Maximum Students Taking Exam
Problem
Given a m * n matrix seats that represent seats distributions in a classroom. If a seat is broken, it is denoted by '#' character otherwise it is denoted by a '.' character.
Students can see the answers of those sitting next to the left, right, upper left and upper right, but he cannot see the answers of the student sitting directly in front or behind him. Return the maximum number of students that can take the exam together without any cheating being possible.
Students must be placed in seats in good condition.
Examples
Example 1
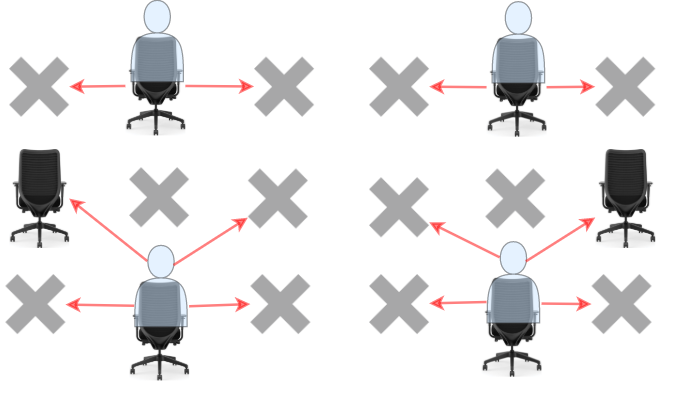
Input: seats = [["#",".","#","#",".","#"],
[".","#","#","#","#","."],
["#",".","#","#",".","#"]]
Output: 4
Explanation: Teacher can place 4 students in available seats so they don't cheat on the exam.
Example 2
Input: seats = [[".","#"],
["#","#"],
["#","."],
["#","#"],
[".","#"]]
Output: 3
Explanation: Place all students in available seats.
Example 3
Input: seats = [["#",".",".",".","#"],
[".","#",".","#","."],
[".",".","#",".","."],
[".","#",".","#","."],
["#",".",".",".","#"]]
Output: 10
Explanation: Place students in available seats in column 1, 3 and 5.
Constraints
seatscontains only characters'.' and``'#'.m == seats.lengthn == seats[i].length1 <= m <= 81 <= n <= 8
Solution
Method 1 – Bitmask Dynamic Programming 1
Intuition
We use bitmask dynamic programming to represent all possible valid seatings for each row. For each row, we try all possible seatings that do not violate the cheating constraints and are compatible with the previous row's seating. The bitmask allows us to efficiently check for conflicts and maximize the number of students.
Approach
- For each row, generate all possible seatings using bitmask, only placing students in good seats ('.').
- For each seating, ensure no two students are adjacent (left/right) in the same row.
- Use DP to keep track of the maximum students for each valid seating in the current row, considering compatibility with the previous row (no cheating via upper left/right).
- Iterate through all rows, updating the DP table for each possible seating.
- The answer is the maximum value in the last row's DP table.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxStudents(vector<vector<char>>& seats) {
int m = seats.size(), n = seats[0].size();
vector<int> valid;
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); ++i) {
bool ok = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((i & (1 << j)) && (seats[0][j] == '#')) ok = false;
if ((i & (1 << j)) && (j > 0) && (i & (1 << (j-1)))) ok = false;
}
if (ok) valid.push_back(i);
}
vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(1 << n, -1));
for (int mask : valid) {
bool ok = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((mask & (1 << j)) && seats[0][j] == '#') ok = false;
}
if (ok) dp[0][mask] = __builtin_popcount(mask);
}
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1 << n); ++mask) {
bool ok = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((mask & (1 << j)) && seats[i][j] == '#') ok = false;
if ((mask & (1 << j)) && (j > 0) && (mask & (1 << (j-1)))) ok = false;
}
if (!ok) continue;
for (int pmask = 0; pmask < (1 << n); ++pmask) {
if (dp[i-1][pmask] == -1) continue;
bool compatible = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((mask & (1 << j)) && ((j > 0 && (pmask & (1 << (j-1)))) || (j < n-1 && (pmask & (1 << (j+1)))))) compatible = false;
}
if (compatible) dp[i][mask] = max(dp[i][mask], dp[i-1][pmask] + __builtin_popcount(mask));
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1 << n); ++mask) ans = max(ans, dp[m-1][mask]);
