Maximum Fruits Harvested After at Most K Steps
Problem
Fruits are available at some positions on an infinite x-axis. You are given a 2D integer array fruits where fruits[i] = [positioni, amounti] depicts
amounti fruits at the position positioni. fruits is already sorted by positioni in ascending order , and each positioni is unique.
You are also given an integer startPos and an integer k. Initially, you are at the position startPos. From any position, you can either walk to the
left or right. It takes one step to move one unit on the x-axis, and you can walk at most k steps in total. For every position you reach, you harvest all the fruits at that position, and the fruits will disappear from that position.
Return themaximum total number of fruits you can harvest.
Examples
Example 1
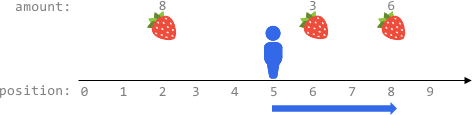
Input: fruits = [[2,8],[6,3],[8,6]], startPos = 5, k = 4
Output: 9
Explanation:
The optimal way is to:
- Move right to position 6 and harvest 3 fruits
- Move right to position 8 and harvest 6 fruits
You moved 3 steps and harvested 3 + 6 = 9 fruits in total.
Example 2
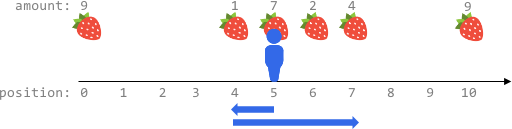
Input: fruits = [[0,9],[4,1],[5,7],[6,2],[7,4],[10,9]], startPos = 5, k = 4
Output: 14
Explanation:
You can move at most k = 4 steps, so you cannot reach position 0 nor 10.
The optimal way is to:
- Harvest the 7 fruits at the starting position 5
- Move left to position 4 and harvest 1 fruit
- Move right to position 6 and harvest 2 fruits
- Move right to position 7 and harvest 4 fruits
You moved 1 + 3 = 4 steps and harvested 7 + 1 + 2 + 4 = 14 fruits in total.
Example 3
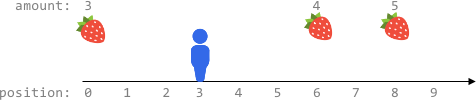
Input: fruits = [[0,3],[6,4],[8,5]], startPos = 3, k = 2
Output: 0
Explanation:
You can move at most k = 2 steps and cannot reach any position with fruits.
Constraints
1 <= fruits.length <= 10^5fruits[i].length == 20 <= startPos, positioni <= 2 * 10^5positioni-1 < positionifor anyi > 0(0-indexed)1 <= amounti <= 10^40 <= k <= 2 * 10^5
Solution
Method 1 – Sliding Window + Prefix Sum
Intuition
The key insight is to use a sliding window approach to find all possible contiguous subarrays of fruits that can be reached within k steps. For any subarray from left to right, we have two strategies: go left first then sweep right, or go right first then sweep left. We choose the strategy that requires fewer steps.
Approach
- Use two pointers (left and right) to maintain a sliding window of fruits.
- Expand the right boundary by including more fruits in our window.
- For each window, calculate the minimum steps needed using the formula:
min(|startPos - leftPos|, |startPos - rightPos|) + |rightPos - leftPos|. - If the steps exceed k, shrink the window from the left until it's valid.
- Track the maximum sum of fruits in any valid window.
