Maximum Sum Circular Subarray
Problem
Given a circular integer array nums of length n, return the maximum possible sum of a non-empty subarray of nums.
A circular array means the end of the array connects to the beginning of the array. Formally, the next element of nums[i] is nums[(i + 1) % n] and the previous element of nums[i] is nums[(i - 1 + n) % n].
A subarray may only include each element of the fixed buffer nums at most once. Formally, for a subarray nums[i], nums[i + 1], ..., nums[j], there does not exist i <= k1, k2 <= j with k1 % n == k2 % n.
Examples
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,-2,3,-2]
Output: 3
Explanation: Subarray [3] has maximum sum 3.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,-3,5]
Output: 10
Explanation: Subarray [5,5] has maximum sum 5 + 5 = 10.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [-3,-2,-3]
Output: -2
Explanation: Subarray [-2] has maximum sum -2.
Related Problem
We have already seen [Maximum Subarray Sum](maximum-subarray-sum). We can handle something similar.
Solution
Method 1 - Using Kadane for Max and Min Sum Subarray and Total Sum
So there are two case:
- Case 1. The first is that the subarray take only a middle part, and we know how to find the max subarray sum using [Maximum Subarray Sum](maximum-subarray-sum).
- Case2. The second is that the subarray take a part of head array and a part of tail array. Inversion: If max subarray occurs at ends, then min subarray occurs in the middle. So we just need to find the smallest one in the middle, the use
totalSum - minSumcan the the possible answer. Also, to calculate minSum, while calculating maxSum. Look at the code below.
Here is diagramatic view:
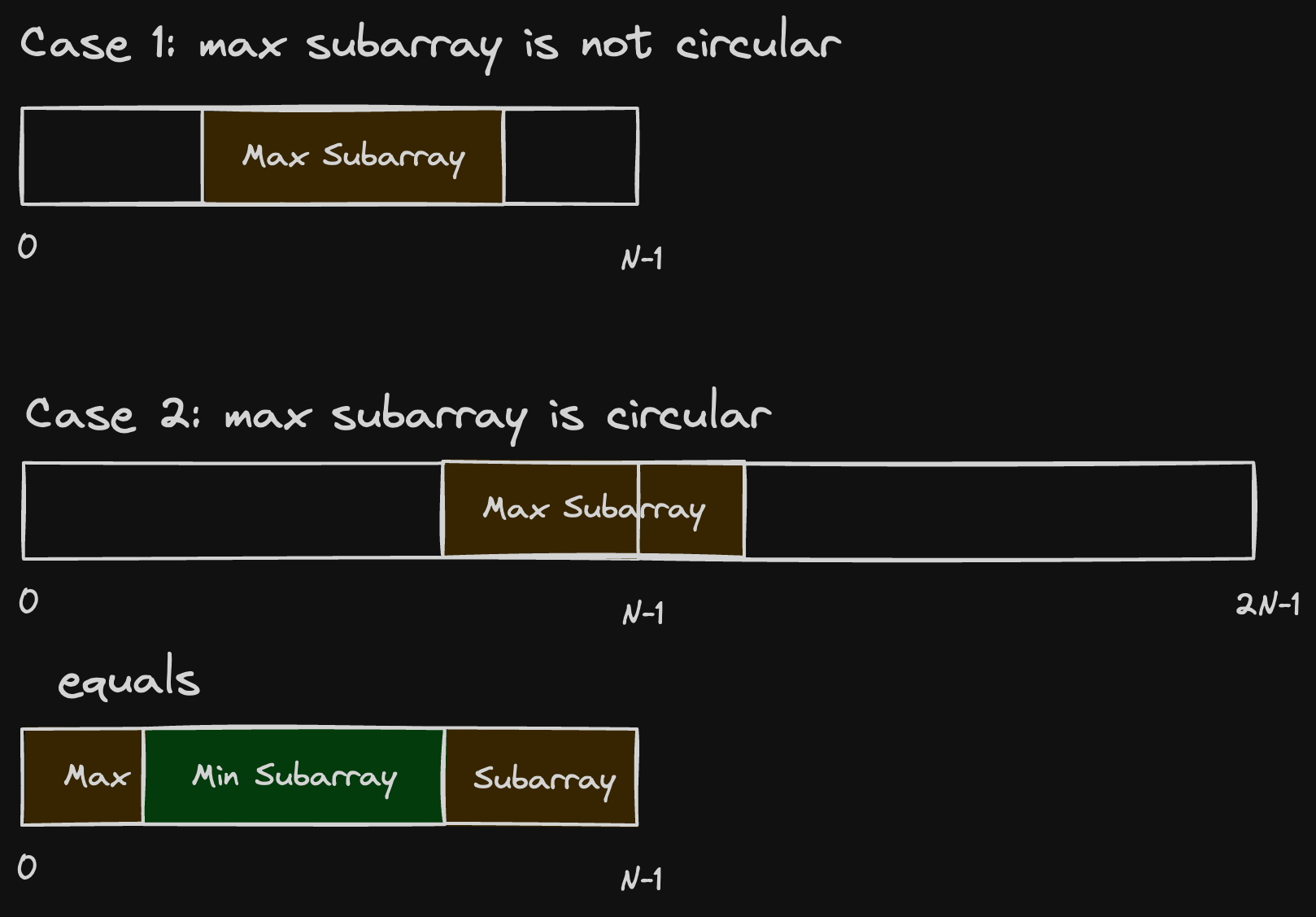
So the max subarray circular sum equals to
ans = max(maxSum, totalSum - minSum)
Corner Case
Just one to pay attention:
If all numbers are negative, maxSum = max(A) and minSum = sum(A).