return ans;
}
};
Go
func maxStudents(seats [][]byte) int {
m, n := len(seats), len(seats[0])
valid := []int{}
for i := 0; i < 1<<n; i++ {
ok := true
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if (i>>j)&1 == 1 && seats[0][j] == '#' {
ok = false
}
if (i>>j)&1 == 1 && j > 0 && (i>>(j-1))&1 == 1 {
ok = false
}
}
if ok {
valid = append(valid, i)
}
}
dp := make([][]int, m)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int, 1<<n)
for j := range dp[i] {
dp[i][j] = -1
}
}
for _, mask := range valid {
ok := true
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if (mask>>j)&1 == 1 && seats[0][j] == '#' {
ok = false
}
}
if ok {
dp[0][mask] = bits.OnesCount(uint(mask))
}
}
for i := 1; i < m; i++ {
for mask := 0; mask < 1<<n; mask++ {
ok := true
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if (mask>>j)&1 == 1 && seats[i][j] == '#' {
ok = false
}
if (mask>>j)&1 == 1 && j > 0 && (mask>>(j-1))&1 == 1 {
ok = false
}
}
if !ok {
continue
}
for pmask := 0; pmask < 1<<n; pmask++ {
if dp[i-1][pmask] == -1 {
continue
}
compatible := true
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if (mask>>j)&1 == 1 && ((j > 0 && (pmask>>(j-1))&1 == 1) || (j < n-1 && (pmask>>(j+1))&1 == 1)) {
compatible = false
}
}
if compatible {
dp[i][mask] = max(dp[i][mask], dp[i-1][pmask]+bits.OnesCount(uint(mask)))
}
}
}
}
ans := 0
for mask := 0; mask < 1<<n; mask++ {
if dp[m-1][mask] > ans {
ans = dp[m-1][mask]
}
}
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a }; return b }
Java
class Solution {
public int maxStudents(char[][] seats) {
int m = seats.length, n = seats[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[m][1 << n];
for (int[] row : dp) Arrays.fill(row, -1);
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1 << n); ++mask) {
boolean ok = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (((mask >> j) & 1) == 1 && seats[0][j] == '#') ok = false;
if (((mask >> j) & 1) == 1 && j > 0 && ((mask >> (j-1)) & 1) == 1) ok = false;
}
if (ok) dp[0][mask] = Integer.bitCount(mask);
}
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1 << n); ++mask) {
boolean ok = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (((mask >> j) & 1) == 1 && seats[i][j] == '#') ok = false;
if (((mask >> j) & 1) == 1 && j > 0 && ((mask >> (j-1)) & 1) == 1) ok = false;
}
if (!ok) continue;
for (int pmask = 0; pmask < (1 << n); ++pmask) {
if (dp[i-1][pmask] == -1) continue;
boolean compatible = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (((mask >> j) & 1) == 1 && ((j > 0 && ((pmask >> (j-1)) & 1) == 1) || (j < n-1 && ((pmask >> (j+1)) & 1) == 1))) compatible = false;
}
if (compatible) dp[i][mask] = Math.max(dp[i][mask], dp[i-1][pmask] + Integer.bitCount(mask));
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1 << n); ++mask) ans = Math.max(ans, dp[m-1][mask]);
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maxStudents(seats: Array<CharArray>): Int {
val m = seats.size
val n = seats[0].size
val dp = Array(m) { IntArray(1 shl n) { -1 } }
for (mask in 0 until (1 shl n)) {
var ok = true
for (j in 0 until n) {
if ((mask shr j) and 1 == 1 && seats[0][j] == '#') ok = false
if ((mask shr j) and 1 == 1 && j > 0 && (mask shr (j-1)) and 1 == 1) ok = false
}
if (ok) dp[0][mask] = mask.countOneBits()
}
for (i in 1 until m) {
for (mask in 0 until (1 shl n)) {
var ok = true
for (j in 0 until n) {
if ((mask shr j) and 1 == 1 && seats[i][j] == '#') ok = false
if ((mask shr j) and 1 == 1 && j > 0 && (mask shr (j-1)) and 1 == 1) ok = false
}
if (!ok) continue
for (pmask in 0 until (1 shl n)) {
if (dp[i-1][pmask] == -1) continue
