Maximum Sum BST in Binary Tree
HardUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a binary tree root, return the maximum sum of all keys of any sub-tree which is also a Binary Search Tree (BST).
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Examples
Example 1
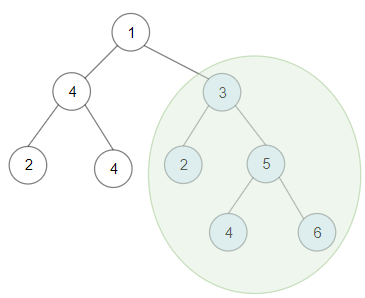
Input: root = [1,4,3,2,4,2,5,null,null,null,null,null,null,4,6]
Output: 20
Explanation: Maximum sum in a valid Binary search tree is obtained in root node with key equal to 3.
Example 2
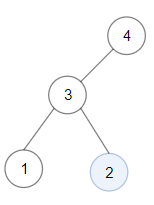
Input: root = [4,3,null,1,2]
Output: 2
Explanation: Maximum sum in a valid Binary search tree is obtained in a single root node with key equal to 2.
Example 3
Input: root = [-4,-2,-5]
Output: 0
Explanation: All values are negatives. Return an empty BST.
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 4 * 10^4]. -4 * 10^4 <= Node.val <= 4 * 10^4
Solution
Method 1 – Postorder Traversal with State Tracking
Intuition
To find the maximum sum BST in a binary tree, we need to check every subtree to see if it is a BST and calculate its sum. By traversing the tree in postorder, we can gather information from the left and right subtrees before making decisions at the current node.
Approach
- Use postorder traversal to visit each node after its children.
- For each node, collect:
- Whether its left and right subtrees are BSTs.
- The minimum and maximum values in its subtrees.
- The sum of its subtree if it is a BST.
- If the current node forms a BST with its children, update the global maximum sum.
- If not a BST, propagate invalid state upwards.
- Return the maximum sum found.
Code
C++
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
};
class Solution {
public:
int ans = 0;
vector<int> dfs(TreeNode* node) {
if (!node) return {1, INT_MAX, INT_MIN, 0};
auto l = dfs(node->left), r = dfs(node->right);
if (l[0] && r[0] && node->val > l[2] && node->val < r[1]) {
int sum = l[3] + r[3] + node->val;
ans = max(ans, sum);
return {1, min(l[1], node->val), max(r[2], node->val), sum};
}
return {0, 0, 0, 0};
}
int maxSumBST(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};
Go
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left, Right *TreeNode
}
func maxSumBST(root *TreeNode) int {
ans := 0
var dfs func(*TreeNode) (bool, int, int, int)
dfs = func(node *TreeNode) (bool, int, int, int) {
if node == nil {
return true, 1<<31-1, -1<<31, 0
}
lbst, lmin, lmax, lsum := dfs(node.Left)
rbst, rmin, rmax, rsum := dfs(node.Right)
if lbst && rbst && node.Val > lmax && node.Val < rmin {
sum := lsum + rsum + node.Val
if sum > ans {
ans = sum
}
minv := lmin
if node.Val < minv {
minv = node.Val
}
maxv := rmax
if node.Val > maxv {
maxv = node.Val
}
return true, minv, maxv, sum
}
return false, 0, 0, 0
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}
Java
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left, right;
}
class Solution {
int ans = 0;
int[] dfs(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return new int[]{1, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MIN_VALUE, 0};
int[] l = dfs(node.left), r = dfs(node.right);
if (l[0]==1 && r[0]==1 && node.val > l[2] && node.val < r[1]) {
int sum = l[3] + r[3] + node.val;
ans = Math.max(ans, sum);
return new int[]{1, Math.min(l[1], node.val), Math.max(r[2], node.val), sum};
}
return new int[]{0, 0, 0, 0};
}
public int maxSumBST(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
data class TreeNode(var `val`: Int, var left: TreeNode? = null, var right: TreeNode? = null)
class Solution {
var ans = 0
fun dfs(node: TreeNode?): IntArray {
if (node == null) return intArrayOf(1, Int.MAX_VALUE, Int.MIN_VALUE, 0)
val l = dfs(node.left)
val r = dfs(node.right)
if (l[0]==1 && r[0]==1 && node.`val` > l[2] && node.`val` < r[1]) {
val sum = l[3] + r[3] + node.`val`
ans = maxOf(ans, sum)
return intArrayOf(1, minOf(l[1], node.`val`), maxOf(r[2], node.`val`), sum)
}
return intArrayOf(0, 0, 0, 0)
}
fun maxSumBST(root: TreeNode?): Int {
dfs(root)
return ans
}
}
Python
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val: int, left: 'TreeNode' = None, right: 'TreeNode' = None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxSumBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
ans = 0
def dfs(node: TreeNode) -> tuple[int, int, int, int]:
if not node:
return 1, float('inf'), float('-inf'), 0
lbst, lmin, lmax, lsum = dfs(node.left)
rbst, rmin, rmax, rsum = dfs(node.right)
if lbst and rbst and node.val > lmax and node.val < rmin:
s = lsum + rsum + node.val
nonlocal ans
ans = max(ans, s)
return 1, min(lmin, node.val), max(rmax, node.val), s
return 0, 0, 0, 0
dfs(root)
return ans
Rust
pub struct TreeNode {
pub val: i32,
pub left: Option<Box<TreeNode>>,
pub right: Option<Box<TreeNode>>,
}
impl Solution {
pub fn max_sum_bst(root: Option<Box<TreeNode>>) -> i32 {
fn dfs(node: &Option<Box<TreeNode>>, ans: &mut i32) -> (bool, i32, i32, i32) {
if let Some(n) = node {
let (lbst, lmin, lmax, lsum) = dfs(&n.left, ans);
let (rbst, rmin, rmax, rsum) = dfs(&n.right, ans);
if lbst && rbst && n.val > lmax && n.val < rmin {
let sum = lsum + rsum + n.val;
*ans = (*ans).max(sum);
return (true, lmin.min(n.val), rmax.max(n.val), sum);
}
(false, 0, 0, 0)
} else {
(true, i32::MAX, i32::MIN, 0)
}
}
let mut ans = 0;
dfs(&root, &mut ans);
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class TreeNode {
val: number;
left: TreeNode | null;
right: TreeNode | null;
constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
this.val = val ?? 0;
this.left = left ?? null;
this.right = right ?? null;
}
}
class Solution {
ans = 0;
dfs(node: TreeNode | null): [boolean, number, number, number] {
if (!node) return [true, Infinity, -Infinity, 0];
const [lbst, lmin, lmax, lsum] = this.dfs(node.left);
const [rbst, rmin, rmax, rsum] = this.dfs(node.right);
if (lbst && rbst && node.val > lmax && node.val < rmin) {
const sum = lsum + rsum + node.val;
this.ans = Math.max(this.ans, sum);
return [true, Math.min(lmin, node.val), Math.max(rmax, node.val), sum];
}
return [false, 0, 0, 0];
}
maxSumBST(root: TreeNode | null): number {
this.dfs(root);
return this.ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), since each node is visited once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(h), wherehis the height of the tree due to recursion stack.