Maximize Grid Happiness
Problem
You are given four integers, m, n, introvertsCount, and extrovertsCount. You have an m x n grid, and there are two types of people: introverts and extroverts. There are introvertsCount introverts and extrovertsCount extroverts.
You should decide how many people you want to live in the grid and assign each of them one grid cell. Note that you do not have to have all the people living in the grid.
The happiness of each person is calculated as follows:
- Introverts start with
120happiness and lose30happiness for each neighbor (introvert or extrovert). - Extroverts start with
40happiness and gain20happiness for each neighbor (introvert or extrovert).
Neighbors live in the directly adjacent cells north, east, south, and west of a person's cell.
The grid happiness is the sum of each person's happiness. Return the maximum possible grid happiness.
Examples
Example 1
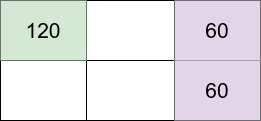
Input: m = 2, n = 3, introvertsCount = 1, extrovertsCount = 2
Output: 240
Explanation: Assume the grid is 1-indexed with coordinates (row, column).
We can put the introvert in cell (1,1) and put the extroverts in cells (1,3) and (2,3).
- Introvert at (1,1) happiness: 120 (starting happiness) - (0 * 30) (0 neighbors) = 120
- Extrovert at (1,3) happiness: 40 (starting happiness) + (1 * 20) (1 neighbor) = 60
- Extrovert at (2,3) happiness: 40 (starting happiness) + (1 * 20) (1 neighbor) = 60
The grid happiness is 120 + 60 + 60 = 240.
The above figure shows the grid in this example with each person's happiness. The introvert stays in the light green cell while the extroverts live on the light purple cells.
Example 2
Input: m = 3, n = 1, introvertsCount = 2, extrovertsCount = 1
Output: 260
Explanation: Place the two introverts in (1,1) and (3,1) and the extrovert at (2,1).
- Introvert at (1,1) happiness: 120 (starting happiness) - (1 * 30) (1 neighbor) = 90
- Extrovert at (2,1) happiness: 40 (starting happiness) + (2 * 20) (2 neighbors) = 80
- Introvert at (3,1) happiness: 120 (starting happiness) - (1 * 30) (1 neighbor) = 90
The grid happiness is 90 + 80 + 90 = 260.
Example 3
Input: m = 2, n = 2, introvertsCount = 4, extrovertsCount = 0
Output: 240
Constraints
1 <= m, n <= 50 <= introvertsCount, extrovertsCount <= min(m * n, 6)
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming with Bitmasking
Intuition
The problem can be solved using dynamic programming with bitmasking to represent the state of each row. By exploring all possible placements of introverts and extroverts, and keeping track of their interactions, we can maximize the grid happiness.
Approach
- Use a DP function that tracks the current cell, remaining introverts/extroverts, and the state of the previous row (bitmask).
- For each cell, try placing an introvert, extrovert, or leaving it empty.
- Calculate happiness changes based on neighbors (left and above).
- Memoize results to avoid recomputation.
- Return the maximum happiness achievable.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int m, n;
int dp[6][6][7][7][1 << 10];
int dfs(int r, int c, int intro, int extro, int mask, vector<int>& grid) {
if (r == m) return 0;
if (c == n) return dfs(r + 1, 0, intro, extro, mask, grid);
int key = mask;
int& ans = dp[r][c][intro][extro][mask];
if (ans != -1) return ans;
ans = dfs(r, c + 1, intro, extro, mask << 2 & ((1 << (2 * n)) - 1), grid);
if (intro > 0) {
int happy = 120;
if (c > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) == 1) happy -= 30, happy -= 30;
if (r > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) == 1) happy -= 30, happy -= 30;
if (c > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) == 2) happy -= 30, happy += 20;
if (r > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) == 2) happy -= 30, happy += 20;
ans = max(ans, happy + dfs(r, c + 1, intro - 1, extro, (mask << 2 | 1) & ((1 << (2 * n)) - 1), grid));
}
if (extro > 0) {
int happy = 40;
if (c > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) == 1) happy += 20, happy -= 30;
if (r > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) == 1) happy += 20, happy -= 30;
