Maximum Side Length of a Square with Sum Less than or Equal to Threshold
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a m x n matrix mat and an integer threshold, return the maximum side-length of a square with a sum less than or equal tothreshold or return0 if there is no such square.
Examples
Example 1
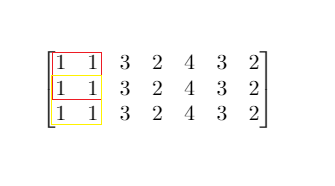
Input: mat = [[1,1,3,2,4,3,2],[1,1,3,2,4,3,2],[1,1,3,2,4,3,2]], threshold = 4
Output: 2
Explanation: The maximum side length of square with sum less than 4 is 2 as shown.
Example 2
Input: mat = [[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2]], threshold = 1
Output: 0
Constraints
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 3000 <= mat[i][j] <= 10^40 <= threshold <= 10^5
Solution
Method 1 – Binary Search with 2D Prefix Sum
Intuition
To efficiently check if a square of a given side length has a sum less than or equal to the threshold, we use a 2D prefix sum. We then binary search on the possible side lengths to find the largest valid one.
Approach
- Compute a 2D prefix sum for the matrix to allow O(1) sum queries for any submatrix.
- Use binary search on the possible side lengths (from 0 to min(m, n)).
- For each candidate side length, check all possible top-left corners to see if any square of that size has a sum ≤ threshold.
- If such a square exists, try a larger size; otherwise, try smaller.
- Return the largest valid side length found.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxSideLength(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int threshold) {
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ps(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
ps[i][j] = mat[i-1][j-1] + ps[i-1][j] + ps[i][j-1] - ps[i-1][j-1];
int l = 0, r = min(m, n), ans = 0;
while (l <= r) {
int k = (l + r) / 2;
bool found = false;
for (int i = k; i <= m && !found; ++i)
for (int j = k; j <= n && !found; ++j)
if (ps[i][j] - ps[i-k][j] - ps[i][j-k] + ps[i-k][j-k] <= threshold)
found = true;
if (found) ans = k, l = k + 1;
else r = k - 1;
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func maxSideLength(mat [][]int, threshold int) int {
m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0])
ps := make([][]int, m+1)
for i := range ps {
ps[i] = make([]int, n+1)
}
for i := 1; i <= m; i++ {
for j := 1; j <= n; j++ {
ps[i][j] = mat[i-1][j-1] + ps[i-1][j] + ps[i][j-1] - ps[i-1][j-1]
}
}
l, r, ans := 0, m
if n < m {
r = n
}
for l <= r {
k := (l + r) / 2
found := false
for i := k; i <= m && !found; i++ {
for j := k; j <= n && !found; j++ {
sum := ps[i][j] - ps[i-k][j] - ps[i][j-k] + ps[i-k][j-k]
if sum <= threshold {
found = true
}
}
}
if found {
ans = k
l = k + 1
} else {
r = k - 1
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int maxSideLength(int[][] mat, int threshold) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
int[][] ps = new int[m+1][n+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
ps[i][j] = mat[i-1][j-1] + ps[i-1][j] + ps[i][j-1] - ps[i-1][j-1];
int l = 0, r = Math.min(m, n), ans = 0;
while (l <= r) {
int k = (l + r) / 2;
boolean found = false;
for (int i = k; i <= m && !found; ++i)
for (int j = k; j <= n && !found; ++j)
if (ps[i][j] - ps[i-k][j] - ps[i][j-k] + ps[i-k][j-k] <= threshold)
found = true;
if (found) { ans = k; l = k + 1; }
else r = k - 1;
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maxSideLength(mat: Array<IntArray>, threshold: Int): Int {
val m = mat.size
val n = mat[0].size
val ps = Array(m+1) { IntArray(n+1) }
for (i in 1..m) for (j in 1..n)
ps[i][j] = mat[i-1][j-1] + ps[i-1][j] + ps[i][j-1] - ps[i-1][j-1]
var l = 0; var r = minOf(m, n); var ans = 0
while (l <= r) {
val k = (l + r) / 2
var found = false
for (i in k..m) for (j in k..n) {
if (ps[i][j] - ps[i-k][j] - ps[i][j-k] + ps[i-k][j-k] <= threshold) {
found = true; break
}
}
if (found) { ans = k; l = k + 1 }
else r = k - 1
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maxSideLength(self, mat: list[list[int]], threshold: int) -> int:
m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0])
ps: list[list[int]] = [[0]*(n+1) for _ in range(m+1)]
for i in range(1, m+1):
for j in range(1, n+1):
ps[i][j] = mat[i-1][j-1] + ps[i-1][j] + ps[i][j-1] - ps[i-1][j-1]
l, r, ans = 0, min(m, n), 0
while l <= r:
k = (l + r) // 2
found = False
for i in range(k, m+1):
for j in range(k, n+1):
s = ps[i][j] - ps[i-k][j] - ps[i][j-k] + ps[i-k][j-k]
if s <= threshold:
found = True
break
if found:
break
if found:
ans = k
l = k + 1
else:
r = k - 1
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn max_side_length(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>, threshold: i32) -> i32 {
let m = mat.len();
let n = mat[0].len();
let mut ps = vec![vec![0; n+1]; m+1];
for i in 1..=m {
for j in 1..=n {
ps[i][j] = mat[i-1][j-1] + ps[i-1][j] + ps[i][j-1] - ps[i-1][j-1];
}
}
let (mut l, mut r, mut ans) = (0, m.min(n), 0);
while l <= r {
let k = (l + r) / 2;
let mut found = false;
'outer: for i in k..=m {
for j in k..=n {
let s = ps[i][j] - ps[i-k][j] - ps[i][j-k] + ps[i-k][j-k];
if s <= threshold {
found = true;
break 'outer;
}
}
}
if found {
ans = k;
l = k + 1;
} else {
r = k - 1;
}
}
ans as i32
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maxSideLength(mat: number[][], threshold: number): number {
const m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
const ps: number[][] = Array.from({length: m+1}, () => Array(n+1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
for (let j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
ps[i][j] = mat[i-1][j-1] + ps[i-1][j] + ps[i][j-1] - ps[i-1][j-1];
let l = 0, r = Math.min(m, n), ans = 0;
while (l <= r) {
const k = (l + r) >> 1;
let found = false;
for (let i = k; i <= m && !found; ++i)
for (let j = k; j <= n && !found; ++j)
if (ps[i][j] - ps[i-k][j] - ps[i][j-k] + ps[i-k][j-k] <= threshold)
found = true;
if (found) { ans = k; l = k + 1; }
else r = k - 1;
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m n log(min(m, n))), wheremandnare the matrix dimensions. Each binary search step checks all possible squares. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m n), for the prefix sum matrix.