Maximum Strictly Increasing Cells in a Matrix
Problem
Given a 1-indexed m x n integer matrix mat, you can select any cell in the matrix as your starting cell.
From the starting cell, you can move to any other cell in the same row or column , but only if the value of the destination cell is strictly greater than the value of the current cell. You can repeat this process as many times as possible, moving from cell to cell until you can no longer make any moves.
Your task is to find the maximum number of cells that you can visit in the matrix by starting from some cell.
Return an integer denoting the maximum number of cells that can be visited.
Examples
Example 1
**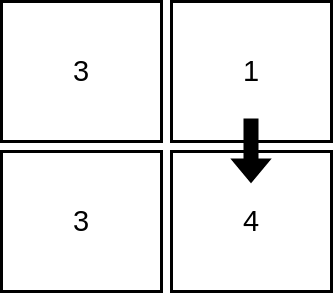**
Input: mat = [[3,1],[3,4]]
Output: 2
Explanation: The image shows how we can visit 2 cells starting from row 1, column 2. It can be shown that we cannot visit more than 2 cells no matter where we start from, so the answer is 2.
Example 2
**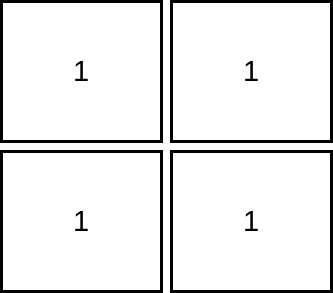**
Input: mat = [[1,1],[1,1]]
Output: 1
Explanation: Since the cells must be strictly increasing, we can only visit one cell in this example.
Example 3
**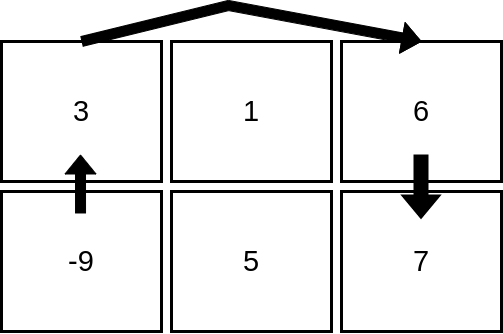**
Input: mat = [[3,1,6],[-9,5,7]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The image above shows how we can visit 4 cells starting from row 2, column 1. It can be shown that we cannot visit more than 4 cells no matter where we start from, so the answer is 4.
Constraints
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10^51 <= m * n <= 10^5-10^5 <= mat[i][j] <= 10^5
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming with Value Grouping
Intuition
To find the longest strictly increasing path where you can move in the same row or column to a strictly greater value, process the matrix cells in increasing order of their values. For each cell, the best you can do is 1 plus the best result in its row or column for smaller values. Use dynamic programming and value grouping to efficiently update and query the best results for each row and column.
Approach
- Collect all cells and sort them by value.
- For each group of cells with the same value, compute the best result for each cell as 1 plus the max of the best results so far in its row or column.
- After processing a group, update the best results for each row and column for this value.
- The answer is the maximum value among all computed results.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxIncreasingCells(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
vector<tuple<int,int,int>> cells;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
cells.emplace_back(mat[i][j], i, j);
sort(cells.begin(), cells.end());
vector<int> row(m), col(n);
vector<int> dp(m * n);
int ans = 1;
for (int l = 0, r; l < cells.size(); l = r) {
r = l;
while (r < cells.size() && get<0>(cells[r]) == get<0>(cells[l])) ++r;
vector<pair<int,int>> updates;
for (int k = l; k < r; ++k) {
auto [v, i, j] = cells[k];
dp[k] = max(row[i], col[j]) + 1;
ans = max(ans, dp[k]);
updates.emplace_back(i, j);
}
for (int k = l; k < r; ++k) {
auto [v, i, j] = cells[k];
row[i] = max(row[i], dp[k]);
col[j] = max(col[j], dp[k]);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
import "sort"
func maxIncreasingCells(mat [][]int) int {
m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0])
type cell struct{v, i, j int}
var cells []cell
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
cells = append(cells, cell{mat[i][j], i, j})
}
}
sort.Slice(cells, func(a, b int) bool { return cells[a].v < cells[b].v })
row := make([]int, m)
col := make([]int, n)
dp := make([]int, m*n)
ans := 1
for l := 0; l < len(cells); {
r := l
for r < len(cells) && cells[r].v == cells[l].v { r++ }
for k := l; k < r; k++ {
i, j := cells[k].i, cells[k].j
dp[k] = max(row[i], col[j]) + 1
if dp[k] > ans { ans = dp[k] }
}
for k := l; k < r; k++ {
i, j := cells[k].i, cells[k].j
row[i] = max(row[i], dp[k])
col[j] = max(col[j], dp[k])
