Minimum Degree of a Connected Trio in a Graph
Problem
You are given an undirected graph. You are given an integer n which is the number of nodes in the graph and an array edges, where each edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between ui and vi.
A connected trio is a set of three nodes where there is an edge between every pair of them.
The degree of a connected trio is the number of edges where one endpoint is in the trio, and the other is not.
Return theminimum degree of a connected trio in the graph, or -1 if the graph has no connected trios.
Examples
Example 1
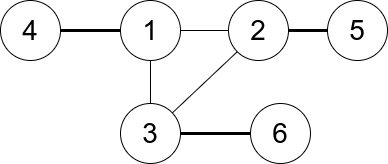
Input: n = 6, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[3,2],[4,1],[5,2],[3,6]]
Output: 3
Explanation: There is exactly one trio, which is [1,2,3]. The edges that form its degree are bolded in the figure above.
Example 2
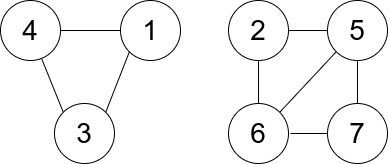
Input: n = 7, edges = [[1,3],[4,1],[4,3],[2,5],[5,6],[6,7],[7,5],[2,6]]
Output: 0
Explanation: There are exactly three trios:
1) [1,4,3] with degree 0.
2) [2,5,6] with degree 2.
3) [5,6,7] with degree 2.
Constraints
2 <= n <= 400edges[i].length == 21 <= edges.length <= n * (n-1) / 21 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi- There are no repeated edges.
Solution
Method 1 – Brute Force with Degree Calculation
Intuition
A connected trio is a triangle in the undirected graph. For each trio, we count the degree of each node and subtract the internal edges to get the degree of the trio. We check all possible trios and keep track of the minimum degree.
Approach
- Build the adjacency matrix and degree array for all nodes.
- For every combination of three nodes
(i, j, k), check if all three edges exist (i.e., they form a trio). - For each valid trio, calculate its degree:
- The degree is
deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6(since each internal edge is counted twice for each node).
- The degree is
- Track the minimum degree among all trios.
- If no trio exists, return -1.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minTrioDegree(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<vector<bool>> adj(n+1, vector<bool>(n+1, false));
vector<int> deg(n+1, 0);
for (auto& e : edges) {
adj[e[0]][e[1]] = adj[e[1]][e[0]] = true;
deg[e[0]]++;
deg[e[1]]++;
}
int ans = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = i+1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (!adj[i][j]) continue;
for (int k = j+1; k <= n; ++k) {
if (adj[i][k] && adj[j][k]) {
int d = deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6;
ans = min(ans, d);
}
}
}
}
return ans == INT_MAX ? -1 : ans;
}
};
Go
func minTrioDegree(n int, edges [][]int) int {
adj := make([][]bool, n+1)
for i := range adj { adj[i] = make([]bool, n+1) }
deg := make([]int, n+1)
for _, e := range edges {
adj[e[0]][e[1]], adj[e[1]][e[0]] = true, true
deg[e[0]]++
deg[e[1]]++
}
ans := 1<<31 - 1
for i := 1; i <= n; i++ {
for j := i+1; j <= n; j++ {
if !adj[i][j] { continue }
for k := j+1; k <= n; k++ {
if adj[i][k] && adj[j][k] {
d := deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6
if d < ans { ans = d }
}
}
}
}
if ans == 1<<31-1 { return -1 } else { return ans }
}
Java
class Solution {
public int minTrioDegree(int n, int[][] edges) {
boolean[][] adj = new boolean[n+1][n+1];
int[] deg = new int[n+1];
for (int[] e : edges) {
adj[e[0]][e[1]] = adj[e[1]][e[0]] = true;
deg[e[0]]++;
deg[e[1]]++;
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = i+1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (!adj[i][j]) continue;
for (int k = j+1; k <= n; ++k) {
if (adj[i][k] && adj[j][k]) {
int d = deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6;
ans = Math.min(ans, d);
}
}
}
}
return ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minTrioDegree(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val adj = Array(n+1) { BooleanArray(n+1) }
val deg = IntArray(n+1)
for (e in edges) {
adj[e[0]][e[1]] = true
adj[e[1]][e[0]] = true
deg[e[0]]++
deg[e[1]]++
}
var ans = Int.MAX_VALUE
for (i in 1..n) {
for (j in i+1..n) {
if (!adj[i][j]) continue
for (k in j+1..n) {
if (adj[i][k] && adj[j][k]) {
val d = deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6
ans = minOf(ans, d)
}
}
}
}
return if (ans == Int.MAX_VALUE) -1 else ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minTrioDegree(self, n: int, edges: list[list[int]]) -> int:
adj = [[False]*(n+1) for _ in range(n+1)]
deg = [0]*(n+1)
for u, v in edges:
adj[u][v] = adj[v][u] = True
deg[u] += 1
deg[v] += 1
ans = float('inf')
for i in range(1, n+1):
for j in range(i+1, n+1):
if not adj[i][j]: continue
for k in range(j+1, n+1):
if adj[i][k] and adj[j][k]:
d = deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6
ans = min(ans, d)
return -1 if ans == float('inf') else ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_trio_degree(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = n as usize;
let mut adj = vec![vec![false; n+1]; n+1];
let mut deg = vec![0; n+1];
for e in &edges {
adj[e[0] as usize][e[1] as usize] = true;
adj[e[1] as usize][e[0] as usize] = true;
deg[e[0] as usize] += 1;
deg[e[1] as usize] += 1;
}
let mut ans = i32::MAX;
for i in 1..=n {
for j in i+1..=n {
if !adj[i][j] { continue; }
for k in j+1..=n {
if adj[i][k] && adj[j][k] {
let d = deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6;
ans = ans.min(d);
}
}
}
}
if ans == i32::MAX { -1 } else { ans }
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minTrioDegree(n: number, edges: number[][]): number {
const adj = Array.from({length: n+1}, () => Array(n+1).fill(false));
const deg = Array(n+1).fill(0);
for (const [u, v] of edges) {
adj[u][v] = adj[v][u] = true;
deg[u]++;
deg[v]++;
}
let ans = Infinity;
for (let i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (let j = i+1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (!adj[i][j]) continue;
for (let k = j+1; k <= n; ++k) {
if (adj[i][k] && adj[j][k]) {
const d = deg[i] + deg[j] + deg[k] - 6;
ans = Math.min(ans, d);
}
}
}
}
return ans === Infinity ? -1 : ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^3)where n is the number of nodes, due to triple nested loops. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n^2)for the adjacency matrix.