Minimum Cost to Cut a Stick
Problem
Given a wooden stick of length n units. The stick is labelled from 0 to n. For example, a stick of length 6 is labelled as follows:
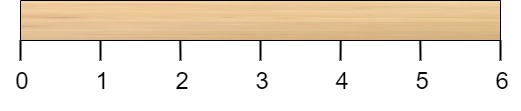
Given an integer array cuts where cuts[i] denotes a position you should perform a cut at.
You should perform the cuts in order, you can change the order of the cuts as you wish.
The cost of one cut is the length of the stick to be cut, the total cost is the sum of costs of all cuts. When you cut a stick, it will be split into two smaller sticks (i.e. the sum of their lengths is the length of the stick before the cut). Please refer to the first example for a better explanation.
Return the minimum total cost of the cuts.
Examples
Example 1
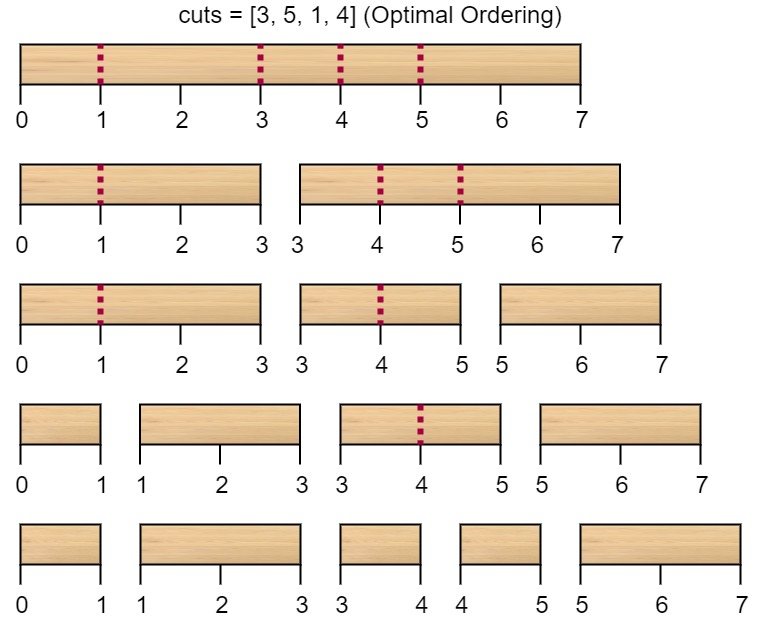
Input: n = 7, cuts = [1,3,4,5]
Output: 16
Explanation: Using cuts order = [1, 3, 4, 5] as in the input leads to the following scenario:
Example 2
Input: n = 9, cuts = [5,6,1,4,2]
Output: 22
Explanation: If you try the given cuts ordering the cost will be 25.
There are much ordering with total cost <= 25, for example, the order [4, 6, 5, 2, 1] has total cost = 22 which is the minimum possible.
Constraints
2 <= n <= 1061 <= cuts.length <= min(n - 1, 100)1 <= cuts[i] <= n - 1- All the integers in
cutsarray are distinct.
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming (Interval DP)
Intuition
Use dynamic programming to find the minimum cost to cut each interval, by trying all possible first cuts and combining the results.
Approach
- Add 0 and n to the cuts array and sort it.
- Let dp[i][j] be the minimum cost to cut the stick between cuts[i] and cuts[j].
- For each interval, try all possible first cuts and recursively compute the cost for left and right segments.
- The answer is dp[0][m-1], where m is the number of cuts (including 0 and n).
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minCost(int n, vector<int>& cuts) {
cuts.push_back(0);
cuts.push_back(n);
sort(cuts.begin(), cuts.end());
int m = cuts.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(m));
for (int l = 2; l < m; ++l) {
for (int i = 0; i + l < m; ++i) {
int j = i + l;
dp[i][j] = INT_MAX;
for (int k = i+1; k < j; ++k)
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]);
dp[i][j] += cuts[j] - cuts[i];
}
}
return dp[0][m-1];
}
};
Go
func minCost(n int, cuts []int) int {
cuts = append(cuts, 0, n)
sort.Ints(cuts)
m := len(cuts)
dp := make([][]int, m)
for i := range dp { dp[i] = make([]int, m) }
for l := 2; l < m; l++ {
for i := 0; i+l < m; i++ {
j := i + l
dp[i][j] = 1<<31-1
for k := i+1; k < j; k++ {
if dp[i][k]+dp[k][j] < dp[i][j] {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k]+dp[k][j]
}
}
dp[i][j] += cuts[j] - cuts[i]
}
}
return dp[0][m-1]
}
Java
class Solution {
public int minCost(int n, int[] cuts) {
int m = cuts.length;
int[] c = new int[m+2];
System.arraycopy(cuts, 0, c, 1, m);
c[0] = 0; c[m+1] = n;
Arrays.sort(c);
int[][] dp = new int[m+2][m+2];
for (int l = 2; l < m+2; ++l) {
for (int i = 0; i + l < m+2; ++i) {
int j = i + l;
dp[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int k = i+1; k < j; ++k)
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]);
dp[i][j] += c[j] - c[i];
}
}
return dp[0][m+1];
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minCost(n: Int, cuts: IntArray): Int {
val c = cuts.toMutableList().apply { add(0); add(n); sort() }
val m = c.size
val dp = Array(m) { IntArray(m) }
for (l in 2 until m) {
for (i in 0 until m-l) {
val j = i + l
dp[i][j] = Int.MAX_VALUE
for (k in i+1 until j)
dp[i][j] = minOf(dp[i][j], dp[i][k] + dp[k][j])
dp[i][j] += c[j] - c[i]
}
}
return dp[0][m-1]
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minCost(self, n: int, cuts: list[int]) -> int:
cuts = sorted(cuts + [0, n])
m = len(cuts)
dp = [[0]*m for _ in range(m)]
for l in range(2, m):
for i in range(m-l):
j = i + l
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] for k in range(i+1, j)) + cuts[j] - cuts[i]
return dp[0][m-1]
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_cost(n: i32, mut cuts: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
cuts.push(0);
cuts.push(n);
cuts.sort();
let m = cuts.len();
let mut dp = vec![vec![0; m]; m];
for l in 2..m {
for i in 0..m-l {
let j = i + l;
dp[i][j] = std::i32::MAX;
for k in i+1..j {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j].min(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]);
}
dp[i][j] += cuts[j] - cuts[i];
}
}
dp[0][m-1]
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minCost(n: number, cuts: number[]): number {
cuts.push(0, n);
cuts.sort((a, b) => a - b);
const m = cuts.length;
const dp: number[][] = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(m).fill(0));
for (let l = 2; l < m; ++l) {
for (let i = 0; i + l < m; ++i) {
const j = i + l;
dp[i][j] = Infinity;
for (let k = i+1; k < j; ++k)
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]);
dp[i][j] += cuts[j] - cuts[i];
}
}
return dp[0][m-1];
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m^3)- We fill a DP table for all intervals, and for each interval, we try all possible first cuts, resulting in O(m^3) operations where m is the number of cuts (including 0 and n).
- 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m^2)- The DP table stores the minimum cost for each interval between cuts.