Maximum Number of Darts Inside of a Circular Dartboard
Problem
Alice is throwing n darts on a very large wall. You are given an array darts where darts[i] = [xi, yi] is the position of the ith dart that Alice threw on the wall.
Bob knows the positions of the n darts on the wall. He wants to place a dartboard of radius r on the wall so that the maximum number of darts that Alice throws lie on the dartboard.
Given the integer r, return the maximum number of darts that can lie on the dartboard.
Examples
Example 1
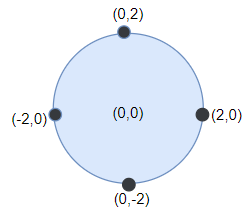
Input: darts = [[-2,0],[2,0],[0,2],[0,-2]], r = 2
Output: 4
Explanation: Circle dartboard with center in (0,0) and radius = 2 contain all points.
Example 2
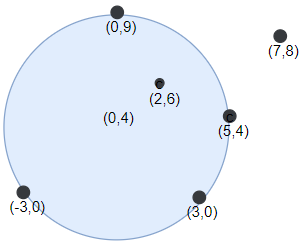
Input: darts = [[-3,0],[3,0],[2,6],[5,4],[0,9],[7,8]], r = 5
Output: 5
Explanation: Circle dartboard with center in (0,4) and radius = 5 contain all points except the point (7,8).
Constraints
1 <= darts.length <= 100darts[i].length == 2-10^4 <= xi, yi <= 10^4- All the
dartsare unique 1 <= r <= 5000
Solution
Method 1 – Geometry: Circle from Two Points
Intuition
To maximize the number of darts inside the dartboard, consider every pair of darts as possible candidates for the circle's boundary. For each pair, compute all possible circle centers of radius r passing through both points, then count how many darts fall inside or on the circle. The answer is the maximum count found.
Approach
- For each pair of darts, calculate the distance between them. If the distance is greater than
2*r, skip (no circle of radiusrcan pass through both). - For valid pairs, compute the two possible centers of circles of radius
rpassing through both points using geometry. - For each center, count how many darts are within or on the circle (distance ≤ r + 1e-8 for floating point tolerance).
- Also, for each dart, consider a circle centered at that dart and count how many darts are inside.
- Return the maximum count found.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int numPoints(vector<vector<int>>& darts, int r) {
int n = darts.size(), ans = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i+1; j < n; ++j) {
double dx = darts[j][0] - darts[i][0];
double dy = darts[j][1] - darts[i][1];
double d = sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy);
if (d > 2*r) continue;
double mx = (darts[i][0] + darts[j][0]) / 2.0;
double my = (darts[i][1] + darts[j][1]) / 2.0;
double h = sqrt(r*r - (d/2)*(d/2));
double ox = -dy * h / d;
double oy = dx * h / d;
for (int sign : {-1, 1}) {
double cx = mx + sign * ox;
double cy = my + sign * oy;
int cnt = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
double ddx = darts[k][0] - cx;
double ddy = darts[k][1] - cy;
if (ddx*ddx + ddy*ddy <= r*r + 1e-8) ++cnt;
}
ans = max(ans, cnt);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
import "math"
func numPoints(darts [][]int, r int) int {
n, ans := len(darts), 1
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := i+1; j < n; j++ {
dx := float64(darts[j][0] - darts[i][0])
dy := float64(darts[j][1] - darts[i][1])
d := math.Hypot(dx, dy)
if d > float64(2*r) { continue }
mx := (float64(darts[i][0]) + float64(darts[j][0])) / 2
my := (float64(darts[i][1]) + float64(darts[j][1])) / 2
h := math.Sqrt(float64(r*r) - (d/2)*(d/2))
ox := -dy * h / d
oy := dx * h / d
for _, sign := range []float64{-1, 1} {
cx := mx + sign*ox
cy := my + sign*oy
cnt := 0
for k := 0; k < n; k++ {
ddx := float64(darts[k][0]) - cx
ddy := float64(darts[k][1]) - cy
if ddx*ddx + ddy*ddy <= float64(r*r)+1e-8 {
cnt++
}
}
if cnt > ans { ans = cnt }
}
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int numPoints(int[][] darts, int r) {
int n = darts.length, ans = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i+1; j < n; ++j) {