In this case, max(maxSum, total - minSum) = 0, which means the sum of an empty subarray.
According to the deacription, We need to return the max(A), instead of sum of am empty subarray.
So we return the maxSum to handle this corner case.
Code
Java
public int maxSubarraySumCircular(int[] A) {
int total = 0, maxSum = A[0], curMax = 0, minSum = A[0], curMin = 0;
for (int a : A) {
curMax = Math.max(curMax + a, a);
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, curMax);
curMin = Math.min(curMin + a, a);
minSum = Math.min(minSum, curMin);
total += a;
}
return maxSum > 0 ? Math.max(maxSum, total - minSum) : maxSum;
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)
Method 2 - Using Prefix Sum
We can apply Kadane's algorithm similar to [Maximum Sum Subarray](maximum-subarray-sum). Here is the approach:
- Find the total sum of the array.
- Find the minimum subarray sum using Kadane's algorithm (by inverting the signs of the array elements and running Kadane's algorithm).
- The maximum subarray sum in the circular case can be found by taking the total sum and subtracting the minimum subarray sum.
- The maximum sum is the greater of the result from the non-circular case and the circular case, unless all elements are negative (in which case, the result from the non-circular case is used).
Code
Java
public class Solution {
public int maxSubarraySumCircular(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// Finding the non-circular maximum subarray sum using Kadane's algorithm
int maxKadane = kadane(nums);
// Calculating the total sum and inverting the elements
int totalSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
totalSum += nums[i];
nums[i] = -nums[i];
}
// Finding the minimum subarray sum by using Kadane's algorithm on the inverted array
int maxInvertedKadane = kadane(nums);
// Restoring the original array elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nums[i] = -nums[i];
}
int maxCircular = totalSum + maxInvertedKadane; // Inverted Kadane gives minimum sum, re-invert it
// If all numbers are negative, maxCircular would be zero which we need to avoid
if (maxCircular == 0) return maxKadane;
// The result is the maximum of the two sums
return Math.max(maxKadane, maxCircular);
}
private int kadane(int[] nums) {
int currentMax = nums[0];
int globalMax = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
currentMax = Math.max(nums[i], currentMax + nums[i]);
if (currentMax > globalMax) {
globalMax = currentMax;
}
}
return globalMax;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maxSubarraySumCircular(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
# Finding the non-circular maximum subarray sum using Kadane's algorithm
def kadane(nums: List[int]) -> int:
current_max = nums[0]
global_max = nums[0]
for num in nums[1:]:
current_max = max(num, current_max + num)
if current_max > global_max:
global_max = current_max
return global_max
total_sum = sum(nums)
max_kadane = kadane(nums) # Non-circular maximum subarray sum
# Invert the elements of the array to find the minimum subarray sum
for i in range(len(nums)):
nums[i] = -nums[i]
max_inverted_kadane = kadane(nums)
# Restore the original array elements
for i in range(len(nums)):
nums[i] = -nums[i]
max_circular = total_sum + max_inverted_kadane # Inverted Kadane gives minimum sum, re-invert it
# Special case: if all elements are negative, max_circular would be zero which is incorrect
if max_circular == 0:
return max_kadane
return max(max_kadane, max_circular)
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), wherenis the number of elements in the array, because we traverse the array a constant number of times. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1), as we use a fixed amount of extra space.