Minimum Number of Lines to Cover Points
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given an array points where points[i] = [xi, yi] represents a point on an X-Y plane.
Straight lines are going to be added to the X-Y plane, such that every point is covered by at least one line.
Return theminimum number of straight lines needed to cover all the points.
Examples
Example 1:
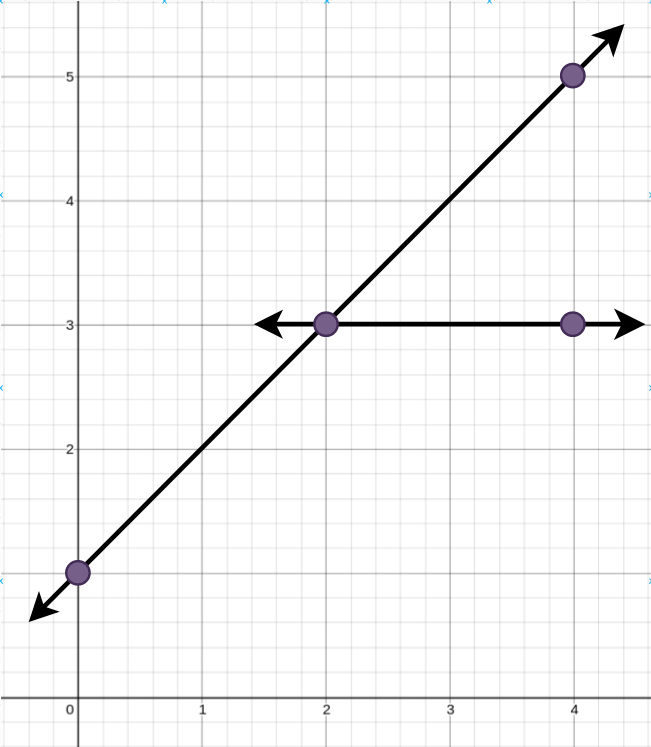
Input: points = [[0,1],[2,3],[4,5],[4,3]]
Output: 2
Explanation: The minimum number of straight lines needed is two. One possible solution is to add:
- One line connecting the point at (0, 1) to the point at (4, 5).
- Another line connecting the point at (2, 3) to the point at (4, 3).
Example 2:
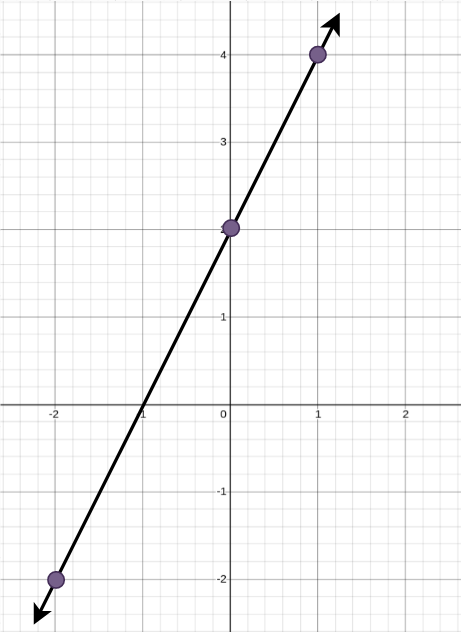
Input: points = [[0,2],[-2,-2],[1,4]]
Output: 1
Explanation: The minimum number of straight lines needed is one. The only solution is to add:
- One line connecting the point at (-2, -2) to the point at (1, 4).
Constraints:
1 <= points.length <= 10points[i].length == 2-100 <= xi, yi <= 100- All the
pointsare unique.
Solution
Method 1 – DP with Bitmask (Backtracking)
Intuition
For each subset of points, we can cover them with a single line if they are collinear. Use DP with bitmask: for each mask, try all possible lines, and recursively cover the rest. The answer is the minimum number of lines needed to cover all points.
Approach
- For each pair of points, find all points collinear with them.
- Use DP: dp[mask] = min number of lines to cover points in mask.
- For each mask, try all possible lines, update dp.
- Return dp[full_mask].
