Maximum Building Height
Problem
You want to build n new buildings in a city. The new buildings will be built in a line and are labeled from 1 to n.
However, there are city restrictions on the heights of the new buildings:
- The height of each building must be a non-negative integer.
- The height of the first building must be
0. - The height difference between any two adjacent buildings cannot exceed
1.
Additionally, there are city restrictions on the maximum height of specific buildings. These restrictions are given as a 2D integer array restrictions
where restrictions[i] = [idi, maxHeighti] indicates that building idi must have a height less than or equal to maxHeighti.
It is guaranteed that each building will appear at most once in
restrictions, and building 1 will not be in restrictions.
Return themaximum possible height of the tallest building.
Examples
Example 1
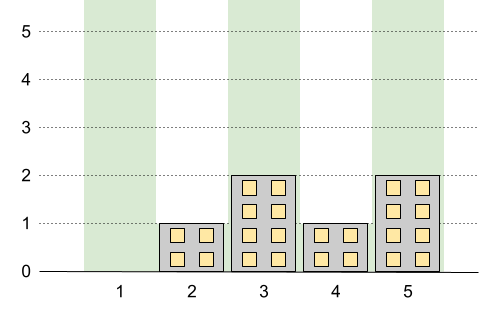
Input: n = 5, restrictions = [[2,1],[4,1]]
Output: 2
Explanation: The green area in the image indicates the maximum allowed height for each building.
We can build the buildings with heights [0,1,2,1,2], and the tallest building has a height of 2.
Example 2
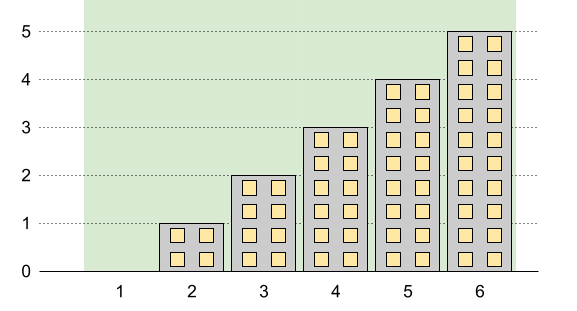
Input: n = 6, restrictions = []
Output: 5
Explanation: The green area in the image indicates the maximum allowed height for each building.
We can build the buildings with heights [0,1,2,3,4,5], and the tallest building has a height of 5.
Example 3
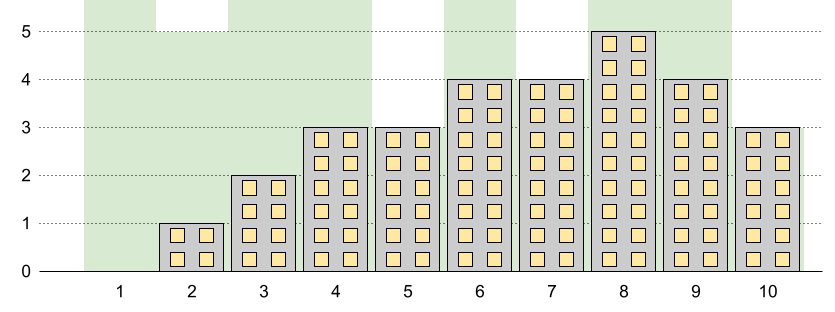
Input: n = 10, restrictions = [[5,3],[2,5],[7,4],[10,3]]
Output: 5
Explanation: The green area in the image indicates the maximum allowed height for each building.
We can build the buildings with heights [0,1,2,3,3,4,4,5,4,3], and the tallest building has a height of 5.
Constraints
2 <= n <= 10^90 <= restrictions.length <= min(n - 1, 105)2 <= idi <= nidiis unique.0 <= maxHeighti <= 10^9
Solution
Method 1 – Two-Pass Restriction Propagation
Intuition
The problem is about maximizing the height of the tallest building under adjacent difference and specific building restrictions. By sorting and propagating restrictions left-to-right and right-to-left, we can ensure all constraints are satisfied. The answer is the maximum possible height between any two restrictions, considering the slope constraint.
Approach
- Add a restriction for building 1 (height 0) and building n (height n-1).
- Sort all restrictions by building index.
- Left-to-right pass: for each restriction, ensure it does not exceed the previous restriction plus the distance.
- Right-to-left pass: for each restriction, ensure it does not exceed the next restriction plus the distance.
- For each interval between restrictions, compute the maximum possible height using the slope constraint.
