Min Cost to Connect All Points
Problem
You are given an array points representing integer coordinates of some points on a 2D-plane, where points[i] = [xi, yi].
The cost of connecting two points [xi, yi] and [xj, yj] is the manhattan distance between them: |xi - xj| + |yi - yj|, where |val| denotes the absolute value of val.
Return the minimum cost to make all points connected. All points are connected if there is exactly one simple path between any two points.
Examples
Example 1:
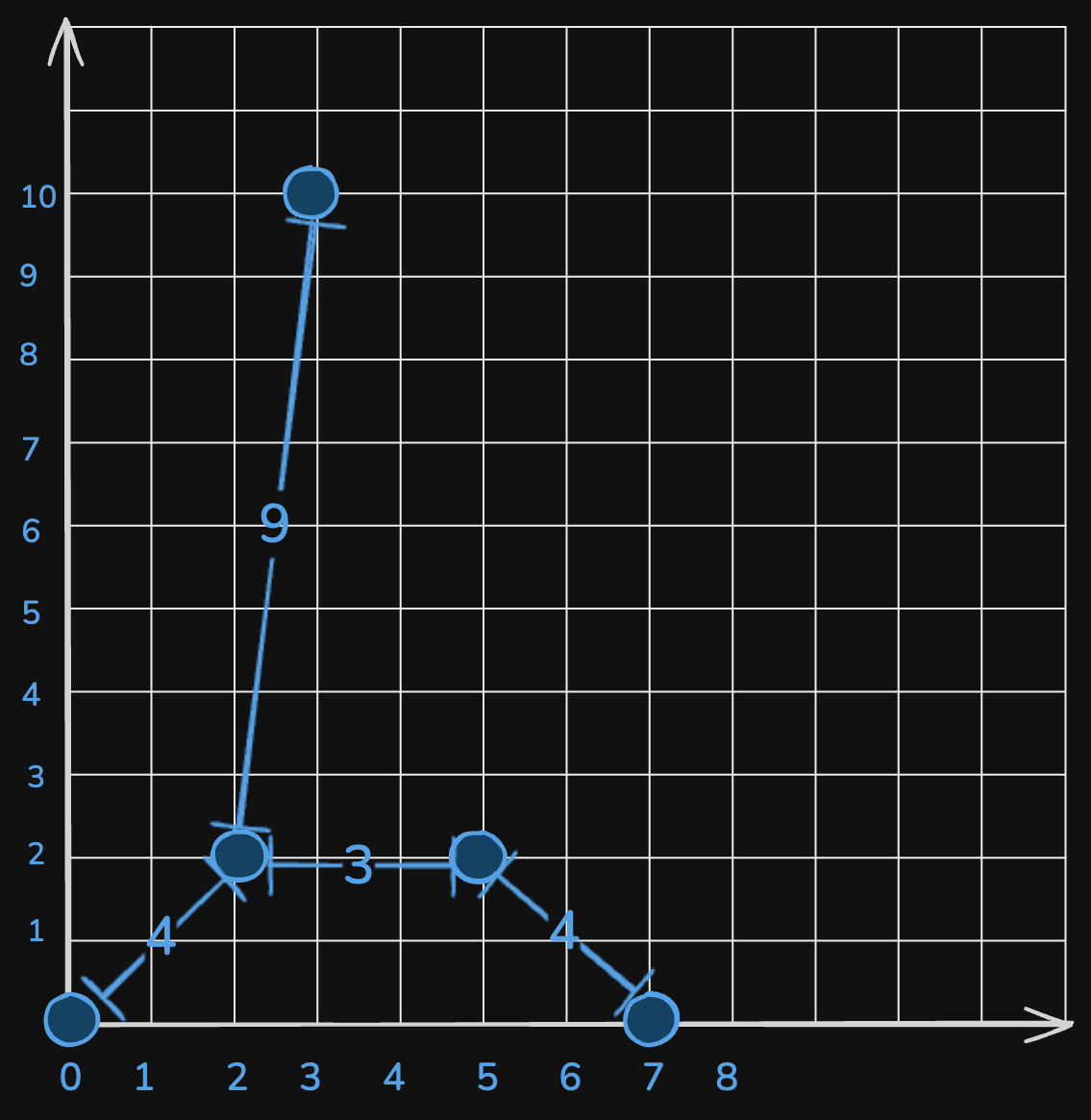
Input: points = [[0,0],[2,2],[3,10],[5,2],[7,0]]
Output: 20
Explanation:
We can connect the points as shown above to get the minimum cost of 20.
