Minimum Number of Flips to Convert Binary Matrix to Zero Matrix
HardUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a m x n binary matrix mat. In one step, you can choose one cell and flip it and all the four neighbors of it if they exist (Flip is changing 1
to 0 and 0 to 1). A pair of cells are called neighbors if they share one edge.
Return the minimum number of steps required to convert mat to a zero matrix or -1 if you cannot.
A binary matrix is a matrix with all cells equal to 0 or 1 only.
A zero matrix is a matrix with all cells equal to 0.
Examples
Example 1
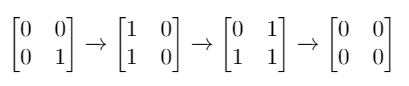
Input: mat = [[0,0],[0,1]]
Output: 3
Explanation: One possible solution is to flip (1, 0) then (0, 1) and finally (1, 1) as shown.
Example 2
Input: mat = [[0]]
Output: 0
Explanation: Given matrix is a zero matrix. We do not need to change it.
Example 3
Input: mat = [[1,0,0],[1,0,0]]
Output: -1
Explanation: Given matrix cannot be a zero matrix.
Constraints
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 3mat[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution
Method 1 – BFS with Bitmask State
Intuition
Represent the matrix as a bitmask integer, where each bit is a cell. BFS explores all possible flip sequences, and the minimum number of flips to reach the zero matrix is the answer.
Approach
- Encode the matrix as a bitmask integer.
- Use BFS to explore all possible states, flipping each cell and its neighbors.
- For each state, try flipping every cell and update the bitmask accordingly.
- Track visited states to avoid cycles.
- Stop when the bitmask is zero (all cells are zero).
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minFlips(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
int start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (mat[i][j]) start |= 1 << (i * n + j);
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
unordered_set<int> vis;
q.push({start, 0});
vis.insert(start);
vector<pair<int,int>> dirs{{0,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [mask, steps] = q.front(); q.pop();
if (mask == 0) return steps;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int next = mask;
for (auto& d : dirs) {
int ni = i + d.first, nj = j + d.second;
if (ni >= 0 && ni < m && nj >= 0 && nj < n)
next ^= 1 << (ni * n + nj);
}
if (!vis.count(next)) {
vis.insert(next);
q.push({next, steps+1});
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
Go
func minFlips(mat [][]int) int {
m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0])
start := 0
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if mat[i][j] == 1 {
start |= 1 << (i*n + j)
}
}
}
type state struct{ mask, steps int }
vis := map[int]bool{start: true}
q := []state{{start, 0}}
dirs := [][2]int{{0,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}}
for len(q) > 0 {
s := q[0]; q = q[1:]
if s.mask == 0 { return s.steps }
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
next := s.mask
for _, d := range dirs {
ni, nj := i+d[0], j+d[1]
if ni >= 0 && ni < m && nj >= 0 && nj < n {
next ^= 1 << (ni*n + nj)
}
}
if !vis[next] {
vis[next] = true
q = append(q, state{next, s.steps+1})
}
}
}
}
return -1
}
Java
class Solution {
public int minFlips(int[][] mat) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
int start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (mat[i][j] == 1) start |= 1 << (i * n + j);
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>();
q.offer(new int[]{start, 0});
vis.add(start);
int[][] dirs = {{0,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] s = q.poll();
int mask = s[0], steps = s[1];
if (mask == 0) return steps;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int next = mask;
for (int[] d : dirs) {
int ni = i + d[0], nj = j + d[1];
if (ni >= 0 && ni < m && nj >= 0 && nj < n)
next ^= 1 << (ni * n + nj);
}
if (!vis.contains(next)) {
vis.add(next);
q.offer(new int[]{next, steps+1});
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minFlips(mat: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = mat.size
val n = mat[0].size
var start = 0
for (i in 0 until m)
for (j in 0 until n)
if (mat[i][j] == 1) start = start or (1 shl (i * n + j))
val vis = mutableSetOf<Int>()
val q = ArrayDeque<Pair<Int, Int>>()
q.add(start to 0)
vis.add(start)
val dirs = arrayOf(intArrayOf(0,0), intArrayOf(0,1), intArrayOf(0,-1), intArrayOf(1,0), intArrayOf(-1,0))
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val (mask, steps) = q.removeFirst()
if (mask == 0) return steps
for (i in 0 until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
var next = mask
for (d in dirs) {
val ni = i + d[0]; val nj = j + d[1]
if (ni in 0 until m && nj in 0 until n)
next = next xor (1 shl (ni * n + nj))
}
if (next !in vis) {
vis.add(next)
q.add(next to steps+1)
}
}
}
}
return -1
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minFlips(self, mat: list[list[int]]) -> int:
from collections import deque
m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0])
start: int = 0
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if mat[i][j]:
start |= 1 << (i * n + j)
vis = set()
q = deque([(start, 0)])
vis.add(start)
dirs = [(0,0),(0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0)]
while q:
mask, steps = q.popleft()
if mask == 0:
return steps
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
next = mask
for dx, dy in dirs:
ni, nj = i+dx, j+dy
if 0<=ni<m and 0<=nj<n:
next ^= 1 << (ni * n + nj)
if next not in vis:
vis.add(next)
q.append((next, steps+1))
return -1
Rust
use std::collections::{HashSet, VecDeque};
impl Solution {
pub fn min_flips(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = mat.len();
let n = mat[0].len();
let mut start = 0;
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if mat[i][j] == 1 {
start |= 1 << (i * n + j);
}
}
}
let mut vis = HashSet::new();
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
q.push_back((start, 0));
vis.insert(start);
let dirs = [(0,0),(0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0)];
while let Some((mask, steps)) = q.pop_front() {
if mask == 0 { return steps; }
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
let mut next = mask;
for &(dx, dy) in &dirs {
let ni = i as i32 + dx;
let nj = j as i32 + dy;
if ni >= 0 && ni < m as i32 && nj >= 0 && nj < n as i32 {
next ^= 1 << (ni as usize * n + nj as usize);
}
}
if !vis.contains(&next) {
vis.insert(next);
q.push_back((next, steps+1));
}
}
}
}
-1
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minFlips(mat: number[][]): number {
const m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
let start = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (mat[i][j]) start |= 1 << (i * n + j);
const vis = new Set<number>();
const q: [number, number][] = [[start, 0]];
vis.add(start);
const dirs = [[0,0],[0,1],[0,-1],[1,0],[-1,0]];
while (q.length) {
const [mask, steps] = q.shift()!;
if (mask === 0) return steps;
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
let next = mask;
for (const [dx, dy] of dirs) {
const ni = i + dx, nj = j + dy;
if (ni >= 0 && ni < m && nj >= 0 && nj < n)
next ^= 1 << (ni * n + nj);
}
if (!vis.has(next)) {
vis.add(next);
q.push([next, steps+1]);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n * 2^(m*n)), as each state is visited at most once and there are up to2^(m*n)states. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(2^(m*n)), for the visited set and BFS queue.