- Return the maximum found.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxBuilding(int n, vector<vector<int>>& restrictions) {
restrictions.push_back({1, 0});
restrictions.push_back({n, n-1});
sort(restrictions.begin(), restrictions.end());
int m = restrictions.size();
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i)
restrictions[i][1] = min(restrictions[i][1], restrictions[i-1][1] + restrictions[i][0] - restrictions[i-1][0]);
for (int i = m-2; i >= 0; --i)
restrictions[i][1] = min(restrictions[i][1], restrictions[i+1][1] + restrictions[i+1][0] - restrictions[i][0]);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
int d = restrictions[i][0] - restrictions[i-1][0];
int h1 = restrictions[i-1][1], h2 = restrictions[i][1];
int maxh = (h1 + h2 + d) / 2;
ans = max(ans, maxh);
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func maxBuilding(n int, restrictions [][]int) int {
restrictions = append(restrictions, []int{1, 0}, []int{n, n-1})
sort.Slice(restrictions, func(i, j int) bool { return restrictions[i][0] < restrictions[j][0] })
m := len(restrictions)
for i := 1; i < m; i++ {
d := restrictions[i][0] - restrictions[i-1][0]
if restrictions[i][1] > restrictions[i-1][1]+d {
restrictions[i][1] = restrictions[i-1][1]+d
}
}
for i := m-2; i >= 0; i-- {
d := restrictions[i+1][0] - restrictions[i][0]
if restrictions[i][1] > restrictions[i+1][1]+d {
restrictions[i][1] = restrictions[i+1][1]+d
}
}
ans := 0
for i := 1; i < m; i++ {
d := restrictions[i][0] - restrictions[i-1][0]
h1, h2 := restrictions[i-1][1], restrictions[i][1]
maxh := (h1 + h2 + d) / 2
if maxh > ans {
ans = maxh
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int maxBuilding(int n, int[][] restrictions) {
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(restrictions));
list.add(new int[]{1, 0});
list.add(new int[]{n, n-1});
list.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
int m = list.size();
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
list.get(i)[1] = Math.min(list.get(i)[1], list.get(i-1)[1] + list.get(i)[0] - list.get(i-1)[0]);
for (int i = m-2; i >= 0; i--)
list.get(i)[1] = Math.min(list.get(i)[1], list.get(i+1)[1] + list.get(i+1)[0] - list.get(i)[0]);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
int d = list.get(i)[0] - list.get(i-1)[0];
int h1 = list.get(i-1)[1], h2 = list.get(i)[1];
int maxh = (h1 + h2 + d) / 2;
ans = Math.max(ans, maxh);
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maxBuilding(n: Int, restrictions: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val list = restrictions.toMutableList()
list.add(intArrayOf(1, 0))
list.add(intArrayOf(n, n-1))
list.sortBy { it[0] }
for (i in 1 until list.size)
list[i][1] = minOf(list[i][1], list[i-1][1] + list[i][0] - list[i-1][0])
for (i in list.size-2 downTo 0)
list[i][1] = minOf(list[i][1], list[i+1][1] + list[i+1][0] - list[i][0])
var ans = 0
for (i in 1 until list.size) {
val d = list[i][0] - list[i-1][0]
val h1 = list[i-1][1]
val h2 = list[i][1]
val maxh = (h1 + h2 + d) / 2
ans = maxOf(ans, maxh)
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maxBuilding(self, n: int, restrictions: list[list[int]]) -> int:
restrictions.append([1, 0])
restrictions.append([n, n-1])
restrictions.sort()
m = len(restrictions)
for i in range(1, m):
restrictions[i][1] = min(restrictions[i][1], restrictions[i-1][1] + restrictions[i][0] - restrictions[i-1][0])
for i in range(m-2, -1, -1):
restrictions[i][1] = min(restrictions[i][1], restrictions[i+1][1] + restrictions[i+1][0] - restrictions[i][0])
ans = 0
for i in range(1, m):
d = restrictions[i][0] - restrictions[i-1][0]
h1, h2 = restrictions[i-1][1], restrictions[i][1]
maxh = (h1 + h2 + d) // 2
ans = max(ans, maxh)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn max_building(n: i32, mut restrictions: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
restrictions.push(vec![1, 0]);
restrictions.push(vec![n, n-1]);
restrictions.sort();
let m = restrictions.len();
for i in 1..m {
let d = restrictions[i][0] - restrictions[i-1][0];
restrictions[i][1] = restrictions[i][1].min(restrictions[i-1][1] + d);
}
for i in (0..m-1).rev() {
let d = restrictions[i+1][0] - restrictions[i][0];
restrictions[i][1] = restrictions[i][1].min(restrictions[i+1][1] + d);
}
let mut ans = 0;
for i in 1..m {
let d = restrictions[i][0] - restrictions[i-1][0];
let h1 = restrictions[i-1][1];
let h2 = restrictions[i][1];
let maxh = (h1 + h2 + d) / 2;
ans = ans.max(maxh);
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maxBuilding(n: number, restrictions: number[][]): number {
restrictions.push([1, 0]);
restrictions.push([n, n-1]);
restrictions.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
const m = restrictions.length;
for (let i = 1; i < m; ++i)
restrictions[i][1] = Math.min(restrictions[i][1], restrictions[i-1][1] + restrictions[i][0] - restrictions[i-1][0]);
for (let i = m-2; i >= 0; --i)
restrictions[i][1] = Math.min(restrictions[i][1], restrictions[i+1][1] + restrictions[i+1][0] - restrictions[i][0]);
let ans = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
const d = restrictions[i][0] - restrictions[i-1][0];
const h1 = restrictions[i-1][1], h2 = restrictions[i][1];
const maxh = Math.floor((h1 + h2 + d) / 2);
ans = Math.max(ans, maxh);
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m log m), where m is the number of restrictions, due to sorting and two passes. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m), for the restrictions array.