var compatible = true
for (j in 0 until n) {
if ((mask shr j) and 1 == 1 && ((j > 0 && (pmask shr (j-1)) and 1 == 1) || (j < n-1 && (pmask shr (j+1)) and 1 == 1))) compatible = false
}
if (compatible) dp[i][mask] = maxOf(dp[i][mask], dp[i-1][pmask] + mask.countOneBits())
}
}
}
var ans = 0
for (mask in 0 until (1 shl n)) ans = maxOf(ans, dp[m-1][mask])
return ans
}
}
Python
def maxStudents(seats: list[list[str]]) -> int:
m, n = len(seats), len(seats[0])
def valid(mask, row):
for j in range(n):
if (mask >> j) & 1 and seats[row][j] == '#':
return False
if (mask >> j) & 1 and j > 0 and (mask >> (j-1)) & 1:
return False
return True
dp = [{} for _ in range(m)]
for mask in range(1 << n):
if valid(mask, 0):
dp[0][mask] = bin(mask).count('1')
for i in range(1, m):
for mask in range(1 << n):
if not valid(mask, i):
continue
for pmask in dp[i-1]:
compatible = True
for j in range(n):
if (mask >> j) & 1 and ((j > 0 and (pmask >> (j-1)) & 1) or (j < n-1 and (pmask >> (j+1)) & 1)):
compatible = False
if compatible:
dp[i][mask] = max(dp[i].get(mask, 0), dp[i-1][pmask] + bin(mask).count('1'))
return max(dp[-1].values() or [0])
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn max_students(seats: Vec<Vec<char>>) -> i32 {
let m = seats.len();
let n = seats[0].len();
let mut dp = vec![vec![-1; 1 << n]; m];
for mask in 0..(1 << n) {
let mut ok = true;
for j in 0..n {
if (mask >> j) & 1 == 1 && seats[0][j] == '#' {
ok = false;
}
if (mask >> j) & 1 == 1 && j > 0 && (mask >> (j-1)) & 1 == 1 {
ok = false;
}
}
if ok {
dp[0][mask] = mask.count_ones() as i32;
}
}
for i in 1..m {
for mask in 0..(1 << n) {
let mut ok = true;
for j in 0..n {
if (mask >> j) & 1 == 1 && seats[i][j] == '#' {
ok = false;
}
if (mask >> j) & 1 == 1 && j > 0 && (mask >> (j-1)) & 1 == 1 {
ok = false;
}
}
if !ok { continue; }
for pmask in 0..(1 << n) {
if dp[i-1][pmask] == -1 { continue; }
let mut compatible = true;
for j in 0..n {
if (mask >> j) & 1 == 1 && ((j > 0 && (pmask >> (j-1)) & 1 == 1) || (j < n-1 && (pmask >> (j+1)) & 1 == 1)) {
compatible = false;
}
}
if compatible {
dp[i][mask] = dp[i][mask].max(dp[i-1][pmask] + mask.count_ones() as i32);
}
}
}
}
let mut ans = 0;
for mask in 0..(1 << n) {
ans = ans.max(dp[m-1][mask]);
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maxStudents(seats: string[][]): number {
const m = seats.length, n = seats[0].length;
const valid = (mask: number, row: number) => {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((mask >> j) & 1 && seats[row][j] === '#') return false;
if ((mask >> j) & 1 && j > 0 && (mask >> (j-1)) & 1) return false;
}
return true;
};
const dp: Record<number, number>[] = Array.from({length: m}, () => ({}));
for (let mask = 0; mask < (1 << n); ++mask) {
if (valid(mask, 0)) dp[0][mask] = mask.toString(2).split('1').length - 1;
}
for (let i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for (let mask = 0; mask < (1 << n); ++mask) {
if (!valid(mask, i)) continue;
for (const pmask in dp[i-1]) {
let compatible = true;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((mask >> j) & 1 && ((j > 0 && (Number(pmask) >> (j-1)) & 1) || (j < n-1 && (Number(pmask) >> (j+1)) & 1))) compatible = false;
}
if (compatible) dp[i][mask] = Math.max(dp[i][mask] || 0, dp[i-1][pmask] + mask.toString(2).split('1').length - 1);
}
}
}
return Math.max(...Object.values(dp[m-1]), 0);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n * 2^n * 2^n), where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns. For each row, we check all possible seatings and all previous seatings. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m * 2^n), for the DP table