double dx = darts[j][0] - darts[i][0];
double dy = darts[j][1] - darts[i][1];
double d = Math.hypot(dx, dy);
if (d > 2*r) continue;
double mx = (darts[i][0] + darts[j][0]) / 2.0;
double my = (darts[i][1] + darts[j][1]) / 2.0;
double h = Math.sqrt(r*r - (d/2)*(d/2));
double ox = -dy * h / d;
double oy = dx * h / d;
for (int sign : new int[]{-1, 1}) {
double cx = mx + sign * ox;
double cy = my + sign * oy;
int cnt = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
double ddx = darts[k][0] - cx;
double ddy = darts[k][1] - cy;
if (ddx*ddx + ddy*ddy <= r*r + 1e-8) ++cnt;
}
ans = Math.max(ans, cnt);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun numPoints(darts: Array<IntArray>, r: Int): Int {
val n = darts.size
var ans = 1
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in i+1 until n) {
val dx = darts[j][0] - darts[i][0]
val dy = darts[j][1] - darts[i][1]
val d = Math.hypot(dx.toDouble(), dy.toDouble())
if (d > 2*r) continue
val mx = (darts[i][0] + darts[j][0]) / 2.0
val my = (darts[i][1] + darts[j][1]) / 2.0
val h = Math.sqrt(r.toDouble()*r - (d/2)*(d/2))
val ox = -dy * h / d
val oy = dx * h / d
for (sign in listOf(-1, 1)) {
val cx = mx + sign * ox
val cy = my + sign * oy
var cnt = 0
for (k in 0 until n) {
val ddx = darts[k][0] - cx
val ddy = darts[k][1] - cy
if (ddx*ddx + ddy*ddy <= r*r + 1e-8) cnt++
}
ans = maxOf(ans, cnt)
}
}
}
return ans
}
}
Python
def numPoints(darts: list[list[int]], r: int) -> int:
from math import hypot, sqrt
n, ans = len(darts), 1
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i+1, n):
dx, dy = darts[j][0] - darts[i][0], darts[j][1] - darts[i][1]
d = hypot(dx, dy)
if d > 2*r: continue
mx, my = (darts[i][0] + darts[j][0]) / 2, (darts[i][1] + darts[j][1]) / 2
h = sqrt(r*r - (d/2)*(d/2))
ox, oy = -dy * h / d, dx * h / d
for sign in [-1, 1]:
cx, cy = mx + sign*ox, my + sign*oy
cnt = 0
for k in range(n):
ddx, ddy = darts[k][0] - cx, darts[k][1] - cy
if ddx*ddx + ddy*ddy <= r*r + 1e-8:
cnt += 1
ans = max(ans, cnt)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn num_points(darts: Vec<Vec<i32>>, r: i32) -> i32 {
let n = darts.len();
let mut ans = 1;
for i in 0..n {
for j in i+1..n {
let dx = (darts[j][0] - darts[i][0]) as f64;
let dy = (darts[j][1] - darts[i][1]) as f64;
let d = (dx*dx + dy*dy).sqrt();
if d > 2.0 * r as f64 { continue; }
let mx = (darts[i][0] + darts[j][0]) as f64 / 2.0;
let my = (darts[i][1] + darts[j][1]) as f64 / 2.0;
let h = ((r*r) as f64 - (d/2.0)*(d/2.0)).sqrt();
let ox = -dy * h / d;
let oy = dx * h / d;
for &sign in &[-1.0, 1.0] {
let cx = mx + sign * ox;
let cy = my + sign * oy;
let mut cnt = 0;
for k in 0..n {
let ddx = darts[k][0] as f64 - cx;
let ddy = darts[k][1] as f64 - cy;
if ddx*ddx + ddy*ddy <= (r*r) as f64 + 1e-8 {
cnt += 1;
}
}
ans = ans.max(cnt);
}
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
numPoints(darts: number[][], r: number): number {
const n = darts.length;
let ans = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (let j = i+1; j < n; ++j) {
const dx = darts[j][0] - darts[i][0];
const dy = darts[j][1] - darts[i][1];
const d = Math.hypot(dx, dy);
if (d > 2*r) continue;
const mx = (darts[i][0] + darts[j][0]) / 2;
const my = (darts[i][1] + darts[j][1]) / 2;
const h = Math.sqrt(r*r - (d/2)*(d/2));
const ox = -dy * h / d;
const oy = dx * h / d;
for (const sign of [-1, 1]) {
const cx = mx + sign * ox;
const cy = my + sign * oy;
let cnt = 0;
for (let k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
const ddx = darts[k][0] - cx;
const ddy = darts[k][1] - cy;
if (ddx*ddx + ddy*ddy <= r*r + 1e-8) ++cnt;
}
ans = Math.max(ans, cnt);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^3)– For each pair, check all darts for inclusion. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)– Only a few variables for computation.