Maximize Area of Square Hole in Grid
Problem
You are given the two integers, n and m and two integer arrays, hBars
and vBars. The grid has n + 2 horizontal and m + 2 vertical bars, creating 1 x 1 unit cells. The bars are indexed starting from 1.
You can remove some of the bars in hBars from horizontal bars and some of the bars in vBars from vertical bars. Note that other bars are fixed and cannot be removed.
Return an integer denoting the maximum area of a square-shaped hole in the grid, after removing some bars (possibly none).
Examples
Example 1
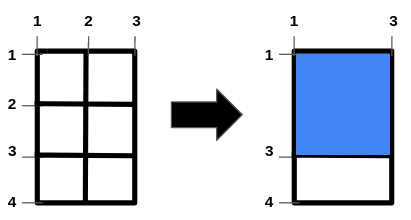
Input: n = 2, m = 1, hBars = [2,3], vBars = [2]
Output: 4
Explanation:
The left image shows the initial grid formed by the bars. The horizontal bars
are `[1,2,3,4]`, and the vertical bars are `[1,2,3]`.
One way to get the maximum square-shaped hole is by removing horizontal bar 2
and vertical bar 2.
Example 2
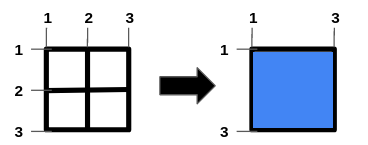
Input: n = 1, m = 1, hBars = [2], vBars = [2]
Output: 4
Explanation:
To get the maximum square-shaped hole, we remove horizontal bar 2 and vertical
bar 2.
Example 3
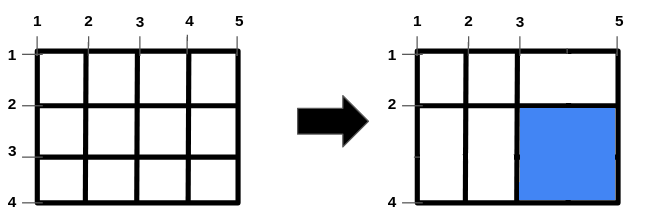
Input: n = 2, m = 3, hBars = [2,3], vBars = [2,4]
Output: 4
Explanation:
One way to get the maximum square-shaped hole is by removing horizontal bar 3,
and vertical bar 4.
Constraints
1 <= n <= 10^91 <= m <= 10^91 <= hBars.length <= 1002 <= hBars[i] <= n + 11 <= vBars.length <= 1002 <= vBars[i] <= m + 1- All values in
hBarsare distinct. - All values in
vBarsare distinct.
Solution
Method 1 – Consecutive Bars and Maximum Gap
Intuition
The largest square hole is formed by removing consecutive horizontal and vertical bars, creating the largest possible gap between remaining bars. The side of the largest square is determined by the maximum number of consecutive removed bars plus one (since a gap of k bars removed creates a hole of size k+1).
Approach
- Sort
hBarsandvBars. - Find the largest number of consecutive horizontal bars removed (i.e., the largest streak where each next bar is exactly 1 more than the previous).
- For each streak, the possible square side is its length + 1.
- Do the same for vertical bars.
- The answer is the square of the minimum of the two maximum streaks (since the square must fit both horizontally and vertically).
