Maximum Score After Applying Operations on a Tree
Problem
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n -1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes
ai and bi in the tree.
You are also given a 0-indexed integer array values of length n, where
values[i] is the value associated with the ith node.
You start with a score of 0. In one operation, you can:
- Pick any node
i. - Add
values[i]to your score. - Set
values[i]to0.
A tree is healthy if the sum of values on the path from the root to any leaf node is different than zero.
Return themaximum score you can obtain after performing these operations on the tree any number of times so that it remains healthy.
Examples
Example 1
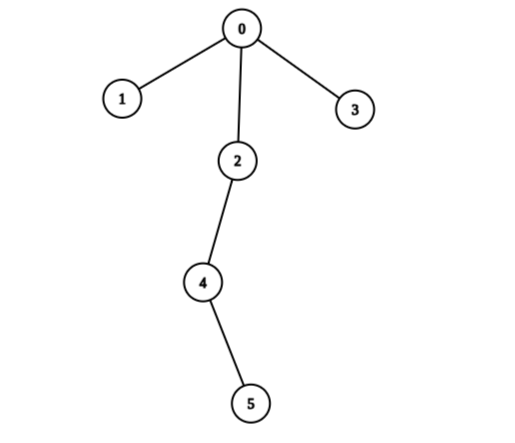
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[2,4],[4,5]], values = [5,2,5,2,1,1]
Output: 11
Explanation: We can choose nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. The value of the root is non-zero. Hence, the sum of values on the path from the root to any leaf is different than zero. Therefore, the tree is healthy and the score is values[1] + values[2] + values[3] + values[4] + values[5] = 11.
It can be shown that 11 is the maximum score obtainable after any number of operations on the tree.
Example 2

Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]], values = [20,10,9,7,4,3,5]
Output: 40
Explanation: We can choose nodes 0, 2, 3, and 4.
- The sum of values on the path from 0 to 4 is equal to 10.
- The sum of values on the path from 0 to 3 is equal to 10.
- The sum of values on the path from 0 to 5 is equal to 3.
- The sum of values on the path from 0 to 6 is equal to 5.
Therefore, the tree is healthy and the score is values[0] + values[2] + values[3] + values[4] = 40.
It can be shown that 40 is the maximum score obtainable after any number of operations on the tree.
Constraints
2 <= n <= 2 * 10^4edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nvalues.length == n1 <= values[i] <= 10^9- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution
Method 1 – DFS with Path Sum Tracking
Intuition
We want to maximize the sum of selected node values, but after any number of operations, the tree must remain "healthy": the sum of values on the path from the root to any leaf must not be zero. If we set a node's value to zero, all its descendants' path sums are affected. The only way the tree becomes unhealthy is if all values on a root-to-leaf path are set to zero. So, the minimum sum among all root-to-leaf paths must remain nonzero.
Approach
- Build the tree as an adjacency list.
- Use DFS to compute the sum of values on each root-to-leaf path.
- The minimum path sum among all root-to-leaf paths is the minimum value that must remain (cannot be set to zero) to keep the tree healthy.
- The answer is the total sum of all node values minus the minimum root-to-leaf path sum.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maximumScoreAfterOperations(vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& values) {
int n = values.size();
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (auto& e : edges) {
g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
g[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
function<long long(int, int)> minPath = [&](int u, int p) {
if (g[u].size() == 1 && u != 0) return (long long)values[u];
long long res = LLONG_MAX;
for (int v : g[u]) {
if (v == p) continue;
res = min(res, minPath(v, u));
}
return res + values[u];
};
long long total = accumulate(values.begin(), values.end(), 0LL);
long long minSum = LLONG_MAX;
for (int v : g[0]) minSum = min(minSum, minPath(v, 0));
return total - minSum;
}
};
Go
func maximumScoreAfterOperations(edges [][]int, values []int) int {
n := len(values)
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
g[e[0]] = append(g[e[0]], e[1])
g[e[1]] = append(g[e[1]], e[0])
}
var minPath func(u, p int) int
minPath = func(u, p int) int {
isLeaf := true
res := 1<<60
for _, v := range g[u] {
if v == p { continue }
isLeaf = false
res = min(res, minPath(v, u))
}
if isLeaf { return values[u] }
return res + values[u]
}
total := 0
for _, v := range values { total += v }
minSum := 1<<60
for _, v := range g[0] {
minSum = min(minSum, minPath(v, 0))
}
return total - minSum
}
func min(a, b int) int { if a < b { return a }; return b }
Java
class Solution {
public int maximumScoreAfterOperations(int[][] edges, int[] values) {
int n = values.length;
List<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) g[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] e : edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1]);
g[e[1]].add(e[0]);
}
int total = 0;
for (int v : values) total += v;
int minSum = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int v : g[0]) minSum = Math.min(minSum, minPath(g, values, v, 0));
return total - minSum;
}
private int minPath(List<Integer>[] g, int[] values, int u, int p) {
if (g[u].size() == 1 && u != 0) return values[u];
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int v : g[u]) {
if (v == p) continue;
res = Math.min(res, minPath(g, values, v, u));
}
return res + values[u];
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maximumScoreAfterOperations(edges: Array<IntArray>, values: IntArray): Int {
val n = values.size
val g = Array(n) { mutableListOf<Int>() }
for (e in edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1])
g[e[1]].add(e[0])
}
fun minPath(u: Int, p: Int): Int {
if (g[u].size == 1 && u != 0) return values[u]
var res = Int.MAX_VALUE
for (v in g[u]) {
if (v == p) continue
res = minOf(res, minPath(v, u))
}
return res + values[u]
}
val total = values.sum()
var minSum = Int.MAX_VALUE
for (v in g[0]) minSum = minOf(minSum, minPath(v, 0))
return total - minSum
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maximumScoreAfterOperations(self, edges: list[list[int]], values: list[int]) -> int:
n = len(values)
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
def min_path(u, p):
if len(g[u]) == 1 and u != 0:
return values[u]
res = float('inf')
for v in g[u]:
if v == p: continue
res = min(res, min_path(v, u))
return res + values[u]
total = sum(values)
min_sum = float('inf')
for v in g[0]:
min_sum = min(min_sum, min_path(v, 0))
return total - min_sum
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn maximum_score_after_operations(edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, values: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let n = values.len();
let mut g = vec![vec![]; n];
for e in &edges {
g[e[0] as usize].push(e[1] as usize);
g[e[1] as usize].push(e[0] as usize);
}
fn min_path(g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>, values: &Vec<i32>, u: usize, p: usize) -> i32 {
if g[u].len() == 1 && u != 0 { return values[u]; }
let mut res = i32::MAX;
for &v in &g[u] {
if v == p { continue; }
res = res.min(min_path(g, values, v, u));
}
res + values[u]
}
let total: i32 = values.iter().sum();
let mut min_sum = i32::MAX;
for &v in &g[0] {
min_sum = min_sum.min(min_path(&g, &values, v, 0));
}
total - min_sum
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maximumScoreAfterOperations(edges: number[][], values: number[]): number {
const n = values.length;
const g: number[][] = Array.from({length: n}, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
g[a].push(b);
g[b].push(a);
}
function minPath(u: number, p: number): number {
if (g[u].length === 1 && u !== 0) return values[u];
let res = Infinity;
for (const v of g[u]) {
if (v === p) continue;
res = Math.min(res, minPath(v, u));
}
return res + values[u];
}
const total = values.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0);
let minSum = Infinity;
for (const v of g[0]) minSum = Math.min(minSum, minPath(v, 0));
return total - minSum;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), since each node is visited once in the DFS. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the adjacency list and recursion stack.