Minimum Cost to Connect Two Groups of Points
Problem
You are given two groups of points where the first group has size1 points, the second group has size2 points, and size1 >= size2.
The cost of the connection between any two points are given in an size1 x size2 matrix where cost[i][j] is the cost of connecting point i of the first group and point j of the second group. The groups are connected if each point in both groups is connected to one or more points in the opposite group. In other words, each point in the first group must be connected to at least one point in the second group, and each point in the second group must be connected to at least one point in the first group.
Return the minimum cost it takes to connect the two groups.
Examples
Example 1
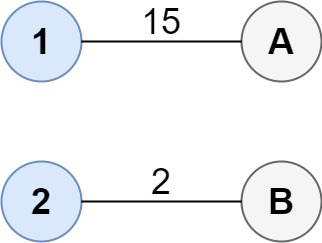
Input: cost = [[15, 96], [36, 2]]
Output: 17
Explanation: The optimal way of connecting the groups is:
1--A
2--B
This results in a total cost of 17.
Example 2
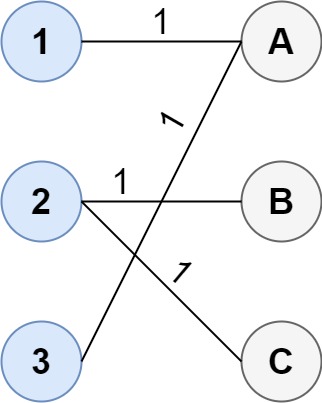
Input: cost = [[1, 3, 5], [4, 1, 1], [1, 5, 3]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The optimal way of connecting the groups is:
1--A
2--B
2--C
3--A
This results in a total cost of 4.
Note that there are multiple points connected to point 2 in the first group and point A in the second group. This does not matter as there is no limit to the number of points that can be connected. We only care about the minimum total cost.
Example 3
Input: cost = [[2, 5, 1], [3, 4, 7], [8, 1, 2], [6, 2, 4], [3, 8, 8]]
Output: 10
Constraints
size1 == cost.lengthsize2 == cost[i].length1 <= size1, size2 <= 12size1 >= size20 <= cost[i][j] <= 100
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming with Bitmask
Intuition
We need to connect every point in both groups, minimizing the cost. Since the number of points is small, we can use DP with bitmasking to represent which points in the second group are already connected. For each point in the first group, we try all possible connections to the second group and update the DP state.
Approach
- Use a DP table
dp[i][mask]whereiis the index in the first group andmaskis a bitmask representing which points in the second group are connected. - For each point in the first group, try connecting it to every point in the second group, updating the mask and cost.
- After connecting all points in the first group, ensure all points in the second group are connected (mask == all ones).
- The answer is the minimum cost to reach the final state.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int connectTwoGroups(vector<vector<int>>& cost) {
int n = cost.size(), m = cost[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(n+1, vector<int>(1<<m, 1e9));
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<m); ++mask) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
int nmask = mask | (1<<j);
dp[i+1][nmask] = min(dp[i+1][nmask], dp[i][mask] + cost[i][j]);
}
}
}
int ans = 1e9;
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<m); ++mask) {
if (__builtin_popcount(mask) == m) {
ans = min(ans, dp[n][mask]);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func connectTwoGroups(cost [][]int) int {
n, m := len(cost), len(cost[0])
dp := make([][]int, n+1)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int, 1<<m)
for j := range dp[i] {
dp[i][j] = 1e9
}
}
dp[0][0] = 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for mask := 0; mask < 1<<m; mask++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
nmask := mask | (1<<j)
if dp[i+1][nmask] > dp[i][mask]+cost[i][j] {
dp[i+1][nmask] = dp[i][mask]+cost[i][j]
}
}
}
}
ans := 1e9
for mask := 0; mask < 1<<m; mask++ {
cnt := 0
for k := 0; k < m; k++ {
if mask&(1<<k) > 0 {
cnt++
}
}
if cnt == m && dp[n][mask] < ans {
ans = dp[n][mask]
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int connectTwoGroups(List<List<Integer>> cost) {
int n = cost.size(), m = cost.get(0).size();
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][1<<m];
for (int[] row : dp) Arrays.fill(row, Integer.MAX_VALUE/2);
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<m); mask++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int nmask = mask | (1<<j);
dp[i+1][nmask] = Math.min(dp[i+1][nmask], dp[i][mask] + cost.get(i).get(j));
}
}
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<m); mask++) {
if (Integer.bitCount(mask) == m) {
ans = Math.min(ans, dp[n][mask]);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun connectTwoGroups(cost: List<List<Int>>): Int {
val n = cost.size
val m = cost[0].size
val dp = Array(n+1) { IntArray(1 shl m) { Int.MAX_VALUE/2 } }
dp[0][0] = 0
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (mask in 0 until (1 shl m)) {
for (j in 0 until m) {
val nmask = mask or (1 shl j)
dp[i+1][nmask] = minOf(dp[i+1][nmask], dp[i][mask] + cost[i][j])
}
}
}
var ans = Int.MAX_VALUE/2
for (mask in 0 until (1 shl m)) {
if (mask.countOneBits() == m) {
ans = minOf(ans, dp[n][mask])
}
}
return ans
}
}
Python
def connectTwoGroups(cost: list[list[int]]) -> int:
n, m = len(cost), len(cost[0])
dp = [[float('inf')] * (1<<m) for _ in range(n+1)]
dp[0][0] = 0
for i in range(n):
for mask in range(1<<m):
for j in range(m):
nmask = mask | (1<<j)
dp[i+1][nmask] = min(dp[i+1][nmask], dp[i][mask] + cost[i][j])
ans = float('inf')
for mask in range(1<<m):
if bin(mask).count('1') == m:
ans = min(ans, dp[n][mask])
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn connect_two_groups(cost: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = cost.len();
let m = cost[0].len();
let mut dp = vec![vec![i32::MAX/2; 1<<m]; n+1];
dp[0][0] = 0;
for i in 0..n {
for mask in 0..(1<<m) {
for j in 0..m {
let nmask = mask | (1<<j);
dp[i+1][nmask] = dp[i+1][nmask].min(dp[i][mask] + cost[i][j]);
}
}
}
let mut ans = i32::MAX/2;
for mask in 0..(1<<m) {
if mask.count_ones() == m as u32 {
ans = ans.min(dp[n][mask]);
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
connectTwoGroups(cost: number[][]): number {
const n = cost.length, m = cost[0].length;
const dp: number[][] = Array.from({length: n+1}, () => Array(1<<m).fill(Infinity));
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let mask = 0; mask < (1<<m); mask++) {
for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) {
const nmask = mask | (1<<j);
dp[i+1][nmask] = Math.min(dp[i+1][nmask], dp[i][mask] + cost[i][j]);
}
}
}
let ans = Infinity;
for (let mask = 0; mask < (1<<m); mask++) {
if (mask.toString(2).split('1').length-1 === m) {
ans = Math.min(ans, dp[n][mask]);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n * m * 2^m), since for each point and mask, we try all connections. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n * 2^m), for the DP table.