if (c > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) == 2) happy += 20, happy += 20;
if (r > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) == 2) happy += 20, happy += 20;
ans = max(ans, happy + dfs(r, c + 1, intro, extro - 1, (mask << 2 | 2) & ((1 << (2 * n)) - 1), grid));
}
return ans;
}
int getMaxGridHappiness(int M, int N, int introvertsCount, int extrovertsCount) {
m = M; n = N;
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
vector<int> grid(m * n);
return dfs(0, 0, introvertsCount, extrovertsCount, 0, grid);
}
};
Go
func getMaxGridHappiness(m, n, introvertsCount, extrovertsCount int) int {
type key struct{r, c, intro, extro, mask int}
memo := map[key]int{}
var dfs func(r, c, intro, extro, mask int) int
dfs = func(r, c, intro, extro, mask int) int {
if r == m { return 0 }
if c == n { return dfs(r+1, 0, intro, extro, mask) }
k := key{r, c, intro, extro, mask}
if v, ok := memo[k]; ok { return v }
res := dfs(r, c+1, intro, extro, (mask<<2)&((1<<(2*n))-1))
if intro > 0 {
happy := 120
if c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 1 { happy -= 30; happy -= 30 }
if r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 1 { happy -= 30; happy -= 30 }
if c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 2 { happy -= 30; happy += 20 }
if r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 2 { happy -= 30; happy += 20 }
res = max(res, happy+dfs(r, c+1, intro-1, extro, ((mask<<2)|1)&((1<<(2*n))-1)))
}
if extro > 0 {
happy := 40
if c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 1 { happy += 20; happy -= 30 }
if r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 1 { happy += 20; happy -= 30 }
if c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 2 { happy += 20; happy += 20 }
if r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 2 { happy += 20; happy += 20 }
res = max(res, happy+dfs(r, c+1, intro, extro-1, ((mask<<2)|2)&((1<<(2*n))-1)))
}
memo[k] = res
return res
}
return dfs(0, 0, introvertsCount, extrovertsCount, 0)
}
func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a }; return b }
Java
class Solution {
int m, n;
int[][][][][] dp;
public int getMaxGridHappiness(int M, int N, int introvertsCount, int extrovertsCount) {
m = M; n = N;
dp = new int[m+1][n+1][introvertsCount+1][extrovertsCount+1][1 << (2*n)];
for (int[][][][] arr1 : dp)
for (int[][][] arr2 : arr1)
for (int[][] arr3 : arr2)
for (int[] arr4 : arr3)
Arrays.fill(arr4, -1);
return dfs(0, 0, introvertsCount, extrovertsCount, 0);
}
int dfs(int r, int c, int intro, int extro, int mask) {
if (r == m) return 0;
if (c == n) return dfs(r+1, 0, intro, extro, mask);
if (dp[r][c][intro][extro][mask] != -1) return dp[r][c][intro][extro][mask];
int res = dfs(r, c+1, intro, extro, (mask<<2)&((1<<(2*n))-1));
if (intro > 0) {
int happy = 120;
if (c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 1) happy -= 30;
if (r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 1) happy -= 30;
if (c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 2) happy -= 30;
if (r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 2) happy -= 30;
res = Math.max(res, happy + dfs(r, c+1, intro-1, extro, ((mask<<2)|1)&((1<<(2*n))-1)));
}
if (extro > 0) {
int happy = 40;
if (c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 1) happy += 20;
if (r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 1) happy += 20;
if (c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 2) happy += 20;
if (r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 2) happy += 20;
res = Math.max(res, happy + dfs(r, c+1, intro, extro-1, ((mask<<2)|2)&((1<<(2*n))-1)));
}
return dp[r][c][intro][extro][mask] = res;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun getMaxGridHappiness(m: Int, n: Int, introvertsCount: Int, extrovertsCount: Int): Int {
val dp = HashMap<String, Int>()
fun dfs(r: Int, c: Int, intro: Int, extro: Int, mask: Int): Int {
if (r == m) return 0
if (c == n) return dfs(r + 1, 0, intro, extro, mask)
val key = "$r,$c,$intro,$extro,$mask"
if (key in dp) return dp[key]!!