Notice that there is a unique path between every pair of points.
Example 2:
Input: points = [[3,12],[-2,5],[-4,1]]
Output: 18
Solution
Method 1 – Prim's MST Using minHeap
Intuition
and also we know
In this problem, we already know that given points are the nodes. The distance between each of the nodes, i.e. the manhattan distance is the edges. We want min of these distance, which means this is like Prim's algorithm. Read here - Minimum Spanning Trees MST - Prim's Algorithm and also we see
We treat each point as a node and the Manhattan distance between any two points as the edge weight. The goal is to connect all points with the minimum total cost, which is a classic Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) problem. Prim's algorithm is well-suited here, as it grows the MST by always adding the lowest-cost edge that connects a new node. We have seen implementation of Prim's Algorithm here - [Prims Algorithm Using Adjacency List and Priority Queue](/cs/algorithms/graph/mst/prims-algorithm-using-adjacency-list-and-priority-queue). Also, see - Weighted Graph Representation - Adjacency List - Creating Edge Class.
Approach
- Start with any point (node) and add it to the MST.
- Use a min-heap (priority queue) to always select the edge with the smallest cost that connects a new point to the MST.
- For each newly added point, push all edges from it to unvisited points into the heap.
- Continue until all points are included in the MST.
- The sum of the selected edge weights is the minimum cost to connect all points.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minCostConnectPoints(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
int n = points.size(), ans = 0, cnt = 0;
vector<bool> vis(n, false);
vector<int> minDist(n, INT_MAX);
minDist[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int u = -1;
for (int v = 0; v < n; ++v) {
if (!vis[v] && (u == -1 || minDist[v] < minDist[u])) u = v;
}
vis[u] = true;
ans += minDist[u];
for (int v = 0; v < n; ++v) {
int cost = abs(points[u][0] - points[v][0]) + abs(points[u][1] - points[v][1]);
if (!vis[v] && cost < minDist[v]) minDist[v] = cost;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func minCostConnectPoints(points [][]int) int {
n := len(points)
vis := make([]bool, n)
minDist := make([]int, n)
for i := range minDist { minDist[i] = 1<<31-1 }
minDist[0] = 0
ans := 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
u := -1
for v := 0; v < n; v++ {
if !vis[v] && (u == -1 || minDist[v] < minDist[u]) {
u = v
}
}
vis[u] = true
ans += minDist[u]
for v := 0; v < n; v++ {
cost := abs(points[u][0]-points[v][0]) + abs(points[u][1]-points[v][1])
if !vis[v] && cost < minDist[v] {
minDist[v] = cost
}
}
}
return ans
}
func abs(x int) int { if x < 0 { return -x }; return x }
Java
class Solution {
public int minCostConnectPoints(int[][] points) {
int n = points.length, ans = 0;
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
int[] minDist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(minDist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
minDist[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int u = -1;
for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if (!vis[v] && (u == -1 || minDist[v] < minDist[u])) u = v;
}
vis[u] = true;
ans += minDist[u];
for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {
int cost = Math.abs(points[u][0] - points[v][0]) + Math.abs(points[u][1] - points[v][1]);
if (!vis[v] && cost < minDist[v]) minDist[v] = cost;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minCostConnectPoints(points: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val n = points.size
val vis = BooleanArray(n)
val minDist = IntArray(n) { Int.MAX_VALUE }
minDist[0] = 0
var ans = 0
repeat(n) {
var u = -1
for (v in 0 until n) {
if (!vis[v] && (u == -1 || minDist[v] < minDist[u])) u = v
}
vis[u] = true
ans += minDist[u]
for (v in 0 until n) {
val cost = Math.abs(points[u][0] - points[v][0]) + Math.abs(points[u][1] - points[v][1])
if (!vis[v] && cost < minDist[v]) minDist[v] = cost
}
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minCostConnectPoints(self, points: list[list[int]]) -> int:
n = len(points)
vis = [False] * n
min_dist = [float('inf')] * n
min_dist[0] = 0
ans = 0
for _ in range(n):
u = -1
for v in range(n):
if not vis[v] and (u == -1 or min_dist[v] < min_dist[u]):
u = v
vis[u] = True
ans += min_dist[u]
for v in range(n):
