Maximum Weighted K-Edge Path
MediumUpdated: Oct 13, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given an integer n and a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. This is represented by a 2D array edges, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates a directed edge from node ui to vi with weight wi.
You are also given two integers, k and t.
Your task is to determine the maximum possible sum of edge weights for any path in the graph such that:
- The path contains exactly
kedges. - The total sum of edge weights in the path is strictly less than
t.
Return the maximum possible sum of weights for such a path. If no such path exists, return -1.
Examples
Example 1
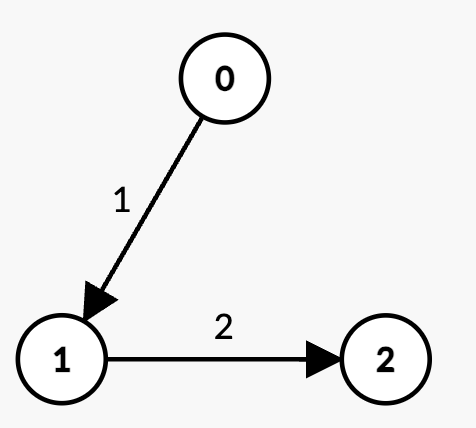
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,2]], k = 2, t = 4
Output: 3
Explanation:
* The only path with `k = 2` edges is `0 -> 1 -> 2` with weight `1 + 2 = 3 < t`.
* Thus, the maximum possible sum of weights less than `t` is 3.
Example 2
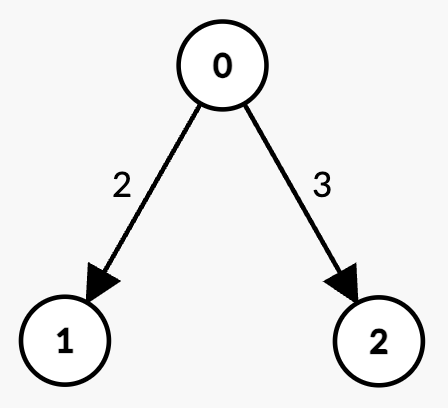
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,2],[0,2,3]], k = 1, t = 3
Output: 2
Explanation:
* There are two paths with `k = 1` edge:
* `0 -> 1` with weight `2 < t`.
* `0 -> 2` with weight `3 = t`, which is not strictly less than `t`.
* Thus, the maximum possible sum of weights less than `t` is 2.
Example 3
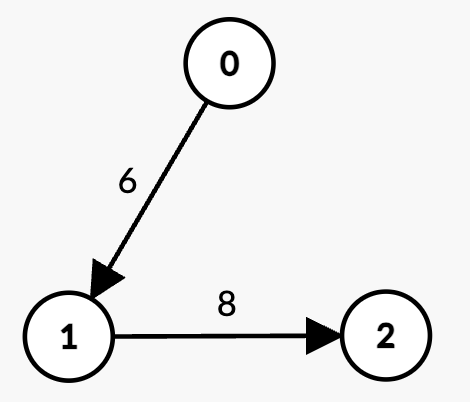
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,6],[1,2,8]], k = 1, t = 6
Output: -1
Explanation:
* There are two paths with k = 1 edge:
* `0 -> 1` with weight `6 = t`, which is not strictly less than `t`.
* `1 -> 2` with weight `8 > t`, which is not strictly less than `t`.
* Since there is no path with sum of weights strictly less than `t`, the answer is -1.
Constraints
1 <= n <= 3000 <= edges.length <= 300edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi]0 <= ui, vi < nui != vi1 <= wi <= 100 <= k <= 3001 <= t <= 600- The input graph is guaranteed to be a DAG.
- There are no duplicate edges.
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming on DAG
Intuition
Since the graph is a DAG, we can use dynamic programming to compute the maximum sum for each node and edge count. By processing nodes in topological order, we ensure all dependencies are resolved before updating the DP table.
Approach
- Build the adjacency list and in-degree array for topological sorting.
- Initialize a DP table
dp[node][edges]to store the max sum for each node with a given number of edges. - Set
dp[node][0] = 0for all nodes. - Process nodes in topological order:
- For each outgoing edge
(u, v, w), for each possible edge count:- If
dp[u][edges]is valid, updatedp[v][edges+1]withdp[u][edges] + wif the sum is less thant.
- If
- For each outgoing edge
- The answer is the maximum value among all
dp[node][k]for all nodes, or-1if none is valid.
