();
s.add(0);
int sum = 0;
for (int x : colSum) {
sum += x;
Integer it = s.ceiling(sum - k);
if (it != null) ans = Math.max(ans, sum - it);
s.add(sum);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maxSumSubmatrix(matrix: Array<IntArray>, k: Int): Int {
val m = matrix.size
val n = matrix[0].size
var ans = Int.MIN_VALUE
for (top in 0 until m) {
val colSum = IntArray(n)
for (bottom in top until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) colSum[j] += matrix[bottom][j]
val s = java.util.TreeSet<Int>()
s.add(0)
var sum = 0
for (x in colSum) {
sum += x
val it = s.ceiling(sum - k)
if (it != null) ans = maxOf(ans, sum - it)
s.add(sum)
}
}
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maxSumSubmatrix(self, matrix: list[list[int]], k: int) -> int:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
ans = float('-inf')
for top in range(m):
col_sum = [0] * n
for bottom in range(top, m):
for j in range(n):
col_sum[j] += matrix[bottom][j]
s = [0]
curr_sum = 0
for x in col_sum:
curr_sum += x
idx = bisect_left(s, curr_sum - k)
if idx < len(s):
ans = max(ans, curr_sum - s[idx])
insort(s, curr_sum)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn max_sum_submatrix(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>, k: i32) -> i32 {
let m = matrix.len();
let n = matrix[0].len();
let mut ans = i32::MIN;
for top in 0..m {
let mut col_sum = vec![0; n];
for bottom in top..m {
for j in 0..n {
col_sum[j] += matrix[bottom][j];
}
let mut s = vec![0];
let mut sum = 0;
for &x in &col_sum {
sum += x;
if let Ok(idx) = s.binary_search(&(sum - k)) {
ans = ans.max(sum - s[idx]);
} else if let Err(idx) = s.binary_search(&(sum - k)) {
if idx < s.len() {
ans = ans.max(sum - s[idx]);
}
}
s.push(sum);
s.sort();
}
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maxSumSubmatrix(matrix: number[][], k: number): number {
const m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
let ans = -Infinity;
for (let top = 0; top < m; ++top) {
const colSum = Array(n).fill(0);
for (let bottom = top; bottom < m; ++bottom) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) colSum[j] += matrix[bottom][j];
const s = [0];
let sum = 0;
for (const x of colSum) {
sum += x;
let idx = s.findIndex(v => v >= sum - k);
if (idx !== -1) ans = Math.max(ans, sum - s[idx]);
s.push(sum);
s.sort((a, b) => a - b);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m^2 n log n)— For each pair of rows, we process columns and use binary search for prefix sums. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)— For column sums and prefix sum set.