cost = abs(points[u][0] - points[v][0]) + abs(points[u][1] - points[v][1])
if not vis[v] and cost < min_dist[v]:
min_dist[v] = cost
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_cost_connect_points(points: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = points.len();
let mut vis = vec![false; n];
let mut min_dist = vec![i32::MAX; n];
min_dist[0] = 0;
let mut ans = 0;
for _ in 0..n {
let mut u = None;
for v in 0..n {
if !vis[v] && (u.is_none() || min_dist[v] < min_dist[u.unwrap()]) {
u = Some(v);
}
}
let u = u.unwrap();
vis[u] = true;
ans += min_dist[u];
for v in 0..n {
let cost = (points[u][0] - points[v][0]).abs() + (points[u][1] - points[v][1]).abs();
if !vis[v] && cost < min_dist[v] {
min_dist[v] = cost;
}
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minCostConnectPoints(points: number[][]): number {
const n = points.length;
const vis = Array(n).fill(false);
const minDist = Array(n).fill(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER);
minDist[0] = 0;
let ans = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let u = -1;
for (let v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if (!vis[v] && (u === -1 || minDist[v] < minDist[u])) u = v;
}
vis[u] = true;
ans += minDist[u];
for (let v = 0; v < n; v++) {
const cost = Math.abs(points[u][0] - points[v][0]) + Math.abs(points[u][1] - points[v][1]);
if (!vis[v] && cost < minDist[v]) minDist[v] = cost;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^2)— For each of thennodes, we scan all other nodes to find the minimum edge. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)— For the visited and minDist arrays.
Method 2 – Kruskal's MST Using Union-Find
Intuition
We can also solve the minimum cost to connect all points by building all possible edges (with their Manhattan distances) and sorting them by cost. Then, using Kruskal's algorithm, we add the smallest edges one by one, connecting components using Union-Find, until all points are connected. This approach is efficient when the number of points is not too large.
Approach
- Generate all possible edges between points, with their Manhattan distances as weights.
- Sort all edges by weight (cost).
- Initialize a Union-Find (Disjoint Set Union) structure to keep track of connected components.
- Iterate through the sorted edges:
- For each edge, if the two points are not already connected, add the edge to the MST and union their components.
- Stop when all points are connected (n-1 edges added).
- The sum of the selected edge weights is the minimum cost to connect all points.
Code
Java
class Solution {
public int minCostConnectPoints(int[][] points) {
int n = points.length, ans = 0;
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
pq.add(new int[]{findDist(points, i, j), i, j});
}
}
int count = 0;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n);
while (count < n - 1) {
int[] edge = pq.poll();
if (uf.find(edge[1]) != uf.find(edge[2])) {
ans += edge[0];
count++;
uf.union(edge[1], edge[2]);
}
}
return ans;
}
private int findDist(int[][] points, int a, int b) {
return Math.abs(points[a][0] - points[b][0]) + Math.abs(points[a][1] - points[b][1]);
}
class UnionFind {
int[] parent;
UnionFind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) parent[i] = i;
}
void union(int a, int b) {
parent[find(a)] = parent[find(b)];
}
int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x) parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
}
}
C++
class UnionFind {
public:
vector<int> parent;
UnionFind(int n) : parent(n) {
iota(parent.begin(), parent.end(), 0);
}
int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x) parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
void unite(int x, int y) {
parent[find(x)] = find(y);
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int minCostConnectPoints(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
int n = points.size(), ans = 0, count = 0;
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> edges;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j)
edges.emplace_back(abs(points[i][0] - points[j][0]) + abs(points[i][1] - points[j][1]), i, j);
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
UnionFind uf(n);
for (auto& [cost, u, v] : edges) {
if (uf.find(u) != uf.find(v)) {
ans += cost;
uf.unite(u, v);
if (++count == n - 1) break;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
type edge struct{cost, u, v int}
type UnionFind struct{parent []int}
