Minimum Flips in Binary Tree to Get Result
Problem
You are given the root of a binary tree with the following properties:
- Leaf nodes have either the value
0or1, representingfalseandtruerespectively. - Non-leaf nodes have either the value
2,3,4, or5, representing the boolean operationsOR,AND,XOR, andNOT, respectively.
You are also given a boolean result, which is the desired result of the evaluation of the root node.
The evaluation of a node is as follows:
- If the node is a leaf node, the evaluation is the value of the node, i.e.
trueorfalse. - Otherwise, evaluate the node's children and apply the boolean operation of its value with the children's evaluations.
In one operation, you can flip a leaf node, which causes a false node to become true, and a true node to become false.
Return the minimum number of operations that need to be performed such that the evaluation ofroot yieldsresult. It can be shown that there is always a way to achieve result.
A leaf node is a node that has zero children.
Note: NOT nodes have either a left child or a right child, but other non-leaf nodes have both a left child and a right child.
Examples
Example 1:
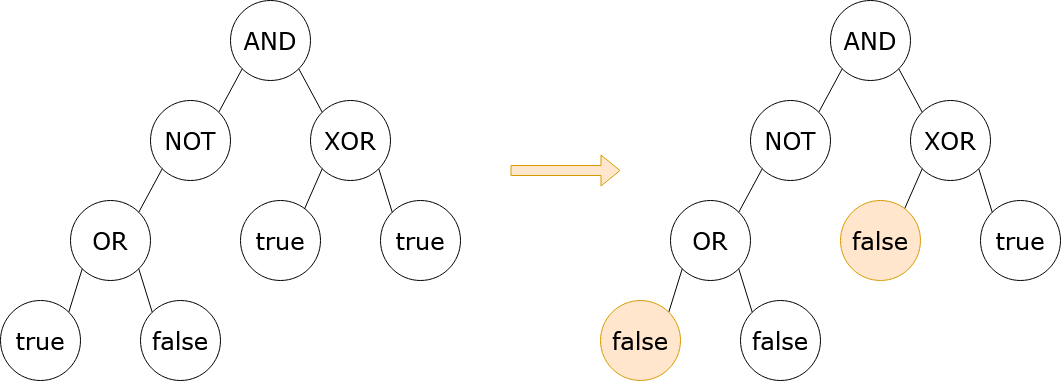
Input: root = [3,5,4,2,null,1,1,1,0], result = true
Output: 2
Explanation:
It can be shown that a minimum of 2 nodes have to be flipped to make the root of the tree
evaluate to true. One way to achieve this is shown in the diagram above.
Example 2:
Input: root = [0], result = false
Output: 0
Explanation:
The root of the tree already evaluates to false, so 0 nodes have to be flipped.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 5OR,AND, andXORnodes have2children.NOTnodes have1child.- Leaf nodes have a value of
0or1. - Non-leaf nodes have a value of
2,3,4, or5.
Solution
Method 1 – DFS with Dynamic Programming
Intuition
We recursively compute the minimum flips needed for each subtree to achieve both True and False results. For each node, we consider all possible ways to flip its value or its children's values to achieve the desired result, using the operation type at the node.
Approach
- For each node, recursively compute the minimum flips needed to make its subtree evaluate to
TrueandFalse. - For leaf nodes, flips are needed only if their value does not match the target.
- For non-leaf nodes, use the operation type to combine the results from children, considering all possible combinations and flips.
- Use memoization to avoid recomputation.
- Return the minimum flips needed for the root to achieve the desired result.