- The step calculation represents either going to the closer end first, then sweeping to the other end.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxTotalFruits(vector<vector<int>>& fruits, int startPos, int k) {
int n = fruits.size(), ans = 0, sum = 0;
int left = 0, right = 0;
while (right < n) {
sum += fruits[right][1];
while (left <= right && getSteps(fruits, startPos, left, right) > k) {
sum -= fruits[left][1];
left++;
}
ans = max(ans, sum);
right++;
}
return ans;
}
private:
int getSteps(vector<vector<int>>& fruits, int startPos, int left, int right) {
return min(abs(startPos - fruits[left][0]),
abs(startPos - fruits[right][0])) +
fruits[right][0] - fruits[left][0];
}
};
Go
func maxTotalFruits(fruits [][]int, startPos int, k int) int {
n := len(fruits)
ans, sum := 0, 0
left, right := 0, 0
for right < n {
sum += fruits[right][1]
for left <= right && getSteps(fruits, startPos, left, right) > k {
sum -= fruits[left][1]
left++
}
ans = max(ans, sum)
right++
}
return ans
}
func getSteps(fruits [][]int, startPos, left, right int) int {
return min(abs(startPos-fruits[left][0]), abs(startPos-fruits[right][0])) +
fruits[right][0] - fruits[left][0]
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -x
}
return x
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
Java
class Solution {
public int maxTotalFruits(int[][] fruits, int startPos, int k) {
int n = fruits.length, ans = 0, sum = 0;
int left = 0, right = 0;
// Sliding window approach
while (right < n) {
sum += fruits[right][1];
// Check if current window is valid
while (left <= right && getSteps(fruits, startPos, left, right) > k) {
sum -= fruits[left][1];
left++;
}
ans = Math.max(ans, sum);
right++;
}
return ans;
}
private int getSteps(int[][] fruits, int startPos, int left, int right) {
return Math.min(Math.abs(startPos - fruits[left][0]),
Math.abs(startPos - fruits[right][0])) +
fruits[right][0] - fruits[left][0];
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maxTotalFruits(fruits: Array<IntArray>, startPos: Int, k: Int): Int {
val n = fruits.size
var ans = 0
var sum = 0
var left = 0
var right = 0
while (right < n) {
sum += fruits[right][1]
while (left <= right && getSteps(fruits, startPos, left, right) > k) {
sum -= fruits[left][1]
left++
}
ans = maxOf(ans, sum)
right++
}
return ans
}
private fun getSteps(fruits: Array<IntArray>, startPos: Int, left: Int, right: Int): Int {
return minOf(kotlin.math.abs(startPos - fruits[left][0]),
kotlin.math.abs(startPos - fruits[right][0])) +
fruits[right][0] - fruits[left][0]
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maxTotalFruits(self, fruits: list[list[int]], startPos: int, k: int) -> int:
n: int = len(fruits)
ans: int = 0
sum_: int = 0
left: int = 0
right: int = 0
while right < n:
sum_ += fruits[right][1]
while left <= right and self._get_steps(fruits, startPos, left, right) > k:
sum_ -= fruits[left][1]
left += 1
ans = max(ans, sum_)
right += 1
return ans
def _get_steps(self, fruits: list[list[int]], startPos: int, left: int, right: int) -> int:
return (min(abs(startPos - fruits[left][0]),
abs(startPos - fruits[right][0])) +
fruits[right][0] - fruits[left][0])
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn max_total_fruits(fruits: Vec<Vec<i32>>, start_pos: i32, k: i32) -> i32 {
let n = fruits.len();
let mut ans = 0;
let mut sum = 0;
let mut left = 0;
let mut right = 0;
while right < n {
sum += fruits[right][1];
while left <= right && Self::get_steps(&fruits, start_pos, left, right) > k {
sum -= fruits[left][1];
left += 1;
}
ans = ans.max(sum);
right += 1;
}
ans
}
fn get_steps(fruits: &Vec<Vec<i32>>, start_pos: i32, left: usize, right: usize) -> i32 {
(start_pos - fruits[left][0]).abs().min((start_pos - fruits[right][0]).abs()) +
fruits[right][0] - fruits[left][0]
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maxTotalFruits(fruits: number[][], startPos: number, k: number): number {
const n = fruits.length;
let ans = 0, sum = 0;
let left = 0, right = 0;
while (right < n) {
sum += fruits[right][1];
while (left <= right && this.getSteps(fruits, startPos, left, right) > k) {
sum -= fruits[left][1];
left++;
}
ans = Math.max(ans, sum);
right++;
}
return ans;
}
private getSteps(fruits: number[][], startPos: number, left: number, right: number): number {
return Math.min(Math.abs(startPos - fruits[left][0]),
Math.abs(startPos - fruits[right][0])) +
fruits[right][0] - fruits[left][0];
}
}
p#### Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n)— Each fruit position is visited at most twice (once when expanding right pointer, once when contracting left pointer), making it linear time. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)— Only using a constant amount of extra variables (left, right, sum, ans) regardless of input size.