Minimum Number of Flips to Make Binary Grid Palindromic II
Problem
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid.
A row or column is considered palindromic if its values read the same forward and backward.
You can flip any number of cells in grid from 0 to 1, or from 1 to
0.
Return the minimum number of cells that need to be flipped to make all rows and columns palindromic , and the total number of 1's in grid
divisible by 4.
Examples
Example 1
Input: grid = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
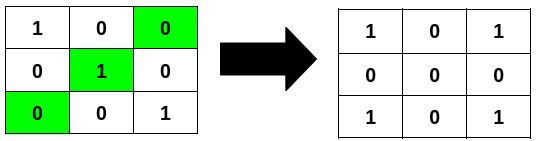
Example 2
Input: grid = [[0,1],[0,1],[0,0]]
Output: 2
Explanation:
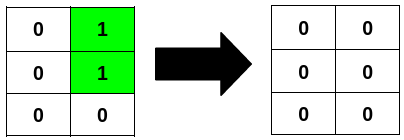
Example 3
Input: grid = [[1],[1]]
Output: 2
Explanation:

Constraints
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m * n <= 2 * 10^50 <= grid[i][j] <= 1
Solution
Method 1 – Grouped Symmetry and Modulo Constraint
Intuition
To make all rows and columns palindromic, each group of symmetric cells (under row and column reversal) must be made equal. For each group, we can flip some cells to make all values the same, and the minimum flips for each group is the number of cells minus the majority value count. Additionally, the total number of 1's must be divisible by 4, so we need to try all possible assignments for each group to satisfy this constraint.
Approach
- For each group of symmetric cells, count the number of 1's and 0's.
- For each group, try both assignments (all 0 or all 1), and keep track of total flips and total 1's.
- Use DP to find the minimum total flips such that the total number of 1's is divisible by 4.
- Return the minimum flips found.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minFlips(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> groups;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int a = i, b = j, c = m-1-i, d = n-1-j;
vector<pair<int,int>> group = {{a,b},{c,b},{a,d},{c,d}};
sort(group.begin(), group.end());
group.erase(unique(group.begin(), group.end()), group.end());
if (groups.empty() || groups.back() != group) groups.push_back(group);
}
}
int g = groups.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(g+1, vector<int>(4, INT_MAX));
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < g; ++i) {
int cnt1 = 0, sz = groups[i].size();
for (auto& p : groups[i]) cnt1 += grid[p.first][p.second];
int cnt0 = sz - cnt1;
for (int mod = 0; mod < 4; ++mod) {
if (dp[i][mod] == INT_MAX) continue;
// Make all 0
int new_mod = (mod + 0) % 4;
dp[i+1][new_mod] = min(dp[i+1][new_mod], dp[i][mod] + cnt1);
// Make all 1
new_mod = (mod + sz) % 4;
dp[i+1][new_mod] = min(dp[i+1][new_mod], dp[i][mod] + cnt0);
}
}
return dp[g][0] == INT_MAX ? -1 : dp[g][0];
}
};
Go
func minFlips(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
type cell struct{ r, c int }
groups := [][]cell{}
vis := map[cell]bool{}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
group := []cell{{i,j},{m-1-i,j},{i,n-1-j},{m-1-i,n-1-j}}
sort.Slice(group, func(a, b int) bool {
if group[a].r != group[b].r { return group[a].r < group[b].r }
return group[a].c < group[b].c
})
uniq := []cell{}
for _, p := range group {
if !vis[p] {
uniq = append(uniq, p)
vis[p] = true
}
}
if len(uniq) > 0 {
groups = append(groups, uniq)
}
}
}
g := len(groups)
dp := make([][]int, g+1)
for i := range dp { dp[i] = make([]int, 4); for j := range dp[i] { dp[i][j] = 1<<30 } }
dp[0][0] = 0
for i := 0; i < g; i++ {
cnt1 := 0; sz := len(groups[i])
for _, p := range groups[i] { cnt1 += grid[p.r][p.c] }
cnt0 := sz - cnt1
for mod := 0; mod < 4; mod++ {
if dp[i][mod] == 1<<30 { continue }
new_mod := (mod + 0) % 4
if dp[i][mod]+cnt1 < dp[i+1][new_mod] { dp[i+1][new_mod] = dp[i][mod]+cnt1 }
new_mod = (mod + sz) % 4
if dp[i][mod]+cnt0 < dp[i+1][new_mod] { dp[i+1][new_mod] = dp[i][mod]+cnt0 }
}
}
if dp[g][0] == 1<<30 { return -1 }
return dp[g][0]
}
Java
class Solution {
public int minFlips(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
List<List<int[]>> groups = new ArrayList<>();
Set<String> vis = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int[][] group = new int[][]{{i,j},{m-1-i,j},{i,n-1-j},{m-1-i,n-1-j}};
Arrays.sort(group, (a,b)->a[0]!=b[0]?a[0]-b[0]:a[1]-b[1]);
List<int[]> uniq = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] p : group) {
String key = p[0]+","+p[1];
if (!vis.contains(key)) {
uniq.add(p);
vis.add(key);
}
}
if (!uniq.isEmpty()) groups.add(uniq);
}
}
int g = groups.size();
int[][] dp = new int[g+1][4];
for (int[] row : dp) Arrays.fill(row, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < g; ++i) {
int cnt1 = 0, sz = groups.get(i).size();
for (int[] p : groups.get(i)) cnt1 += grid[p[0]][p[1]];