Code
C++
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
};
class Solution {
private:
unordered_map<TreeNode*, array<int,2>> dp;
void dfs(TreeNode* node) {
if (!node) return;
if (node->val == 0 || node->val == 1) {
dp[node][node->val] = 0;
dp[node][1-node->val] = 1;
return;
}
if (dp.count(node)) return;
// Process children first
if (node->left) dfs(node->left);
if (node->right) dfs(node->right);
dp[node] = {1e9, 1e9};
if (node->val == 2) { // OR
for (int a = 0; a < 2; ++a)
for (int b = 0; b < 2; ++b) {
int res = a | b;
dp[node][res] = min(dp[node][res], dp[node->left][a] + dp[node->right][b]);
}
} else if (node->val == 3) { // AND
for (int a = 0; a < 2; ++a)
for (int b = 0; b < 2; ++b) {
int res = a & b;
dp[node][res] = min(dp[node][res], dp[node->left][a] + dp[node->right][b]);
}
} else if (node->val == 4) { // XOR
for (int a = 0; a < 2; ++a)
for (int b = 0; b < 2; ++b) {
int res = a ^ b;
dp[node][res] = min(dp[node][res], dp[node->left][a] + dp[node->right][b]);
}
} else if (node->val == 5) { // NOT
TreeNode* child = node->left ? node->left : node->right;
for (int a = 0; a < 2; ++a) {
int res = 1 - a;
dp[node][res] = min(dp[node][res], dp[child][a]);
}
}
}
public:
int minimumFlips(TreeNode* root, bool result) {
dfs(root);
return dp[root][result];
}
};
Go
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
func minimumFlips(root *TreeNode, result bool) int {
var dfs func(*TreeNode) [2]int
dfs = func(node *TreeNode) [2]int {
if node == nil {
return [2]int{0, 0}
}
// Leaf nodes
if node.Val == 0 {
return [2]int{0, 1} // [false_cost, true_cost]
}
if node.Val == 1 {
return [2]int{1, 0} // [false_cost, true_cost]
}
// Process children
var left, right [2]int
if node.Left != nil {
left = dfs(node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
right = dfs(node.Right)
}
dp := [2]int{1e9, 1e9}
if node.Val == 2 { // OR
for a := 0; a < 2; a++ {
for b := 0; b < 2; b++ {
res := a | b
cost := left[a] + right[b]
if cost < dp[res] {
dp[res] = cost
}
}
}
} else if node.Val == 3 { // AND
for a := 0; a < 2; a++ {
for b := 0; b < 2; b++ {
res := a & b
cost := left[a] + right[b]
if cost < dp[res] {
dp[res] = cost
}
}
}
} else if node.Val == 4 { // XOR
for a := 0; a < 2; a++ {
for b := 0; b < 2; b++ {
res := a ^ b
cost := left[a] + right[b]
if cost < dp[res] {
dp[res] = cost
}
}
}
} else if node.Val == 5 { // NOT
var child [2]int
if node.Left != nil {
child = left
} else {
child = right
}
for a := 0; a < 2; a++ {
res := 1 - a
if child[a] < dp[res] {
dp[res] = child[a]
}
}
}
return dp
}
res := dfs(root)
if result {
return res[1]
}
return res[0]
}
Java
class Solution {
public int minimumFlips(TreeNode root, boolean result) {
int[] res = dfs(root);
return result ? res[1] : res[0];
}
private int[] dfs(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return new int[]{0, 0};
if (node.val == 0) return new int[]{0, 1};
if (node.val == 1) return new int[]{1, 0};
int[] left = node.left != null ? dfs(node.left) : null;
int[] right = node.right != null ? dfs(node.right) : null;
int[] dp = new int[]{Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE};
if (node.val == 2) { // OR
for (int a = 0; a < 2; a++)
for (int b = 0; b < 2; b++)
dp[a|b] = Math.min(dp[a|b], left[a] + right[b]);
} else if (node.val == 3) { // AND
for (int a = 0; a < 2; a++)
for (int b = 0; b < 2; b++)
dp[a&b] = Math.min(dp[a&b], left[a] + right[b]);
} else if (node.val == 4) { // XOR
for (int a = 0; a < 2; a++)
for (int b = 0; b < 2; b++)
dp[a^b] = Math.min(dp[a^b], left[a] + right[b]);
} else if (node.val == 5) { // NOT
for (int a = 0; a < 2; a++)
dp[1-a] = Math.min(dp[1-a], left != null ? left[a] : right[a]);
}
return dp;
}
}
Kotlin
class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
var left: TreeNode? = null
var right: TreeNode? = null
}
class Solution {
fun minimumFlips(root: TreeNode?, result: Boolean): Int {
fun dfs(node: TreeNode?): IntArray {
if (node == null) {
return intArrayOf(0, 0)
}
// Leaf nodes
if (node.`val` == 0) {
return intArrayOf(0, 1) // [false_cost, true_cost]
}
if (node.`val` == 1) {
return intArrayOf(1, 0) // [false_cost, true_cost]
}
// Process children
val left = node.left?.let { dfs(it) }
val right = node.right?.let { dfs(it) }
val dp = intArrayOf(Int.MAX_VALUE, Int.MAX_VALUE)
when (node.`val`) {
2 -> { // OR
for (a in 0..1) {
for (b in 0..1) {
val res = a or b
val cost = (left?.get(a) ?: 0) + (right?.get(b) ?: 0)
