Maximum Area of a Piece of Cake After Horizontal and Vertical Cuts
MediumUpdated: Oct 12, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given a rectangular cake of size h x w and two arrays of integers horizontalCuts and verticalCuts where:
horizontalCuts[i]is the distance from the top of the rectangular cake to theithhorizontal cut and similarly, andverticalCuts[j]is the distance from the left of the rectangular cake to thejthvertical cut.
Return the maximum area of a piece of cake after you cut at each horizontal and vertical position provided in the arrays horizontalCuts and verticalCuts. Since the answer can be a large number, return this modulo 10^9 + 7.
Examples
Example 1

Input: h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [1,2,4], verticalCuts = [1,3]
Output: 4
Explanation: The figure above represents the given rectangular cake. Red lines are the horizontal and vertical cuts. After you cut the cake, the green piece of cake has the maximum area.
Example 2

Input: h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [3,1], verticalCuts = [1]
Output: 6
Explanation: The figure above represents the given rectangular cake. Red lines are the horizontal and vertical cuts. After you cut the cake, the green and yellow pieces of cake have the maximum area.
Example 3
Input: h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [3], verticalCuts = [3]
Output: 9
Constraints
- All the elements in
horizontalCutsare distinct. - All the elements in
verticalCutsare distinct.
Solution
Method 1 - Sorting and Gap Calculation
Intuition
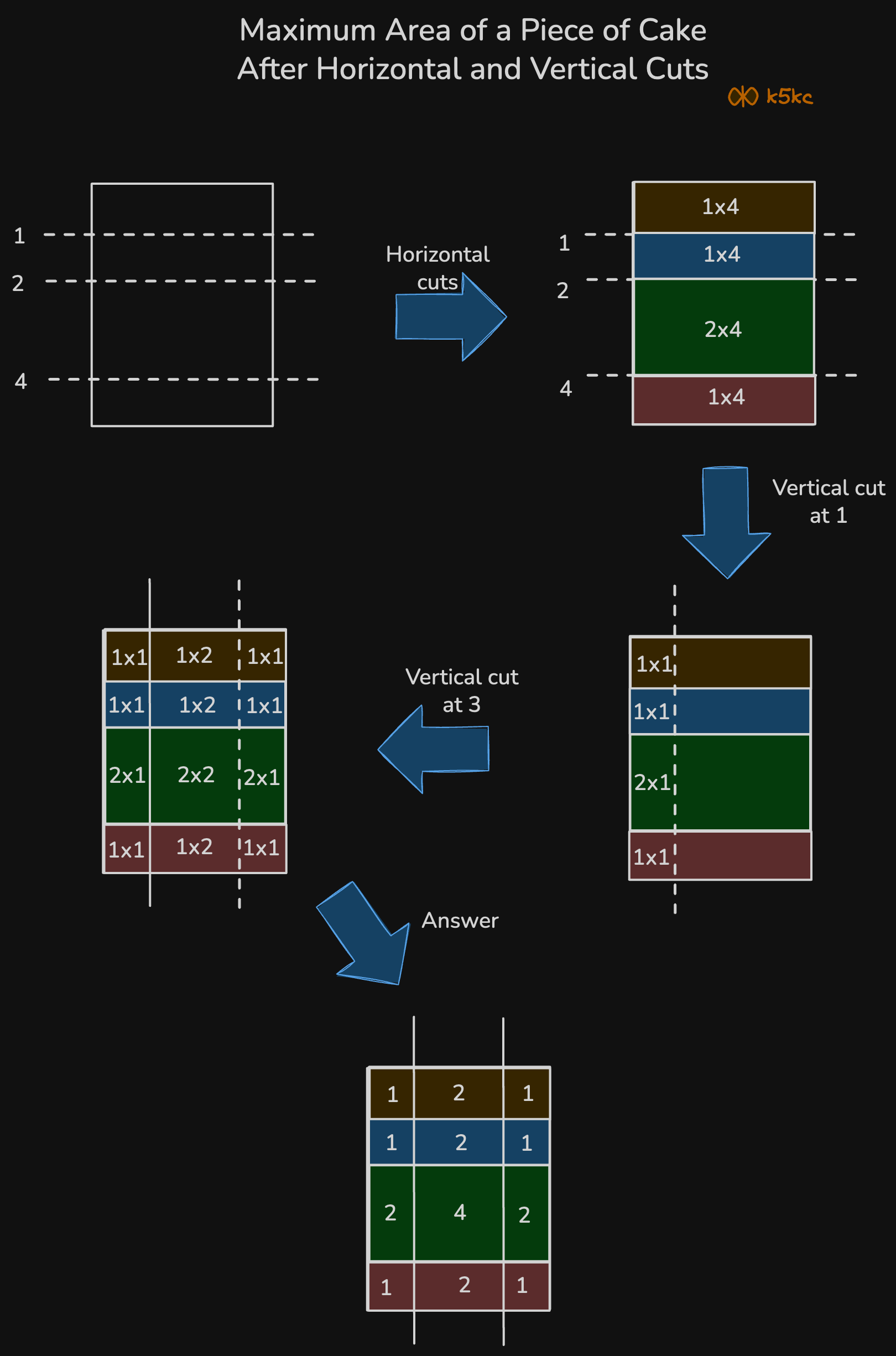
We want the largest rectangular piece formed by the cuts. The height of any piece is a gap between two consecutive horizontal cut positions (including edges 0 and h). Similarly, the width is a gap between two consecutive vertical cuts (including edges 0 and w). The maximum area is simply maxHeightGap * maxWidthGap. Sorting lets us compute these gaps in one linear scan per list.
Approach
- Sort
horizontalCutsandverticalCuts. - Compute
maxHas the maximum among: first gaphorizontalCuts[0] - 0, last gaph - horizontalCuts[last], and gaps between consecutive cuts. - Compute
maxWsimilarly for vertical cuts. - The answer is
(maxH * maxW) % 1_000_000_007using 64-bit multiplication to avoid overflow. - Return the result.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(int h, int w, vector<int>& horizontalCuts, vector<int>& verticalCuts) {
