Maximum Number of Visible Points
Problem
You are given an array points, an integer angle, and your location, where location = [posx, posy] and points[i] = [xi, yi] both denote
integral coordinates on the X-Y plane.
Initially, you are facing directly east from your position. You cannot move from your position, but you can rotate. In other words, posx and
posy cannot be changed. Your field of view in degrees is represented by
angle, determining how wide you can see from any given view direction. Let
d be the amount in degrees that you rotate counterclockwise. Then, your field of view is the inclusive range of angles [d - angle/2, d + angle/2].
Your browser does not support the video tag or this video format.
You can see some set of points if, for each point, the angle formed by the point, your position, and the immediate east direction from your position is in your field of view.
There can be multiple points at one coordinate. There may be points at your location, and you can always see these points regardless of your rotation. Points do not obstruct your vision to other points.
Return the maximum number of points you can see.
Examples
Example 1
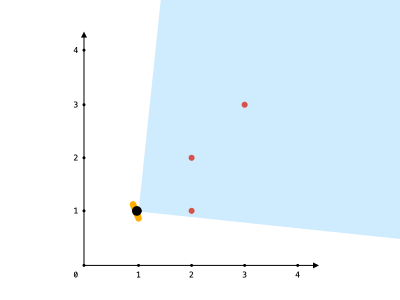
Input: points = [[2,1],[2,2],[3,3]], angle = 90, location = [1,1]
Output: 3
Explanation: The shaded region represents your field of view. All points can be made visible in your field of view, including [3,3] even though [2,2] is in front and in the same line of sight.
Example 2
Input: points = [[2,1],[2,2],[3,4],[1,1]], angle = 90, location = [1,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: All points can be made visible in your field of view, including the one at your location.
Example 3
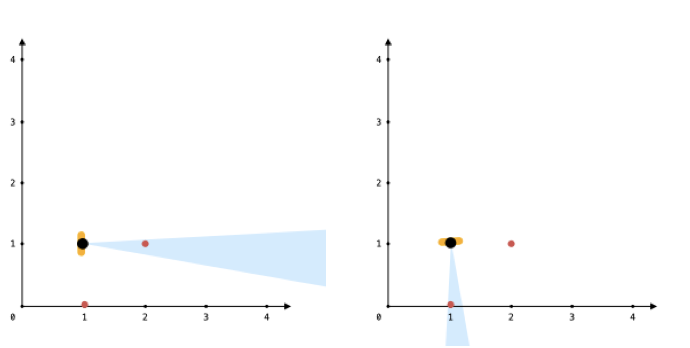
Input: points = [[1,0],[2,1]], angle = 13, location = [1,1]
Output: 1
Explanation: You can only see one of the two points, as shown above.
Constraints
1 <= points.length <= 10^5points[i].length == 2location.length == 20 <= angle < 3600 <= posx, posy, xi, yi <= 100
Solution
Method 1 – Geometry + Sliding Window
Intuition
For each point, compute the angle it makes with the observer's location and the east direction. The problem reduces to finding the maximum number of points whose angles fit in any window of size angle (degrees) on the circle. Points at the observer's location are always visible.
Approach
- For each point, if it is at the observer's location, count it separately.
- For other points, compute the angle (in degrees) from the observer to the point using
atan2. - Sort all angles.
- Duplicate the angle list by adding 360 to each angle to handle the circular wrap-around.