dp[res] = minOf(dp[res], cost)
}
}
}
3 -> { // AND
for (a in 0..1) {
for (b in 0..1) {
val res = a and b
val cost = (left?.get(a) ?: 0) + (right?.get(b) ?: 0)
dp[res] = minOf(dp[res], cost)
}
}
}
4 -> { // XOR
for (a in 0..1) {
for (b in 0..1) {
val res = a xor b
val cost = (left?.get(a) ?: 0) + (right?.get(b) ?: 0)
dp[res] = minOf(dp[res], cost)
}
}
}
5 -> { // NOT
val child = left ?: right
for (a in 0..1) {
val res = 1 - a
dp[res] = minOf(dp[res], child?.get(a) ?: 0)
}
}
}
return dp
}
val res = dfs(root)
return if (result) res[1] else res[0]
}
}
Python
def minimum_flips(root: 'TreeNode', result: bool) -> int:
def dfs(node):
if not node:
return [0, 0]
if node.val == 0:
return [0, 1]
if node.val == 1:
return [1, 0]
left = dfs(node.left) if node.left else None
right = dfs(node.right) if node.right else None
dp = [float('inf'), float('inf')]
if node.val == 2: # OR
for a in range(2):
for b in range(2):
dp[a|b] = min(dp[a|b], left[a] + right[b])
elif node.val == 3: # AND
for a in range(2):
for b in range(2):
dp[a&b] = min(dp[a&b], left[a] + right[b])
elif node.val == 4: # XOR
for a in range(2):
for b in range(2):
dp[a^b] = min(dp[a^b], left[a] + right[b])
elif node.val == 5: # NOT
for a in range(2):
dp[1-a] = min(dp[1-a], (left if left else right)[a])
##### Rust
```rust
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub struct TreeNode {
pub val: i32,
pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
}
impl Solution {
pub fn minimum_flips(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, result: bool) -> i32 {
fn dfs(node: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> [i32; 2] {
if let Some(n) = node {
let n = n.borrow();
// Leaf nodes
if n.val == 0 {
return [0, 1]; // [false_cost, true_cost]
}
if n.val == 1 {
return [1, 0]; // [false_cost, true_cost]
}
// Process children
let left = if n.left.is_some() { dfs(&n.left) } else { [0, 0] };
let right = if n.right.is_some() { dfs(&n.right) } else { [0, 0] };
let mut dp = [i32::MAX, i32::MAX];
match n.val {
2 => { // OR
for a in 0..2 {
for b in 0..2 {
let res = (a | b) as usize;
let cost = left[a] + right[b];
dp[res] = dp[res].min(cost);
}
}
}
3 => { // AND
for a in 0..2 {
for b in 0..2 {
let res = (a & b) as usize;
let cost = left[a] + right[b];
dp[res] = dp[res].min(cost);
}
}
}
4 => { // XOR
for a in 0..2 {
for b in 0..2 {
let res = (a ^ b) as usize;
let cost = left[a] + right[b];
dp[res] = dp[res].min(cost);
}
}
}
5 => { // NOT
let child = if n.left.is_some() { left } else { right };
for a in 0..2 {
let res = (1 - a) as usize;
dp[res] = dp[res].min(child[a]);
}
}
_ => {}
}
dp
} else {
[0, 0]
}
}
let res = dfs(&root);
if result { res[1] } else { res[0] }
}
}
TypeScript
class TreeNode {
val: number;
left: TreeNode | null;
right: TreeNode | null;
constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
this.val = val ?? 0;
this.left = left ?? null;
this.right = right ?? null;
}
}
function minimumFlips(root: TreeNode | null, result: boolean): number {
const dfs = (node: TreeNode | null): [number, number] => {
if (!node) {
return [0, 0];
}
// Leaf nodes
if (node.val === 0) {
return [0, 1]; // [false_cost, true_cost]
}
if (node.val === 1) {
return [1, 0]; // [false_cost, true_cost]
}
// Process children
const left = node.left ? dfs(node.left) : [0, 0];
const right = node.right ? dfs(node.right) : [0, 0];
const dp: [number, number] = [Infinity, Infinity];
if (node.val === 2) { // OR
for (let a = 0; a < 2; a++) {
for (let b = 0; b < 2; b++) {
const res = a | b;
const cost = left[a] + right[b];
dp[res] = Math.min(dp[res], cost);
}
}
} else if (node.val === 3) { // AND
for (let a = 0; a < 2; a++) {
for (let b = 0; b < 2; b++) {
const res = a & b;
const cost = left[a] + right[b];
dp[res] = Math.min(dp[res], cost);
}
}
} else if (node.val === 4) { // XOR
for (let a = 0; a < 2; a++) {
for (let b = 0; b < 2; b++) {
const res = a ^ b;
const cost = left[a] + right[b];
dp[res] = Math.min(dp[res], cost);
}
}
} else if (node.val === 5) { // NOT
const child = node.left ? left : right;
for (let a = 0; a < 2; a++) {
const res = 1 - a;
dp[res] = Math.min(dp[res], child[a]);
}
}
return dp;
};
const res = dfs(root);
return result ? res[1] : res[0];
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is the number of nodes. Each node is visited once and each operation is constant time. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for recursion stack and memoization.