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(nk + m)— Topological sort and DP updates. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(nk)— For the DP table.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maximumWeightedKEdgePath(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int k, int t) {
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> g(n);
vector<int> indeg(n);
for (auto& e : edges) {
g[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1], e[2]);
indeg[e[1]]++;
}
vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(k+1, -1));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) dp[i][0] = 0;
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (indeg[i] == 0) q.push(i);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for (auto& [v, w] : g[u]) {
for (int e = 0; e < k; ++e) {
if (dp[u][e] != -1 && dp[u][e] + w < t) {
dp[v][e+1] = max(dp[v][e+1], dp[u][e] + w);
}
}
if (--indeg[v] == 0) q.push(v);
}
}
int ans = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ans = max(ans, dp[i][k]);
return ans;
}
};
Go
func maximumWeightedKEdgePath(n int, edges [][]int, k, t int) int {
g := make([][][2]int, n)
indeg := make([]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
g[e[0]] = append(g[e[0]], [2]int{e[1], e[2]})
indeg[e[1]]++
}
dp := make([][]int, n)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int, k+1)
for j := range dp[i] { dp[i][j] = -1 }
dp[i][0] = 0
}
q := []int{}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ { if indeg[i] == 0 { q = append(q, i) } }
for len(q) > 0 {
u := q[0]; q = q[1:]
for _, vw := range g[u] {
v, w := vw[0], vw[1]
for e := 0; e < k; e++ {
if dp[u][e] != -1 && dp[u][e]+w < t {
if dp[v][e+1] < dp[u][e]+w {
dp[v][e+1] = dp[u][e]+w
}
}
}
indeg[v]--
if indeg[v] == 0 { q = append(q, v) }
}
}
ans := -1
for i := 0; i < n; i++ { if dp[i][k] > ans { ans = dp[i][k] } }
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int maximumWeightedKEdgePath(int n, int[][] edges, int k, int t) {
List<List<int[]>> g = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) g.add(new ArrayList<>());
int[] indeg = new int[n];
for (int[] e : edges) {
g.get(e[0]).add(new int[]{e[1], e[2]});
indeg[e[1]]++;
}
int[][] dp = new int[n][k+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) dp[i][0] = 0;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (indeg[i] == 0) q.offer(i);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int u = q.poll();
for (int[] vw : g.get(u)) {
int v = vw[0], w = vw[1];
for (int e = 0; e < k; ++e) {
if (dp[u][e] != -1 && dp[u][e] + w < t) {
dp[v][e+1] = Math.max(dp[v][e+1], dp[u][e] + w);
}
}
if (--indeg[v] == 0) q.offer(v);
}
}
int ans = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i][k]);
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maximumWeightedKEdgePath(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>, k: Int, t: Int): Int {
val g = Array(n) { mutableListOf<Pair<Int,Int>>() }
val indeg = IntArray(n)
for (e in edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1] to e[2])
indeg[e[1]]++
}
val dp = Array(n) { IntArray(k+1) { -1 } }
for (i in 0 until n) dp[i][0] = 0
val q = ArrayDeque<Int>()
for (i in 0 until n) if (indeg[i] == 0) q.add(i)
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val u = q.removeFirst()
for ((v, w) in g[u]) {
for (e in 0 until k) {
if (dp[u][e] != -1 && dp[u][e] + w < t) {
dp[v][e+1] = maxOf(dp[v][e+1], dp[u][e] + w)
}
}
indeg[v]--
if (indeg[v] == 0) q.add(v)
}
}
var ans = -1
for (i in 0 until n) ans = maxOf(ans, dp[i][k])
return ans
}
}
Python
def maximum_weighted_k_edge_path(n: int, edges: list[list[int]], k: int, t: int) -> int:
from collections import deque, defaultdict
g: dict[int, list[tuple[int,int]]] = defaultdict(list)
indeg = [0] * n
for u, v, w in edges:
g[u].append((v, w))
indeg[v] += 1
dp = [[-1]*(k+1) for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
dp[i][0] = 0
q = deque(i for i in range(n) if indeg[i] == 0)
while q:
u = q.popleft()
for v, w in g[u]:
for e in range(k):
if dp[u][e] != -1 and dp[u][e] + w < t:
dp[v][e+1] = max(dp[v][e+1], dp[u][e] + w)
indeg[v] -= 1
if indeg[v] == 0:
q.append(v)
ans = max(dp[i][k] for i in range(n))
return ans if ans != -1 else -1
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn maximum_weighted_k_edge_path(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, k: i32, t: i32) -> i32 {
use std::collections::{VecDeque, HashMap};
let n = n as usize;
let k = k as usize;
let mut g: HashMap<usize, Vec<(usize, i32)>> = HashMap::new();
let mut indeg = vec![0; n];
for e in &edges {
g.entry(e[0] as usize).or_default().push((e[1] as usize, e[2]));
indeg[e[1] as usize] += 1;
}
let mut dp = vec![vec![-1; k+1]; n];
for i in 0..n { dp[i][0] = 0; }
let mut q: VecDeque<usize> = (0..n).filter(|&i| indeg[i] == 0).collect();
while let Some(u) = q.pop_front() {
if let Some(adj) = g.get(&u) {
for &(v, w) in adj {
for e in 0..k {
if dp[u][e] != -1 && dp[u][e] + w < t {
dp[v][e+1] = dp[v][e+1].max(dp[u][e] + w);
}
}
indeg[v] -= 1;
if indeg[v] == 0 { q.push_back(v); }
}
}
}
let ans = dp.iter().map(|row| row[k]).max().unwrap();
if ans == -1 { -1 } else { ans }
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maximumWeightedKEdgePath(n: number, edges: number[][], k: number, t: number): number {
const g: Map<number, [number, number][]> = new Map()
const indeg = Array(n).fill(0)
for (const [u, v, w] of edges) {
if (!g.has(u)) g.set(u, [])
g.get(u)!.push([v, w])
indeg[v]++
}
const dp = Array.from({length: n}, () => Array(k+1).fill(-1))
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) dp[i][0] = 0
const q: number[] = []
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (indeg[i] === 0) q.push(i)
while (q.length) {
const u = q.shift()!
for (const [v, w] of g.get(u) ?? []) {
for (let e = 0; e < k; ++e) {
if (dp[u][e] !== -1 && dp[u][e] + w < t) {
dp[v][e+1] = Math.max(dp[v][e+1], dp[u][e] + w)
}
}
indeg[v]--
if (indeg[v] === 0) q.push(v)
}
}
let ans = -1
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i][k])
return ans
}
}