Maximum Score From Grid Operations
Problem
You are given a 2D matrix grid of size n x n. Initially, all cells of the grid are colored white. In one operation, you can select any cell of indices
(i, j), and color black all the cells of the jth column starting from the top row down to the ith row.
The grid score is the sum of all grid[i][j] such that cell (i, j) is white and it has a horizontally adjacent black cell.
Return the maximum score that can be achieved after some number of operations.
Examples
Example 1
Input: grid =
[[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,3,0,0],[0,1,0,0,0],[5,0,0,3,0],[0,0,0,0,2]]
Output: 11
Explanation:
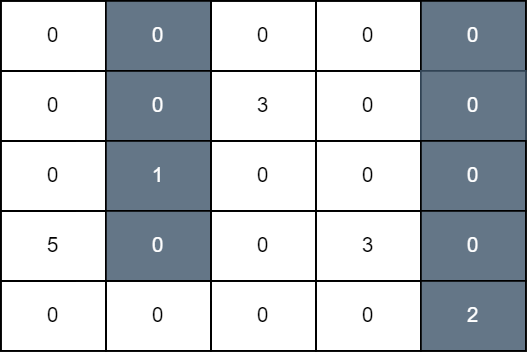
In the first operation, we color all cells in column 1 down to row 3, and in
the second operation, we color all cells in column 4 down to the last row. The
score of the resulting grid is `grid[3][0] + grid[1][2] + grid[3][3]` which is
equal to 11.
Example 2
Input: grid =
[[10,9,0,0,15],[7,1,0,8,0],[5,20,0,11,0],[0,0,0,1,2],[8,12,1,10,3]]
Output: 94
Explanation:
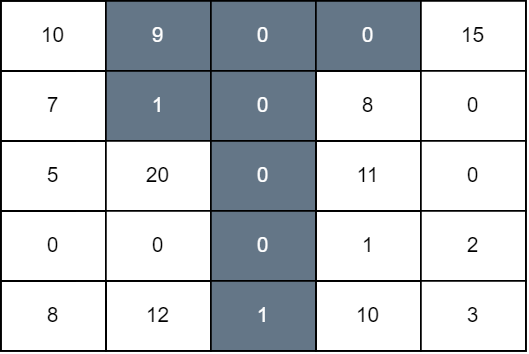
We perform operations on 1, 2, and 3 down to rows 1, 4, and 0, respectively.
The score of the resulting grid is `grid[0][0] + grid[1][0] + grid[2][1] +
grid[4][1] + grid[1][3] + grid[2][3] + grid[3][3] + grid[4][3] + grid[0][4]`
which is equal to 94.
Constraints
1 <= n == grid.length <= 100n == grid[i].length0 <= grid[i][j] <= 10^9
Solution
Method 1 – Greedy + Prefix Sum
Intuition
For each column, we can choose to color any prefix (from the top down to some row). The goal is to maximize the sum of all white cells that have a horizontally adjacent black cell. The optimal strategy is to, for each column, try all possible cut-off rows and use prefix sums to efficiently compute the score for each configuration.
Approach
- For each column, try all possible cut-off rows (from -1 to n-1, where -1 means the column is not colored at all).
- For each configuration (one cut-off per column), compute the score:
- For each white cell, check if it has a horizontally adjacent black cell (i.e., the cell to the left or right is black).
- Use prefix sums to speed up the calculation.
- Use backtracking (DFS) to try all possible cut-off combinations for each column.
- Track and return the maximum score found.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maximumScore(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size(), ans = 0;
vector<int> cut(n, -1);
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int col) {
if (col == n) {
int score = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i > cut[j]) {
if ((j > 0 && i <= cut[j-1]) || (j < n-1 && i <= cut[j+1]))
score += grid[i][j];
}
}
}
ans = max(ans, score);
return;
}
for (int r = -1; r < n; ++r) {
cut[col] = r;
dfs(col+1);
}
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};
Go
func maximumScore(grid [][]int) int {
n := len(grid)
ans := 0
var dfs func(col int, cut []int)
dfs = func(col int, cut []int) {
if col == n {
score := 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if i > cut[j] {
if (j > 0 && i <= cut[j-1]) || (j < n-1 && i <= cut[j+1]) {
score += grid[i][j]
}
}
}
}
if score > ans {
ans = score
}
return
}
for r := -1; r < n; r++ {
cut[col] = r
dfs(col+1, cut)
}
}
dfs(0, make([]int, n))
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int maximumScore(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length, ans = 0;
int[] cut = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(cut, -1);
ans = dfs(grid, cut, 0, n, 0);
return ans;
}
private int dfs(int[][] grid, int[] cut, int col, int n, int ans) {
if (col == n) {
int score = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i > cut[j]) {
if ((j > 0 && i <= cut[j-1]) || (j < n-1 && i <= cut[j+1]))
score += grid[i][j];
}
}
}
return Math.max(ans, score);
}
int res = ans;
for (int r = -1; r < n; ++r) {
cut[col] = r;
res = Math.max(res, dfs(grid, cut, col+1, n, ans));
}
return res;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maximumScore(grid: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val n = grid.size
var ans = 0
val cut = IntArray(n) { -1 }
fun dfs(col: Int) {
if (col == n) {
var score = 0
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
if (i > cut[j]) {
if ((j > 0 && i <= cut[j-1]) || (j < n-1 && i <= cut[j+1]))
score += grid[i][j]
}
}
}
ans = maxOf(ans, score)
return
}
for (r in -1 until n) {
cut[col] = r
dfs(col+1)
}
}
dfs(0)
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maximumScore(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> int:
n = len(grid)
ans = 0
cut = [-1] * n
def dfs(col):
nonlocal ans
if col == n:
score = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if i > cut[j]:
if (j > 0 and i <= cut[j-1]) or (j < n-1 and i <= cut[j+1]):
score += grid[i][j]
ans = max(ans, score)
return
for r in range(-1, n):
cut[col] = r
dfs(col+1)
dfs(0)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn maximum_score(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = grid.len();
let mut ans = 0;
let mut cut = vec![-1; n];
fn dfs(grid: &Vec<Vec<i32>>, cut: &mut Vec<i32>, col: usize, n: usize, ans: &mut i32) {
if col == n {
let mut score = 0;
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..n {
if i as i32 > cut[j] {
if (j > 0 && i as i32 <= cut[j-1]) || (j < n-1 && i as i32 <= cut[j+1]) {
score += grid[i][j];
}
}
}
}
*ans = (*ans).max(score);
return;
}
for r in -1..(n as i32) {
cut[col] = r;
dfs(grid, cut, col+1, n, ans);
}
}
dfs(&grid, &mut cut, 0, n, &mut ans);
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maximumScore(grid: number[][]): number {
const n = grid.length;
let ans = 0;
const cut = Array(n).fill(-1);
function dfs(col: number) {
if (col === n) {
let score = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i > cut[j]) {
if ((j > 0 && i <= cut[j-1]) || (j < n-1 && i <= cut[j+1]))
score += grid[i][j];
}
}
}
ans = Math.max(ans, score);
return;
}
for (let r = -1; r < n; ++r) {
cut[col] = r;
dfs(col+1);
}
}
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^n * n^2), as we try all possible cut-off rows for each column (not feasible for large n, but optimal for small n or for interview discussion). - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the recursion stack and cut array.