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
sort(horizontalCuts.begin(), horizontalCuts.end());
sort(verticalCuts.begin(), verticalCuts.end());
long long maxH = max(horizontalCuts[0], h - horizontalCuts.back());
for (int i = 1; i < horizontalCuts.size(); ++i) {
maxH = max(maxH, (long long)horizontalCuts[i] - horizontalCuts[i - 1]);
}
long long maxW = max(verticalCuts[0], w - verticalCuts.back());
for (int i = 1; i < verticalCuts.size(); ++i) {
maxW = max(maxW, (long long)verticalCuts[i] - verticalCuts[i - 1]);
}
long long area = (maxH % MOD) * (maxW % MOD) % MOD; // both gaps < 1e9 so direct multiply safe in 64-bit
return (int)area;
}
};
Go
func maxArea(h int, w int, horizontalCuts []int, verticalCuts []int) int {
const MOD = 1_000_000_007
sort.Ints(horizontalCuts)
sort.Ints(verticalCuts)
maxH := max(horizontalCuts[0], h-horizontalCuts[len(horizontalCuts)-1])
for i := 1; i < len(horizontalCuts); i++ {
gap := horizontalCuts[i] - horizontalCuts[i-1]
if gap > maxH { maxH = gap }
}
maxW := max(verticalCuts[0], w-verticalCuts[len(verticalCuts)-1])
for i := 1; i < len(verticalCuts); i++ {
gap := verticalCuts[i] - verticalCuts[i-1]
if gap > maxW { maxW = gap }
}
return (int)((int64(maxH) * int64(maxW)) % MOD)
}
func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a }; return b }
Java
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int h, int w, int[] horizontalCuts, int[] verticalCuts) {
final int MOD = 1_000_000_007;
Arrays.sort(horizontalCuts);
Arrays.sort(verticalCuts);
long maxH = Math.max(horizontalCuts[0], h - horizontalCuts[horizontalCuts.length - 1]);
for (int i = 1; i < horizontalCuts.length; i++) {
maxH = Math.max(maxH, horizontalCuts[i] - horizontalCuts[i - 1]);
}
long maxW = Math.max(verticalCuts[0], w - verticalCuts[verticalCuts.length - 1]);
for (int i = 1; i < verticalCuts.length; i++) {
maxW = Math.max(maxW, verticalCuts[i] - verticalCuts[i - 1]);
}
long area = (maxH % MOD) * (maxW % MOD) % MOD;
return (int) area;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maxArea(h: Int, w: Int, horizontalCuts: IntArray, verticalCuts: IntArray): Int {
val MOD = 1_000_000_007
horizontalCuts.sort()
verticalCuts.sort()
var maxH = maxOf(horizontalCuts[0], h - horizontalCuts.last())
for (i in 1 until horizontalCuts.size) {
maxH = maxOf(maxH, horizontalCuts[i] - horizontalCuts[i - 1])
}
var maxW = maxOf(verticalCuts[0], w - verticalCuts.last())