- Use a sliding window to find the maximum number of points within any window of size
angle. - Add the count of points at the observer's location to the result.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int visiblePoints(vector<vector<int>>& points, int angle, vector<int>& location) {
vector<double> angs;
int same = 0;
for (auto& p : points) {
if (p[0] == location[0] && p[1] == location[1]) same++;
else angs.push_back(atan2(p[1] - location[1], p[0] - location[0]) * 180 / M_PI);
}
sort(angs.begin(), angs.end());
int n = angs.size(), ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) angs.push_back(angs[i] + 360);
for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < angs.size(); ++r) {
while (angs[r] - angs[l] > angle) l++;
ans = max(ans, r - l + 1);
}
return ans + same;
}
};
Go
func visiblePoints(points [][]int, angle int, location []int) int {
angs := []float64{}
same := 0
for _, p := range points {
if p[0] == location[0] && p[1] == location[1] {
same++
} else {
angs = append(angs, math.Atan2(float64(p[1]-location[1]), float64(p[0]-location[0]))*180/math.Pi)
}
}
sort.Float64s(angs)
n, ans := len(angs), 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
angs = append(angs, angs[i]+360)
}
l := 0
for r := 0; r < len(angs); r++ {
for angs[r]-angs[l] > float64(angle) {
l++
}
if r-l+1 > ans {
ans = r - l + 1
}
}
return ans + same
}
Java
class Solution {
public int visiblePoints(List<List<Integer>> points, int angle, List<Integer> location) {
List<Double> angs = new ArrayList<>();
int same = 0;
for (List<Integer> p : points) {
if (p.get(0).equals(location.get(0)) && p.get(1).equals(location.get(1))) same++;
else angs.add(Math.atan2(p.get(1) - location.get(1), p.get(0) - location.get(0)) * 180 / Math.PI);
}
Collections.sort(angs);
int n = angs.size(), ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) angs.add(angs.get(i) + 360);
for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < angs.size(); r++) {
while (angs.get(r) - angs.get(l) > angle) l++;
ans = Math.max(ans, r - l + 1);
}
return ans + same;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun visiblePoints(points: List<List<Int>>, angle: Int, location: List<Int>): Int {
val angs = mutableListOf<Double>()
var same = 0
for (p in points) {
if (p[0] == location[0] && p[1] == location[1]) same++
else angs.add(Math.atan2((p[1] - location[1]).toDouble(), (p[0] - location[0]).toDouble()) * 180 / Math.PI)
}
angs.sort()
val n = angs.size
for (i in 0 until n) angs.add(angs[i] + 360)
var ans = 0
var l = 0
for (r in angs.indices) {
while (angs[r] - angs[l] > angle) l++
ans = maxOf(ans, r - l + 1)
}
return ans + same
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def visiblePoints(self, points: list[list[int]], angle: int, location: list[int]) -> int:
from math import atan2, degrees
angs: list[float] = []
same = 0
for x, y in points:
if [x, y] == location:
same += 1
else:
angs.append(degrees(atan2(y - location[1], x - location[0])))
angs.sort()
n = len(angs)
angs += [a + 360 for a in angs]
ans = l = 0
for r in range(len(angs)):
while angs[r] - angs[l] > angle:
l += 1
ans = max(ans, r - l + 1)
return ans + same
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn visible_points(points: Vec<Vec<i32>>, angle: i32, location: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let mut angs = vec![];
let mut same = 0;
for p in points.iter() {
if p[0] == location[0] && p[1] == location[1] {
same += 1;
} else {
angs.push((p[1] - location[1]) as f64).atan2((p[0] - location[0]) as f64).to_degrees());
}
}
angs.sort_by(|a, b| a.partial_cmp(b).unwrap());
let n = angs.len();
for i in 0..n {
angs.push(angs[i] + 360.0);
}
let mut ans = 0;
let mut l = 0;
for r in 0..angs.len() {
while angs[r] - angs[l] > angle as f64 {
l += 1;
}
ans = ans.max(r - l + 1);
}
ans as i32 + same
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
visiblePoints(points: number[][], angle: number, location: number[]): number {
const angs: number[] = [];
let same = 0;
for (const [x, y] of points) {
if (x === location[0] && y === location[1]) same++;
else angs.push(Math.atan2(y - location[1], x - location[0]) * 180 / Math.PI);
}
angs.sort((a, b) => a - b);
const n = angs.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) angs.push(angs[i] + 360);
let ans = 0, l = 0;
for (let r = 0; r < angs.length; r++) {
while (angs[r] - angs[l] > angle) l++;
ans = Math.max(ans, r - l + 1);
}
return ans + same;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n log n)— Sorting the angles dominates. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)— For storing the angles.