Middle of the linked list
Problem
Given the head of a singly linked list, return the middle node of the linked list.
If there are two middle nodes, return the second middle node.
Examples
Example 1:
graph LR A(1) --> B(2) --> C(3):::RedNode --> D(4) --> E(5) classDef RedNode fill:#ff0000;
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [3,4,5]
Explanation: The middle node of the list is node 3.
Example 2:
graph LR F(1) --> G(2) --> H(3) --> I(4):::RedNode --> J(5) -->K(6) classDef RedNode fill:#ff0000;
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: [4,5,6]
Explanation: Since the list has two middle nodes with values 3 and 4, we return the second one.
Follow up
Follow up - How will you get it in first pass.
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution
Video explanation
Here is the video explaining below methods in detail. Please check it out:
<div class="youtube-embed"><iframe src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/hW8Qvt_jonw" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></div>
Method 1 - Get the Length and Travel to Middle
Traverse the whole linked list and count the no. of nodes. Now traverse the list again till count/2 and return the node at count/2.
Code
Java
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
// Step 1: Calculate the length of the list
int length = 0;
ListNode current = head;
while (current != null) {
length++;
current = current.next;
}
// Step 2: Find the middle node's position
int mid = length / 2;
// Step 3: Traverse to the middle node
current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < mid; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def middleNode(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# Step 1: Calculate the length of the list
length = 0
current = head
while current:
length += 1
current = current.next
# Step 2: Find the middle node's position
mid = length // 2
# Step 3: Traverse to the middle node
current = head
for _ in range(mid):
current = current.next
return current
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is length of linked list. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)
Method 2 - Uses One Slow Pointer and One Fast Pointer 🏆
Traverse linked list using two pointers. Move one pointer by one and other pointer by two. When the fast pointer reaches end slow pointer will reach middle of the linked list. This is done in single pass.
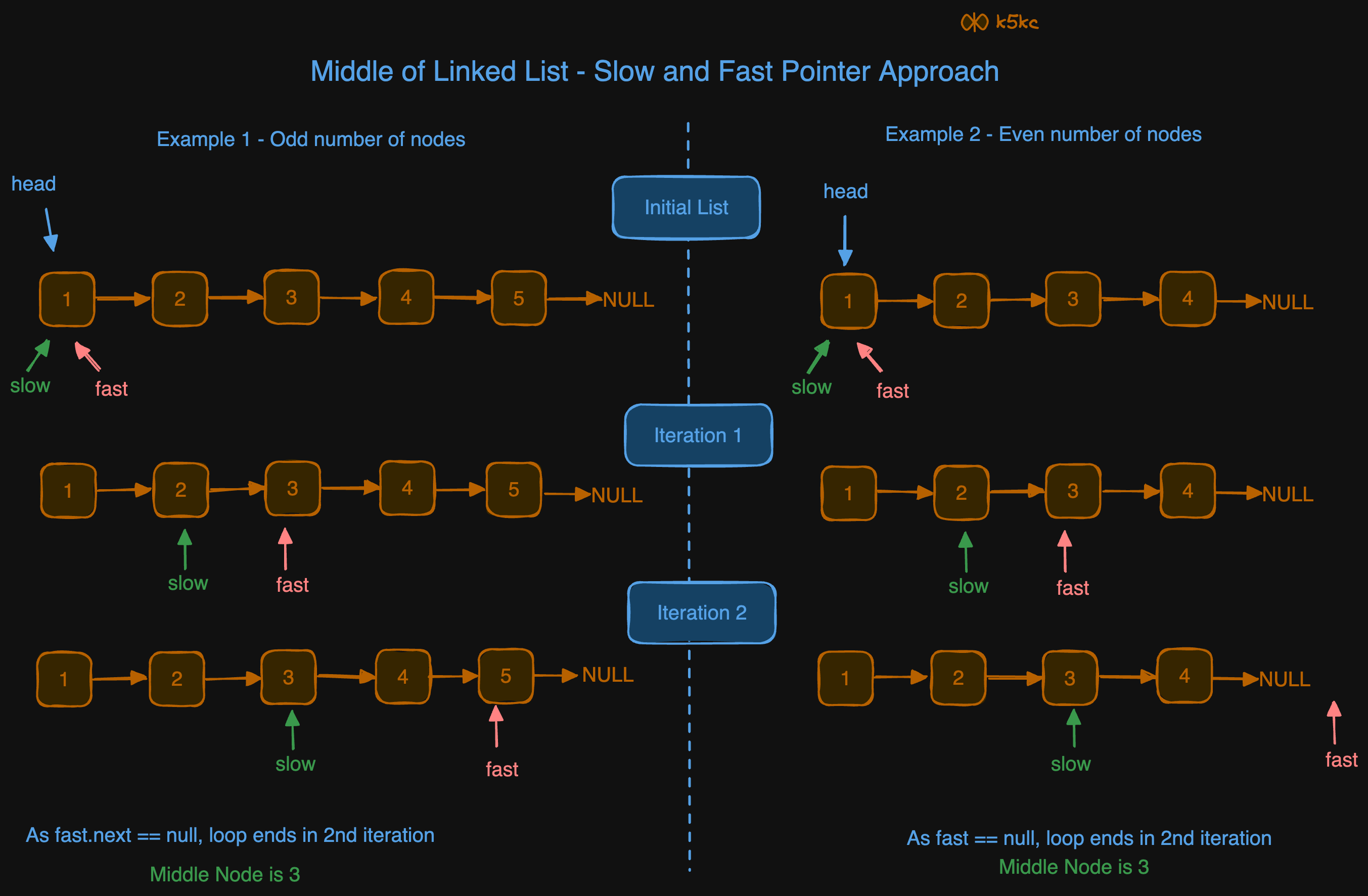
Code
Java
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def middleNode(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
slow, fast = head, head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
Method 3 - Using a Counter
Initialize mid element as head and initialize a counter as 0. Traverse the list from head, while traversing increment the counter and change mid to mid->next whenever the counter is odd. So the mid will move only half of the total length of the list.
Code
C
mynode * getTheMiddle(mynode * head) {
mynode * middle = (mynode * ) NULL;
int i;
for (i = 1; head != (mynode * ) NULL; head = head -> next, i++) {
if (i == 1)
middle = head;
else if ((i % 2) == 1)
middle = middle -> next;
}
return middle;
}