- Return the area.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maximizeSquareArea(int n, int m, vector<int>& hBars, vector<int>& vBars) {
sort(hBars.begin(), hBars.end());
sort(vBars.begin(), vBars.end());
int maxH = 1, curH = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < hBars.size(); ++i) {
if (hBars[i] == hBars[i-1] + 1) curH++;
else curH = 1;
maxH = max(maxH, curH);
}
int maxV = 1, curV = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < vBars.size(); ++i) {
if (vBars[i] == vBars[i-1] + 1) curV++;
else curV = 1;
maxV = max(maxV, curV);
}
int side = min(maxH, maxV) + 1;
return side * side;
}
};
Go
func maximizeSquareArea(n int, m int, hBars []int, vBars []int) int {
sort.Ints(hBars)
sort.Ints(vBars)
maxH, curH := 1, 1
for i := 1; i < len(hBars); i++ {
if hBars[i] == hBars[i-1]+1 {
curH++
} else {
curH = 1
}
if curH > maxH {
maxH = curH
}
}
maxV, curV := 1, 1
for i := 1; i < len(vBars); i++ {
if vBars[i] == vBars[i-1]+1 {
curV++
} else {
curV = 1
}
if curV > maxV {
maxV = curV
}
}
side := maxH
if maxV < maxH {
side = maxV
}
return (side + 1) * (side + 1)
}
Java
class Solution {
public int maximizeSquareArea(int n, int m, int[] hBars, int[] vBars) {
Arrays.sort(hBars);
Arrays.sort(vBars);
int maxH = 1, curH = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < hBars.length; i++) {
if (hBars[i] == hBars[i-1] + 1) curH++;
else curH = 1;
maxH = Math.max(maxH, curH);
}
int maxV = 1, curV = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < vBars.length; i++) {
if (vBars[i] == vBars[i-1] + 1) curV++;
else curV = 1;
maxV = Math.max(maxV, curV);
}
int side = Math.min(maxH, maxV) + 1;
return side * side;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maximizeSquareArea(n: Int, m: Int, hBars: IntArray, vBars: IntArray): Int {
hBars.sort()
vBars.sort()
var maxH = 1
var curH = 1
for (i in 1 until hBars.size) {
if (hBars[i] == hBars[i-1] + 1) curH++
else curH = 1
maxH = maxOf(maxH, curH)
}
var maxV = 1
var curV = 1
for (i in 1 until vBars.size) {
if (vBars[i] == vBars[i-1] + 1) curV++
else curV = 1
maxV = maxOf(maxV, curV)
}
val side = minOf(maxH, maxV) + 1
return side * side
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maximizeSquareArea(self, n: int, m: int, hBars: list[int], vBars: list[int]) -> int:
hBars.sort()
vBars.sort()
max_h = cur_h = 1
for i in range(1, len(hBars)):
if hBars[i] == hBars[i-1] + 1:
cur_h += 1
else:
cur_h = 1
max_h = max(max_h, cur_h)
max_v = cur_v = 1
for i in range(1, len(vBars)):
if vBars[i] == vBars[i-1] + 1:
cur_v += 1
else:
cur_v = 1
max_v = max(max_v, cur_v)
side = min(max_h, max_v) + 1
return side * side
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn maximize_square_area(n: i32, m: i32, mut h_bars: Vec<i32>, mut v_bars: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
h_bars.sort();
v_bars.sort();
let (mut max_h, mut cur_h) = (1, 1);
for i in 1..h_bars.len() {
if h_bars[i] == h_bars[i-1] + 1 {
cur_h += 1;
} else {
cur_h = 1;
}
max_h = max_h.max(cur_h);
}
let (mut max_v, mut cur_v) = (1, 1);
for i in 1..v_bars.len() {
if v_bars[i] == v_bars[i-1] + 1 {
cur_v += 1;
} else {
cur_v = 1;
}
max_v = max_v.max(cur_v);
}
let side = max_h.min(max_v) + 1;
side * side
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maximizeSquareArea(n: number, m: number, hBars: number[], vBars: number[]): number {
hBars.sort((a, b) => a - b);
vBars.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let maxH = 1, curH = 1;
for (let i = 1; i < hBars.length; i++) {
if (hBars[i] === hBars[i-1] + 1) curH++;
else curH = 1;
maxH = Math.max(maxH, curH);
}
let maxV = 1, curV = 1;
for (let i = 1; i < vBars.length; i++) {
if (vBars[i] === vBars[i-1] + 1) curV++;
else curV = 1;
maxV = Math.max(maxV, curV);
}
const side = Math.min(maxH, maxV) + 1;
return side * side;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(h + v)where h and v are the lengths ofhBarsandvBars(since we sort and scan both arrays). - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)extra (ignoring input storage), as only a few variables are used.