func (uf *UnionFind) find(x int) int {
if uf.parent[x] != x { uf.parent[x] = uf.find(uf.parent[x]) }
return uf.parent[x]
}
func (uf *UnionFind) union(x, y int) { uf.parent[uf.find(x)] = uf.find(y) }
func minCostConnectPoints(points [][]int) int {
n := len(points)
edges := []edge{}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := i+1; j < n; j++ {
cost := abs(points[i][0]-points[j][0]) + abs(points[i][1]-points[j][1])
edges = append(edges, edge{cost, i, j})
}
}
sort.Slice(edges, func(i, j int) bool { return edges[i].cost < edges[j].cost })
uf := UnionFind{make([]int, n)}
for i := range uf.parent { uf.parent[i] = i }
ans, count := 0, 0
for _, e := range edges {
if uf.find(e.u) != uf.find(e.v) {
ans += e.cost
uf.union(e.u, e.v)
count++
if count == n-1 { break }
}
}
return ans
}
func abs(x int) int { if x < 0 { return -x }; return x }
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minCostConnectPoints(points: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val n = points.size
val edges = mutableListOf<Triple<Int, Int, Int>>()
for (i in 0 until n) for (j in i+1 until n)
edges.add(Triple(
Math.abs(points[i][0] - points[j][0]) + Math.abs(points[i][1] - points[j][1]), i, j))
edges.sortBy { it.first }
val uf = UnionFind(n)
var ans = 0
var count = 0
for ((cost, u, v) in edges) {
if (uf.find(u) != uf.find(v)) {
ans += cost
uf.union(u, v)
count++
if (count == n-1) break
}
}
return ans
}
class UnionFind(n: Int) {
private val parent = IntArray(n) { it }
fun find(x: Int): Int {
if (parent[x] != x) parent[x] = find(parent[x])
return parent[x]
}
fun union(x: Int, y: Int) { parent[find(x)] = find(y) }
}
}
Python
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.parent = list(range(n))
def find(self, x):
if self.parent[x] != x:
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
def union(self, x, y):
self.parent[self.find(x)] = self.find(y)
class Solution:
def minCostConnectPoints(self, points: list[list[int]]) -> int:
n = len(points)
edges = []
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i+1, n):
cost = abs(points[i][0] - points[j][0]) + abs(points[i][1] - points[j][1])
edges.append((cost, i, j))
edges.sort()
uf = UnionFind(n)
ans = count = 0
for cost, u, v in edges:
if uf.find(u) != uf.find(v):
ans += cost
uf.union(u, v)
count += 1
if count == n-1:
break
return ans
Rust
struct UnionFind {
parent: Vec<usize>,
}
impl UnionFind {
fn new(n: usize) -> Self {
Self { parent: (0..n).collect() }
}
fn find(&mut self, x: usize) -> usize {
if self.parent[x] != x {
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x]);
}
self.parent[x]
}
fn union(&mut self, x: usize, y: usize) {
let px = self.find(x);
let py = self.find(y);
self.parent[px] = py;
}
}
impl Solution {
pub fn min_cost_connect_points(points: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = points.len();
let mut edges = vec![];
for i in 0..n {
for j in i+1..n {
let cost = (points[i][0] - points[j][0]).abs() + (points[i][1] - points[j][1]).abs();
edges.push((cost, i, j));
}
}
edges.sort_unstable();
let mut uf = UnionFind::new(n);
let mut ans = 0;
let mut count = 0;
for (cost, u, v) in edges {
if uf.find(u) != uf.find(v) {
ans += cost;
uf.union(u, v);
count += 1;
if count == n - 1 { break; }
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class UnionFind {
parent: number[];
constructor(n: number) {
this.parent = Array.from({length: n}, (_, i) => i);
}
find(x: number): number {
if (this.parent[x] !== x) this.parent[x] = this.find(this.parent[x]);
return this.parent[x];
}
union(x: number, y: number) {
this.parent[this.find(x)] = this.find(y);
}
}
class Solution {
minCostConnectPoints(points: number[][]): number {
const n = points.length;
const edges: [number, number, number][] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (let j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
edges.push([
Math.abs(points[i][0] - points[j][0]) + Math.abs(points[i][1] - points[j][1]),
i, j
]);
edges.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
const uf = new UnionFind(n);
let ans = 0, count = 0;
for (const [cost, u, v] of edges) {
if (uf.find(u) !== uf.find(v)) {
ans += cost;
uf.union(u, v);
count++;
if (count === n - 1) break;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^2 \, \log n)— Building all edges takesO(n^2), sorting takesO(n^2 \log n), and union-find operations are nearly constant time. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n^2)— For storing all possible edges.