Minimum Distance to Type a Word Using Two Fingers
HardUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
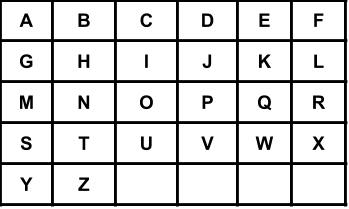
You have a keyboard layout as shown above in the X-Y plane, where each English uppercase letter is located at some coordinate.
- For example, the letter
'A'is located at coordinate(0, 0), the letter'B'is located at coordinate(0, 1), the letter'P'is located at coordinate(2, 3)and the letter'Z'is located at coordinate(4, 1).
Given the string word, return the minimum total distance to type such string using only two fingers.
The distance between coordinates (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is |x1 - x2| + |y1 - y2|.
Note that the initial positions of your two fingers are considered free so do not count towards your total distance, also your two fingers do not have to start at the first letter or the first two letters.
Examples
Example 1
Input: word = "CAKE"
Output: 3
Explanation: Using two fingers, one optimal way to type "CAKE" is:
Finger 1 on letter 'C' -> cost = 0
Finger 1 on letter 'A' -> cost = Distance from letter 'C' to letter 'A' = 2
Finger 2 on letter 'K' -> cost = 0
Finger 2 on letter 'E' -> cost = Distance from letter 'K' to letter 'E' = 1
Total distance = 3
Example 2
Input: word = "HAPPY"
Output: 6
Explanation: Using two fingers, one optimal way to type "HAPPY" is:
Finger 1 on letter 'H' -> cost = 0
Finger 1 on letter 'A' -> cost = Distance from letter 'H' to letter 'A' = 2
Finger 2 on letter 'P' -> cost = 0
Finger 2 on letter 'P' -> cost = Distance from letter 'P' to letter 'P' = 0
Finger 1 on letter 'Y' -> cost = Distance from letter 'A' to letter 'Y' = 4
Total distance = 6
Constraints
2 <= word.length <= 300wordconsists of uppercase English letters.
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming (State Compression)
Intuition
We can use dynamic programming to track the minimum distance for each possible position of the two fingers as we type the word. By considering all possible finger moves at each step, we ensure the optimal solution.
Approach
- Map each letter to its keyboard coordinates.
- Use a DP table where
dp[i][f1][f2]is the minimum distance to type the firstiletters with finger 1 atf1and finger 2 atf2. - At each step, try moving either finger to the next letter and update the DP state.
- The answer is the minimum value after typing all letters.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minimumDistance(string word) {
vector<pair<int,int>> pos(26);
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) pos[i] = {i/6, i%6};
int n = word.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(n+1, vector<int>(27, 1e9));
dp[0][26] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int cur = word[i] - 'A';
for (int f = 0; f <= 26; ++f) {
int cost = dp[i][f];
// Move finger 1
int d1 = (f == 26) ? 0 : abs(pos[f].first - pos[cur].first) + abs(pos[f].second - pos[cur].second);
dp[i+1][cur] = min(dp[i+1][cur], cost + d1);
// Move finger 2 (keep finger 1 at f)
if (i == 0) continue;
int prev = word[i-1] - 'A';
int d2 = abs(pos[prev].first - pos[cur].first) + abs(pos[prev].second - pos[cur].second);
dp[i+1][f] = min(dp[i+1][f], cost + d2);
}
}
return *min_element(dp[n].begin(), dp[n].end());
}
};
Go
func minimumDistance(word string) int {
pos := [26][2]int{}
for i := 0; i < 26; i++ {
pos[i][0], pos[i][1] = i/6, i%6
}
n := len(word)
dp := make([][]int, n+1)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int, 27)
for j := range dp[i] { dp[i][j] = 1e9 }
}
dp[0][26] = 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
cur := int(word[i] - 'A')
for f := 0; f <= 26; f++ {
cost := dp[i][f]
d1 := 0
if f != 26 {
d1 = abs(pos[f][0]-pos[cur][0]) + abs(pos[f][1]-pos[cur][1])
}
if dp[i+1][cur] > cost+d1 {
dp[i+1][cur] = cost + d1
}
if i == 0 { continue }
prev := int(word[i-1] - 'A')
d2 := abs(pos[prev][0]-pos[cur][0]) + abs(pos[prev][1]-pos[cur][1])
if dp[i+1][f] > cost+d2 {
dp[i+1][f] = cost + d2
}
}
}
ans := 1e9