for (i in 1 until verticalCuts.size) {
maxW = maxOf(maxW, verticalCuts[i] - verticalCuts[i - 1])
}
return ((maxH.toLong() * maxW.toLong()) % MOD).toInt()
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, h: int, w: int, horizontalCuts: list[int], verticalCuts: list[int]) -> int:
MOD = 10**9 + 7
horizontalCuts.sort()
verticalCuts.sort()
max_h = max(horizontalCuts[0], h - horizontalCuts[-1])
for i in range(1, len(horizontalCuts)):
gap = horizontalCuts[i] - horizontalCuts[i - 1]
if gap > max_h:
max_h = gap
max_w = max(verticalCuts[0], w - verticalCuts[-1])
for i in range(1, len(verticalCuts)):
gap = verticalCuts[i] - verticalCuts[i - 1]
if gap > max_w:
max_w = gap
return (max_h * max_w) % MOD
Rust
pub struct Solution;
impl Solution {
pub fn max_area(h: i32, w: i32, mut horizontal_cuts: Vec<i32>, mut vertical_cuts: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let m = 1_000_000_007i64;
horizontal_cuts.sort();
vertical_cuts.sort();
let mut max_h = horizontal_cuts[0].max(h - horizontal_cuts[horizontal_cuts.len() - 1]);
for i in 1..horizontal_cuts.len() {
let gap = horizontal_cuts[i] - horizontal_cuts[i - 1];
if gap > max_h { max_h = gap; }
}
let mut max_w = vertical_cuts[0].max(w - vertical_cuts[vertical_cuts.len() - 1]);
for i in 1..vertical_cuts.len() {
let gap = vertical_cuts[i] - vertical_cuts[i - 1];
if gap > max_w { max_w = gap; }
}
((max_h as i64 * max_w as i64) % m) as i32
}
}
Typescript
function maxArea(h: number, w: number, horizontalCuts: number[], verticalCuts: number[]): number {
const MOD = 1_000_000_007;
horizontalCuts.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
verticalCuts.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
let maxH = Math.max(horizontalCuts[0], h - horizontalCuts[horizontalCuts.length - 1]);
for (let i = 1; i < horizontalCuts.length; i++) {
const gap = horizontalCuts[i] - horizontalCuts[i - 1];
if (gap > maxH) maxH = gap;
}
let maxW = Math.max(verticalCuts[0], w - verticalCuts[verticalCuts.length - 1]);
for (let i = 1; i < verticalCuts.length; i++) {
const gap = verticalCuts[i] - verticalCuts[i - 1];
if (gap > maxW) maxW = gap;
}
return (Number(BigInt(maxH) * BigInt(maxW) % BigInt(MOD)));
};
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m log m + n log n)– SortinghorizontalCutsandverticalCutsdominates; gap scans are linear. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)– We sort in-place and use a constant number of extra variables.