Merge In Between Linked Lists
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given two linked lists: list1 and list2 of sizes n and m
respectively.
Remove list1's nodes from the ath node to the bth node, and put list2
in their place.
The blue edges and nodes in the following figure indicate the result:
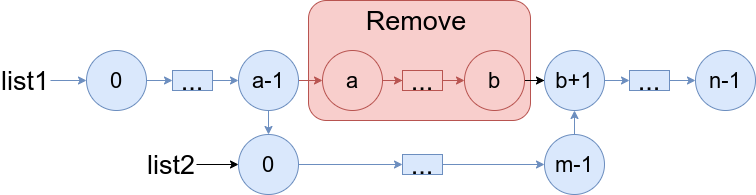
Build the result list and return its head.
Examples
Example 1
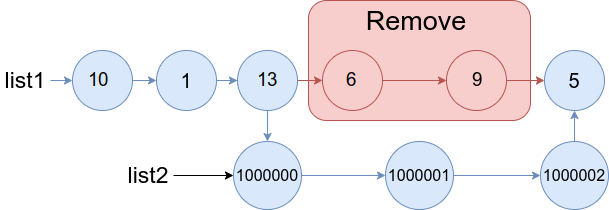
Input: list1 = [10,1,13,6,9,5], a = 3, b = 4, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002]
Output: [10,1,13,1000000,1000001,1000002,5]
Explanation: We remove the nodes 3 and 4 and put the entire list2 in their place. The blue edges and nodes in the above figure indicate the result.
Example 2
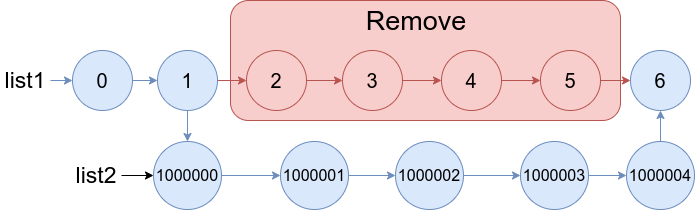
Input: list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6], a = 2, b = 5, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004]
Output: [0,1,1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004,6]
Explanation: The blue edges and nodes in the above figure indicate the result.
Constraints
3 <= list1.length <= 10^41 <= a <= b < list1.length - 11 <= list2.length <= 10^4
Solution
Method 1 – Pointer Manipulation
Intuition
To merge list2 into list1 between nodes a and b, we need to find the node just before a and the node just after b in list1. We then connect the end of list2 to the node after b, and the node before a to the head of list2.
Approach
- Traverse
list1to find the node before positiona(prev_a). - Traverse to find the node at position
b(after_b). - Traverse
list2to find its tail. - Connect
prev_a.nexttolist2's head. - Connect
list2's tail toafter_b.next. - Return the head of
list1.
Code
C++
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeInBetween(ListNode* list1, int a, int b, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* prev_a = list1;
for (int i = 1; i < a; ++i) prev_a = prev_a->next;
ListNode* after_b = prev_a;
for (int i = a; i <= b; ++i) after_b = after_b->next;
ListNode* tail2 = list2;
while (tail2->next) tail2 = tail2->next;
prev_a->next = list2;
tail2->next = after_b;
return list1;
}
};
Go
type ListNode struct {
Val int
Next *ListNode
}
func mergeInBetween(list1 *ListNode, a, b int, list2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
prevA := list1
for i := 1; i < a; i++ {
prevA = prevA.Next
}
afterB := prevA
for i := a; i <= b; i++ {
afterB = afterB.Next
}
tail2 := list2
for tail2.Next != nil {
tail2 = tail2.Next
}
prevA.Next = list2
tail2.Next = afterB
return list1
}
Java
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeInBetween(ListNode list1, int a, int b, ListNode list2) {
ListNode prevA = list1;
for (int i = 1; i < a; i++) prevA = prevA.next;
ListNode afterB = prevA;
for (int i = a; i <= b; i++) afterB = afterB.next;
ListNode tail2 = list2;
while (tail2.next != null) tail2 = tail2.next;
prevA.next = list2;
tail2.next = afterB;
return list1;
}
}
Kotlin
data class ListNode(var `val`: Int, var next: ListNode? = null)
class Solution {
fun mergeInBetween(list1: ListNode, a: Int, b: Int, list2: ListNode): ListNode {
var prevA = list1
repeat(a - 1) { prevA = prevA.next!! }
var afterB = prevA
repeat(b - a + 1) { afterB = afterB.next!! }
var tail2 = list2
while (tail2.next != null) tail2 = tail2.next!!
prevA.next = list2
tail2.next = afterB
return list1
}
}
Python
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val: int, next: 'ListNode' = None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
def merge_in_between(list1: 'ListNode', a: int, b: int, list2: 'ListNode') -> 'ListNode':
prev_a = list1
for _ in range(a - 1):
prev_a = prev_a.next
after_b = prev_a
for _ in range(b - a + 1):
after_b = after_b.next
tail2 = list2
while tail2.next:
tail2 = tail2.next
prev_a.next = list2
tail2.next = after_b
return list1
Rust
struct ListNode {
val: i32,
next: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
}
impl Solution {
pub fn merge_in_between(list1: Box<ListNode>, a: i32, b: i32, list2: Box<ListNode>) -> Box<ListNode> {
let mut prev_a = &list1;
for _ in 1..a {
prev_a = prev_a.next.as_ref().unwrap();
}
let mut after_b = prev_a;
for _ in a..=b {
after_b = after_b.next.as_ref().unwrap();
}
let mut tail2 = &list2;
while let Some(ref next) = tail2.next {
tail2 = next;
}
// Unsafe pointer manipulation for brevity
unsafe {
let prev_a_mut = &mut *(prev_a as *const _ as *mut ListNode);
let tail2_mut = &mut *(tail2 as *const _ as *mut ListNode);
prev_a_mut.next = Some(list2);
tail2_mut.next = Some(after_b.next.clone().unwrap());
}
list1
}
}
TypeScript
class ListNode {
val: number;
next: ListNode | null;
constructor(val: number, next: ListNode | null = null) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
class Solution {
mergeInBetween(list1: ListNode, a: number, b: number, list2: ListNode): ListNode {
let prevA = list1;
for (let i = 1; i < a; ++i) prevA = prevA.next!;
let afterB = prevA;
for (let i = a; i <= b; ++i) afterB = afterB.next!;
let tail2 = list2;
while (tail2.next) tail2 = tail2.next;
prevA.next = list2;
tail2.next = afterB;
return list1;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n + m), traversing both lists once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1), only pointers used.