int cnt0 = sz - cnt1;
for (int mod = 0; mod < 4; ++mod) {
if (dp[i][mod] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) continue;
int new_mod = (mod + 0) % 4;
dp[i+1][new_mod] = Math.min(dp[i+1][new_mod], dp[i][mod] + cnt1);
new_mod = (mod + sz) % 4;
dp[i+1][new_mod] = Math.min(dp[i+1][new_mod], dp[i][mod] + cnt0);
}
}
return dp[g][0] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : dp[g][0];
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minFlips(grid: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = grid.size
val n = grid[0].size
val groups = mutableListOf<List<Pair<Int,Int>>>()
val vis = mutableSetOf<Pair<Int,Int>>()
for (i in 0 until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
val group = listOf(Pair(i,j), Pair(m-1-i,j), Pair(i,n-1-j), Pair(m-1-i,n-1-j)).sortedBy { it.first*100000+it.second }
val uniq = group.filter { vis.add(it) }
if (uniq.isNotEmpty()) groups.add(uniq)
}
}
val g = groups.size
val dp = Array(g+1) { IntArray(4) { Int.MAX_VALUE } }
dp[0][0] = 0
for (i in 0 until g) {
val cnt1 = groups[i].count { grid[it.first][it.second] == 1 }
val sz = groups[i].size
val cnt0 = sz - cnt1
for (mod in 0..3) {
if (dp[i][mod] == Int.MAX_VALUE) continue
var new_mod = (mod + 0) % 4
dp[i+1][new_mod] = minOf(dp[i+1][new_mod], dp[i][mod] + cnt1)
new_mod = (mod + sz) % 4
dp[i+1][new_mod] = minOf(dp[i+1][new_mod], dp[i][mod] + cnt0)
}
}
return if (dp[g][0] == Int.MAX_VALUE) -1 else dp[g][0]
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minFlips(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> int:
m: int = len(grid)
n: int = len(grid[0])
groups: list[list[tuple[int,int]]] = []
vis: set = set()
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
group = sorted({(i,j),(m-1-i,j),(i,n-1-j),(m-1-i,n-1-j)})
uniq = [p for p in group if p not in vis]
for p in uniq: vis.add(p)
if uniq:
groups.append(uniq)
g: int = len(groups)
dp: list[list[int]] = [[float('inf')]*4 for _ in range(g+1)]
dp[0][0] = 0
for i in range(g):
cnt1: int = sum(grid[x][y] for x,y in groups[i])
sz: int = len(groups[i])
cnt0: int = sz - cnt1
for mod in range(4):
if dp[i][mod] == float('inf'): continue
new_mod = (mod + 0) % 4
dp[i+1][new_mod] = min(dp[i+1][new_mod], dp[i][mod] + cnt1)
new_mod = (mod + sz) % 4
dp[i+1][new_mod] = min(dp[i+1][new_mod], dp[i][mod] + cnt0)
return -1 if dp[g][0] == float('inf') else dp[g][0]
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_flips(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut groups = vec![];
let mut vis = std::collections::HashSet::new();
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
let mut group = vec![(i,j),(m-1-i,j),(i,n-1-j),(m-1-i,n-1-j)];
group.sort();
group.dedup();
let uniq: Vec<_> = group.into_iter().filter(|p| vis.insert(*p)).collect();
if !uniq.is_empty() { groups.push(uniq); }
}
}
let g = groups.len();
let mut dp = vec![vec![i32::MAX; 4]; g+1];
dp[0][0] = 0;
for i in 0..g {
let cnt1 = groups[i].iter().map(|&(x,y)| grid[x][y]).sum::<i32>();
let sz = groups[i].len() as i32;
let cnt0 = sz - cnt1;
for modv in 0..4 {
if dp[i][modv] == i32::MAX { continue; }
let new_mod = (modv + 0) % 4;
dp[i+1][new_mod] = dp[i+1][new_mod].min(dp[i][modv] + cnt1);
let new_mod = (modv + sz) % 4;
dp[i+1][new_mod] = dp[i+1][new_mod].min(dp[i][modv] + cnt0);
}
}
if dp[g][0] == i32::MAX { -1 } else { dp[g][0] }
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minFlips(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
const groups: number[][][] = [];
const vis = new Set<string>();
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
const group = [[i,j],[m-1-i,j],[i,n-1-j],[m-1-i,n-1-j]];
group.sort((a,b)=>a[0]-b[0]||a[1]-b[1]);
const uniq = group.filter(([x,y]) => {
const key = `${x},${y}`;
if (!vis.has(key)) { vis.add(key); return true; }
return false;
});
if (uniq.length) groups.push(uniq);
}
}
const g = groups.length;
const dp = Array.from({length:g+1},()=>Array(4).fill(Infinity));
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < g; ++i) {
const cnt1 = groups[i].reduce((a,p)=>a+grid[p[0]][p[1]],0);
const sz = groups[i].length;
const cnt0 = sz - cnt1;
for (let mod = 0; mod < 4; ++mod) {
if (dp[i][mod] === Infinity) continue;
let new_mod = (mod + 0) % 4;
dp[i+1][new_mod] = Math.min(dp[i+1][new_mod], dp[i][mod] + cnt1);
new_mod = (mod + sz) % 4;
dp[i+1][new_mod] = Math.min(dp[i+1][new_mod], dp[i][mod] + cnt0);
}
}
return dp[g][0] === Infinity ? -1 : dp[g][0];
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(mn), as we process each cell and group once, and DP is efficient. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(mn), for groups and DP table.