var res = dfs(r, c + 1, intro, extro, (mask shl 2) and ((1 shl (2 * n)) - 1))
if (intro > 0) {
var happy = 120
if (c > 0 && ((mask shr (2 * (n - 1))) and 3) == 1) happy -= 30
if (r > 0 && ((mask shr (2 * (n - c - 1))) and 3) == 1) happy -= 30
if (c > 0 && ((mask shr (2 * (n - 1))) and 3) == 2) happy -= 30
if (r > 0 && ((mask shr (2 * (n - c - 1))) and 3) == 2) happy -= 30
res = maxOf(res, happy + dfs(r, c + 1, intro - 1, extro, ((mask shl 2) or 1) and ((1 shl (2 * n)) - 1)))
}
if (extro > 0) {
var happy = 40
if (c > 0 && ((mask shr (2 * (n - 1))) and 3) == 1) happy += 20
if (r > 0 && ((mask shr (2 * (n - c - 1))) and 3) == 1) happy += 20
if (c > 0 && ((mask shr (2 * (n - 1))) and 3) == 2) happy += 20
if (r > 0 && ((mask shr (2 * (n - c - 1))) and 3) == 2) happy += 20
res = maxOf(res, happy + dfs(r, c + 1, intro, extro - 1, ((mask shl 2) or 2) and ((1 shl (2 * n)) - 1)))
}
dp[key] = res
return res
}
return dfs(0, 0, introvertsCount, extrovertsCount, 0)
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def getMaxGridHappiness(self, m: int, n: int, introvertsCount: int, extrovertsCount: int) -> int:
from functools import lru_cache
@lru_cache(None)
def dfs(r: int, c: int, intro: int, extro: int, mask: int) -> int:
if r == m:
return 0
if c == n:
return dfs(r + 1, 0, intro, extro, mask)
res = dfs(r, c + 1, intro, extro, (mask << 2) & ((1 << (2 * n)) - 1))
if intro > 0:
happy = 120
if c > 0 and ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) == 1:
happy -= 30
if r > 0 and ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) == 1:
happy -= 30
if c > 0 and ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) == 2:
happy -= 30
if r > 0 and ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) == 2:
happy -= 30
res = max(res, happy + dfs(r, c + 1, intro - 1, extro, ((mask << 2) | 1) & ((1 << (2 * n)) - 1)))
if extro > 0:
happy = 40
if c > 0 and ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) == 1:
happy += 20
if r > 0 and ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) == 1:
happy += 20
if c > 0 and ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) == 2:
happy += 20
if r > 0 and ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) == 2:
happy += 20
res = max(res, happy + dfs(r, c + 1, intro, extro - 1, ((mask << 2) | 2) & ((1 << (2 * n)) - 1)))
return res
return dfs(0, 0, introvertsCount, extrovertsCount, 0)
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn get_max_grid_happiness(m: i32, n: i32, introverts_count: i32, extroverts_count: i32) -> i32 {
use std::collections::HashMap;
fn dfs(r: i32, c: i32, intro: i32, extro: i32, mask: i32, m: i32, n: i32, memo: &mut HashMap<(i32,i32,i32,i32,i32),i32>) -> i32 {
if r == m { return 0; }
if c == n { return dfs(r+1, 0, intro, extro, mask, m, n, memo); }
if let Some(&v) = memo.get(&(r,c,intro,extro,mask)) { return v; }
let mut res = dfs(r, c+1, intro, extro, (mask<<2)&((1<<(2*n))-1), m, n, memo);
if intro > 0 {
let mut happy = 120;
if c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 1 { happy -= 30; }
if r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 1 { happy -= 30; }
if c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 2 { happy -= 30; }
if r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 2 { happy -= 30; }
res = res.max(happy + dfs(r, c+1, intro-1, extro, ((mask<<2)|1)&((1<<(2*n))-1), m, n, memo));
}
if extro > 0 {
let mut happy = 40;
if c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 1 { happy += 20; }
if r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 1 { happy += 20; }
if c > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-1)))&3) == 2 { happy += 20; }
if r > 0 && ((mask>>(2*(n-c-1)))&3) == 2 { happy += 20; }
res = res.max(happy + dfs(r, c+1, intro, extro-1, ((mask<<2)|2)&((1<<(2*n))-1), m, n, memo));
}
memo.insert((r,c,intro,extro,mask), res);
res
}
let mut memo = HashMap::new();
dfs(0, 0, introverts_count, extroverts_count, 0, m, n, &mut memo)
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
getMaxGridHappiness(m: number, n: number, introvertsCount: number, extrovertsCount: number): number {
const memo = new Map<string, number>();
const dfs = (r: number, c: number, intro: number, extro: number, mask: number): number => {
if (r === m) return 0;
if (c === n) return dfs(r + 1, 0, intro, extro, mask);
const key = `${r},${c},${intro},${extro},${mask}`;
if (memo.has(key)) return memo.get(key)!;
let res = dfs(r, c + 1, intro, extro, (mask << 2) & ((1 << (2 * n)) - 1));
if (intro > 0) {
let happy = 120;
if (c > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) === 1) happy -= 30;
if (r > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) === 1) happy -= 30;
if (c > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) === 2) happy -= 30;
if (r > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) === 2) happy -= 30;
res = Math.max(res, happy + dfs(r, c + 1, intro - 1, extro, ((mask << 2) | 1) & ((1 << (2 * n)) - 1)));
}
if (extro > 0) {
let happy = 40;
if (c > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) === 1) happy += 20;
if (r > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) === 1) happy += 20;
if (c > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - 1))) & 3) === 2) happy += 20;
if (r > 0 && ((mask >> (2 * (n - c - 1))) & 3) === 2) happy += 20;
res = Math.max(res, happy + dfs(r, c + 1, intro, extro - 1, ((mask << 2) | 2) & ((1 << (2 * n)) - 1)));
}
memo.set(key, res);
return res;
};
return dfs(0, 0, introvertsCount, extrovertsCount, 0);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n * introvertsCount * extrovertsCount * 3^(m*n)), since each cell can be empty, introvert, or extrovert, and we memoize states. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m * n * introvertsCount * extrovertsCount * 3^(m*n)), for memoization.