for _, v := range dp[n] {
if v < ans { ans = v }
}
return ans
}
func abs(x int) int { if x < 0 { return -x }; return x }
Java
class Solution {
public int minimumDistance(String word) {
int[][] pos = new int[26][2];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
pos[i][0] = i / 6; pos[i][1] = i % 6;
}
int n = word.length();
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][27];
for (int[] row : dp) Arrays.fill(row, 1000000000);
dp[0][26] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int cur = word.charAt(i) - 'A';
for (int f = 0; f <= 26; ++f) {
int cost = dp[i][f];
int d1 = (f == 26) ? 0 : Math.abs(pos[f][0] - pos[cur][0]) + Math.abs(pos[f][1] - pos[cur][1]);
dp[i+1][cur] = Math.min(dp[i+1][cur], cost + d1);
if (i == 0) continue;
int prev = word.charAt(i-1) - 'A';
int d2 = Math.abs(pos[prev][0] - pos[cur][0]) + Math.abs(pos[prev][1] - pos[cur][1]);
dp[i+1][f] = Math.min(dp[i+1][f], cost + d2);
}
}
int ans = 1000000000;
for (int v : dp[n]) ans = Math.min(ans, v);
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minimumDistance(word: String): Int {
val pos = Array(26) { i -> intArrayOf(i/6, i%6) }
val n = word.length
val dp = Array(n+1) { IntArray(27) { 1_000_000_000 } }
dp[0][26] = 0
for (i in 0 until n) {
val cur = word[i] - 'A'
for (f in 0..26) {
val cost = dp[i][f]
val d1 = if (f == 26) 0 else Math.abs(pos[f][0] - pos[cur][0]) + Math.abs(pos[f][1] - pos[cur][1])
dp[i+1][cur] = minOf(dp[i+1][cur], cost + d1)
if (i == 0) continue
val prev = word[i-1] - 'A'
val d2 = Math.abs(pos[prev][0] - pos[cur][0]) + Math.abs(pos[prev][1] - pos[cur][1])
dp[i+1][f] = minOf(dp[i+1][f], cost + d2)
}
}
return dp[n].minOrNull()!!
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minimumDistance(self, word: str) -> int:
pos = [(i//6, i%6) for i in range(26)]
n = len(word)
dp = [[float('inf')] * 27 for _ in range(n+1)]
dp[0][26] = 0
for i in range(n):
cur = ord(word[i]) - ord('A')
for f in range(27):
cost = dp[i][f]
d1 = 0 if f == 26 else abs(pos[f][0] - pos[cur][0]) + abs(pos[f][1] - pos[cur][1])
dp[i+1][cur] = min(dp[i+1][cur], cost + d1)
if i == 0:
continue
prev = ord(word[i-1]) - ord('A')
d2 = abs(pos[prev][0] - pos[cur][0]) + abs(pos[prev][1] - pos[cur][1])
dp[i+1][f] = min(dp[i+1][f], cost + d2)
return min(dp[n])
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn minimum_distance(word: String) -> i32 {
let pos: Vec<(i32, i32)> = (0..26).map(|i| (i/6, i%6)).collect();
let n = word.len();
let w: Vec<usize> = word.bytes().map(|b| (b - b'A') as usize).collect();
let mut dp = vec![vec![1_000_000_000; 27]; n+1];
dp[0][26] = 0;
for i in 0..n {
let cur = w[i];
for f in 0..=26 {
let cost = dp[i][f];
let d1 = if f == 26 { 0 } else { (pos[f].0 - pos[cur].0).abs() + (pos[f].1 - pos[cur].1).abs() };
dp[i+1][cur] = dp[i+1][cur].min(cost + d1);
if i == 0 { continue; }
let prev = w[i-1];
let d2 = (pos[prev].0 - pos[cur].0).abs() + (pos[prev].1 - pos[cur].1).abs();
dp[i+1][f] = dp[i+1][f].min(cost + d2);
}
}
*dp[n].iter().min().unwrap()
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minimumDistance(word: string): number {
const pos = Array.from({length: 26}, (_, i) => [Math.floor(i/6), i%6]);
const n = word.length;
const dp = Array.from({length: n+1}, () => Array(27).fill(Infinity));
dp[0][26] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const cur = word.charCodeAt(i) - 65;
for (let f = 0; f <= 26; f++) {
const cost = dp[i][f];
const d1 = f === 26 ? 0 : Math.abs(pos[f][0] - pos[cur][0]) + Math.abs(pos[f][1] - pos[cur][1]);
dp[i+1][cur] = Math.min(dp[i+1][cur], cost + d1);
if (i === 0) continue;
const prev = word.charCodeAt(i-1) - 65;
const d2 = Math.abs(pos[prev][0] - pos[cur][0]) + Math.abs(pos[prev][1] - pos[cur][1]);
dp[i+1][f] = Math.min(dp[i+1][f], cost + d2);
}
}
return Math.min(...dp[n]);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n * 27)wherenis the length of the word. Each DP state is updated in constant time. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n * 27)for the DP table.