Minimum Number of Operations to Satisfy Conditions
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given a 2D matrix grid of size m x n. In one operation , you can change the value of any cell to any non-negative number. You need to perform some operations such that each cell grid[i][j] is:
- Equal to the cell below it, i.e.
grid[i][j] == grid[i + 1][j](if it exists). - Different from the cell to its right, i.e.
grid[i][j] != grid[i][j + 1](if it exists).
Return the minimum number of operations needed.
Examples
Example 1
Input: grid = [[1,0,2],[1,0,2]]
Output: 0
Explanation:
**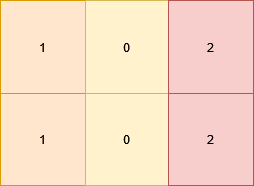**
All the cells in the matrix already satisfy the properties.
Example 2
Input: grid = [[1,1,1],[0,0,0]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
**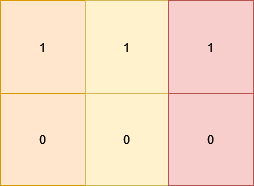**
The matrix becomes `[[1,0,1],[1,0,1]]` which satisfies the properties, by
doing these 3 operations:
* Change `grid[1][0]` to 1.
* Change `grid[0][1]` to 0.
* Change `grid[1][2]` to 1.
Example 3
Input: grid = [[1],[2],[3]]
Output: 2
Explanation:

There is a single column. We can change the value to 1 in each cell using 2
operations.
Constraints
1 <= n, m <= 10000 <= grid[i][j] <= 9
Solution
Method 1 – DP with Coloring (2-Coloring Columns)
Intuition
Each column must be uniform (all cells equal), and adjacent columns must differ. This is a coloring problem: assign each column one value, ensuring adjacent columns differ, and minimize changes.
Approach
- For each column, count how many cells are each value (0-9).
- For each column, try all possible values (0-9) and use DP to track the minimum changes, ensuring adjacent columns differ.
- For column j and value v, dp[j][v] = min over all u != v of dp[j-1][u] + (cells in column j not equal to v).
- The answer is min(dp[last column][v]) over all v.
Code
C++
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int minimumOperations(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> cnt(n, vector<int>(10, 0));
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
cnt[j][grid[i][j]]++;
vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(10, 1e9));
for (int v = 0; v < 10; ++v)
dp[0][v] = m - cnt[0][v];
for (int j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
for (int v = 0; v < 10; ++v) {
for (int u = 0; u < 10; ++u) {
if (u == v) continue;
dp[j][v] = min(dp[j][v], dp[j-1][u] + m - cnt[j][v]);
}
}
}
return *min_element(dp[n-1].begin(), dp[n-1].end());
}
};
Go
func minimumOperations(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
cnt := make([][]int, n)
for j := range cnt {
cnt[j] = make([]int, 10)
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
cnt[j][grid[i][j]]++
}
}
dp := make([][]int, n)
for j := range dp {
dp[j] = make([]int, 10)
for v := 0; v < 10; v++ {
dp[j][v] = 1 << 30
}
}
for v := 0; v < 10; v++ {
dp[0][v] = m - cnt[0][v]
}
for j := 1; j < n; j++ {
for v := 0; v < 10; v++ {
for u := 0; u < 10; u++ {
if u == v {
continue
}
if dp[j][v] > dp[j-1][u]+m-cnt[j][v] {
dp[j][v] = dp[j-1][u]+m-cnt[j][v]
}
}
}
}
res := 1 << 30
for v := 0; v < 10; v++ {
if dp[n-1][v] < res {
res = dp[n-1][v]
}
}
return res
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int minimumOperations(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[][] cnt = new int[n][10];
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
cnt[j][grid[i][j]]++;
int[][] dp = new int[n][10];
for (int[] d : dp) Arrays.fill(d, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for (int v = 0; v < 10; ++v)
dp[0][v] = m - cnt[0][v];
for (int j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
for (int v = 0; v < 10; ++v) {
for (int u = 0; u < 10; ++u) {
if (u == v) continue;
dp[j][v] = Math.min(dp[j][v], dp[j-1][u] + m - cnt[j][v]);
}
}
}
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int v = 0; v < 10; ++v)
res = Math.min(res, dp[n-1][v]);
return res;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minimumOperations(grid: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = grid.size; val n = grid[0].size
val cnt = Array(n) { IntArray(10) }
for (j in 0 until n) for (i in 0 until m) cnt[j][grid[i][j]]++
val dp = Array(n) { IntArray(10) { Int.MAX_VALUE } }
for (v in 0..9) dp[0][v] = m - cnt[0][v]
for (j in 1 until n) {
for (v in 0..9) {
for (u in 0..9) {
if (u == v) continue
dp[j][v] = minOf(dp[j][v], dp[j-1][u] + m - cnt[j][v])
}
}
}
return dp[n-1].minOrNull()!!
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minimumOperations(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
cnt = [[0]*10 for _ in range(n)]
for j in range(n):
for i in range(m):
cnt[j][grid[i][j]] += 1
dp = [[float('inf')]*10 for _ in range(n)]
for v in range(10):
dp[0][v] = m - cnt[0][v]
for j in range(1, n):
for v in range(10):
for u in range(10):
if u == v: continue
dp[j][v] = min(dp[j][v], dp[j-1][u] + m - cnt[j][v])
return min(dp[n-1])
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn minimum_operations(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut cnt = vec![vec![0; 10]; n];
for j in 0..n {
for i in 0..m {
cnt[j][grid[i][j] as usize] += 1;
}
}
let mut dp = vec![vec![i32::MAX; 10]; n];
for v in 0..10 {
dp[0][v] = m as i32 - cnt[0][v];
}
for j in 1..n {
for v in 0..10 {
for u in 0..10 {
if u == v { continue; }
dp[j][v] = dp[j][v].min(dp[j-1][u] + m as i32 - cnt[j][v]);
}
}
}
*dp[n-1].iter().min().unwrap()
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minimumOperations(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
const cnt = Array.from({length: n}, () => Array(10).fill(0));
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j)
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i)
cnt[j][grid[i][j]]++;
const dp = Array.from({length: n}, () => Array(10).fill(Infinity));
for (let v = 0; v < 10; ++v)
dp[0][v] = m - cnt[0][v];
for (let j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
for (let v = 0; v < 10; ++v) {
for (let u = 0; u < 10; ++u) {
if (u === v) continue;
dp[j][v] = Math.min(dp[j][v], dp[j-1][u] + m - cnt[j][v]);
}
}
}
return Math.min(...dp[n-1]);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n * m * 10^2)— n = columns, m = rows, 10 values per column. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n * 10)— DP table.