}
l = r
}
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a }; return b }
Java
class Solution {
public int maxIncreasingCells(int[][] mat) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
List<int[]> cells = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
cells.add(new int[]{mat[i][j], i, j});
cells.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
int[] row = new int[m], col = new int[n], dp = new int[m*n];
int ans = 1;
for (int l = 0, r; l < cells.size(); l = r) {
r = l;
while (r < cells.size() && cells.get(r)[0] == cells.get(l)[0]) ++r;
for (int k = l; k < r; ++k) {
int i = cells.get(k)[1], j = cells.get(k)[2];
dp[k] = Math.max(row[i], col[j]) + 1;
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[k]);
}
for (int k = l; k < r; ++k) {
int i = cells.get(k)[1], j = cells.get(k)[2];
row[i] = Math.max(row[i], dp[k]);
col[j] = Math.max(col[j], dp[k]);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maxIncreasingCells(mat: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = mat.size; val n = mat[0].size
val cells = mutableListOf<Triple<Int,Int,Int>>()
for (i in 0 until m) for (j in 0 until n) cells.add(Triple(mat[i][j], i, j))
cells.sortBy { it.first }
val row = IntArray(m)
val col = IntArray(n)
val dp = IntArray(m*n)
var ans = 1
var l = 0
while (l < cells.size) {
var r = l
while (r < cells.size && cells[r].first == cells[l].first) r++
for (k in l until r) {
val (v, i, j) = cells[k]
dp[k] = maxOf(row[i], col[j]) + 1
ans = maxOf(ans, dp[k])
}
for (k in l until r) {
val (v, i, j) = cells[k]
row[i] = maxOf(row[i], dp[k])
col[j] = maxOf(col[j], dp[k])
}
l = r
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maxIncreasingCells(self, mat: list[list[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0])
cells = sorted((v, i, j) for i, row in enumerate(mat) for j, v in enumerate(row))
row = [0] * m
col = [0] * n
dp = [0] * (m * n)
ans = 1
l = 0
while l < len(cells):
r = l
while r < len(cells) and cells[r][0] == cells[l][0]:
r += 1
for k in range(l, r):
v, i, j = cells[k]
dp[k] = max(row[i], col[j]) + 1
ans = max(ans, dp[k])
for k in range(l, r):
v, i, j = cells[k]
row[i] = max(row[i], dp[k])
col[j] = max(col[j], dp[k])
l = r
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn max_increasing_cells(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = mat.len();
let n = mat[0].len();
let mut cells = vec![];
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
cells.push((mat[i][j], i, j));
}
}
cells.sort();
let mut row = vec![0; m];
let mut col = vec![0; n];
let mut dp = vec![0; m*n];
let mut ans = 1;
let mut l = 0;
while l < cells.len() {
let mut r = l;
while r < cells.len() && cells[r].0 == cells[l].0 { r += 1; }
for k in l..r {
let (_, i, j) = cells[k];
dp[k] = row[i].max(col[j]) + 1;
ans = ans.max(dp[k]);
}
for k in l..r {
let (_, i, j) = cells[k];
row[i] = row[i].max(dp[k]);
col[j] = col[j].max(dp[k]);
}
l = r;
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maxIncreasingCells(mat: number[][]): number {
const m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
const cells: [number, number, number][] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j)
cells.push([mat[i][j], i, j]);
cells.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
const row = Array(m).fill(0), col = Array(n).fill(0), dp = Array(m*n).fill(0);
let ans = 1;
for (let l = 0; l < cells.length;) {
let r = l;
while (r < cells.length && cells[r][0] === cells[l][0]) ++r;
for (let k = l; k < r; ++k) {
const [v, i, j] = cells[k];
dp[k] = Math.max(row[i], col[j]) + 1;
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[k]);
}
for (let k = l; k < r; ++k) {
const [v, i, j] = cells[k];
row[i] = Math.max(row[i], dp[k]);
col[j] = Math.max(col[j], dp[k]);
}
l = r;
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(mn log(mn)), for sorting all cells and processing each cell once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(mn), for storing all cells and DP arrays.