Code
C++
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int minLines(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
int n = points.size();
vector<vector<int>> col(n, vector<int>(n, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int mask = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
int x1 = points[i][0], y1 = points[i][1];
int x2 = points[j][0], y2 = points[j][1];
int x3 = points[k][0], y3 = points[k][1];
if ((x2-x1)*(y3-y1) == (y2-y1)*(x3-x1)) mask |= 1<<k;
}
col[i][j] = mask;
}
}
vector<int> dp(1<<n, n);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<n); ++mask) {
if (dp[mask] == n) continue;
int first = 0;
while (first < n && !(mask & (1<<first))) ++first;
if (first == n) continue;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int new_mask = mask | col[first][j];
dp[new_mask] = min(dp[new_mask], dp[mask] + 1);
}
}
return dp[(1<<n)-1];
}
};
Go
func minLines(points [][]int) int {
n := len(points)
col := make([][]int, n)
for i := range col { col[i] = make([]int, n) }
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
mask := 0
for k := 0; k < n; k++ {
x1, y1 := points[i][0], points[i][1]
x2, y2 := points[j][0], points[j][1]
x3, y3 := points[k][0], points[k][1]
if (x2-x1)*(y3-y1) == (y2-y1)*(x3-x1) {
mask |= 1 << k
}
}
col[i][j] = mask
}
}
dp := make([]int, 1<<n)
for i := range dp { dp[i] = n }
dp[0] = 0
for mask := 0; mask < 1<<n; mask++ {
if dp[mask] == n { continue }
first := 0
for first < n && (mask&(1<<first)) == 0 { first++ }
if first == n { continue }
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
newMask := mask | col[first][j]
if dp[newMask] > dp[mask]+1 {
dp[newMask] = dp[mask]+1
}
}
}
return dp[(1<<n)-1]
}
Java
class Solution {
public int minLines(int[][] points) {
int n = points.length;
int[][] col = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int mask = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
int x1 = points[i][0], y1 = points[i][1];
int x2 = points[j][0], y2 = points[j][1];
int x3 = points[k][0], y3 = points[k][1];
if ((x2-x1)*(y3-y1) == (y2-y1)*(x3-x1)) mask |= 1<<k;
}
col[i][j] = mask;
}
}
int[] dp = new int[1<<n];
java.util.Arrays.fill(dp, n);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<n); ++mask) {
if (dp[mask] == n) continue;
int first = 0;
while (first < n && (mask & (1<<first)) == 0) ++first;
if (first == n) continue;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int new_mask = mask | col[first][j];
dp[new_mask] = Math.min(dp[new_mask], dp[mask] + 1);
}
}
return dp[(1<<n)-1];
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minLines(points: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val n = points.size
val col = Array(n) { IntArray(n) }
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
var mask = 0
for (k in 0 until n) {
val (x1, y1) = points[i]
val (x2, y2) = points[j]
val (x3, y3) = points[k]
if ((x2-x1)*(y3-y1) == (y2-y1)*(x3-x1)) mask = mask or (1 shl k)
}
col[i][j] = mask
}
}
val dp = IntArray(1 shl n) { n }
dp[0] = 0
for (mask in 0 until (1 shl n)) {
if (dp[mask] == n) continue
var first = 0
while (first < n && (mask and (1 shl first)) == 0) first++
if (first == n) continue
for (j in 0 until n) {
val newMask = mask or col[first][j]
dp[newMask] = minOf(dp[newMask], dp[mask] + 1)
}
}
return dp[(1 shl n) - 1]
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minLines(self, points: list[list[int]]) -> int:
n = len(points)
col = [[0]*n for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
mask = 0
for k in range(n):
x1, y1 = points[i]
x2, y2 = points[j]
x3, y3 = points[k]
if (x2-x1)*(y3-y1) == (y2-y1)*(x3-x1):
mask |= 1<<k
col[i][j] = mask
dp = [n]*(1<<n)
dp[0] = 0
for mask in range(1<<n):
if dp[mask] == n: continue
first = 0
while first < n and not (mask & (1<<first)): first += 1
if first == n: continue
for j in range(n):
new_mask = mask | col[first][j]
dp[new_mask] = min(dp[new_mask], dp[mask]+1)
return dp[(1<<n)-1]
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_lines(points: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = points.len();
let mut col = vec![vec![0; n]; n];
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..n {
let mut mask = 0;
for k in 0..n {
let (x1, y1) = (points[i][0], points[i][1]);
let (x2, y2) = (points[j][0], points[j][1]);
let (x3, y3) = (points[k][0], points[k][1]);
if (x2-x1)*(y3-y1) == (y2-y1)*(x3-x1) { mask |= 1<<k; }
}
col[i][j] = mask;
}
}
let mut dp = vec![n; 1<<n];
dp[0] = 0;
for mask in 0..(1<<n) {
if dp[mask] == n { continue; }
let mut first = 0;
while first < n && (mask & (1<<first)) == 0 { first += 1; }
if first == n { continue; }
for j in 0..n {
let new_mask = mask | col[first][j];
dp[new_mask] = dp[new_mask].min(dp[mask]+1);
}
}
dp[(1<<n)-1]
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minLines(points: number[][]): number {
const n = points.length;
const col = Array.from({length: n}, () => Array(n).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
let mask = 0;
for (let k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
const [x1, y1] = points[i], [x2, y2] = points[j], [x3, y3] = points[k];
if ((x2-x1)*(y3-y1) === (y2-y1)*(x3-x1)) mask |= 1<<k;
}
col[i][j] = mask;
}
}
const dp = Array(1<<n).fill(n);
dp[0] = 0;
for (let mask = 0; mask < (1<<n); ++mask) {
if (dp[mask] === n) continue;
let first = 0;
while (first < n && !(mask & (1<<first))) ++first;
if (first === n) continue;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
const new_mask = mask | col[first][j];
dp[new_mask] = Math.min(dp[new_mask], dp[mask]+1);
}
}
return dp[(1<<n)-1];
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^3 * 2^n)— n = number of points. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(2^n)— for DP array.