Minimum Number of Taps to Open to Water a Garden
Problem
There is a one-dimensional garden on the x-axis. The garden starts at the point 0 and ends at the point n. (i.e., the length of the garden is n).
There are n + 1 taps located at points [0, 1, ..., n] in the garden.
Given an integer n and an integer array ranges of length n + 1 where ranges[i] (0-indexed) means the i-th tap can water the area [i - ranges[i], i + ranges[i]] if it was open.
Return the minimum number of taps that should be open to water the whole garden, If the garden cannot be watered return -1.
Examples
Example 1
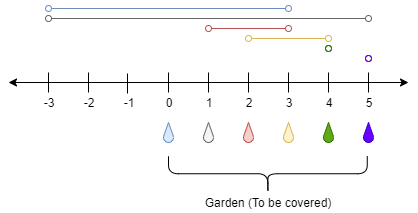
Input: n = 5, ranges = [3,4,1,1,0,0]
Output: 1
Explanation: The tap at point 0 can cover the interval [-3,3]
The tap at point 1 can cover the interval [-3,5]
The tap at point 2 can cover the interval [1,3]
The tap at point 3 can cover the interval [2,4]
The tap at point 4 can cover the interval [4,4]
The tap at point 5 can cover the interval [5,5]
Opening Only the second tap will water the whole garden [0,5]
Example 2
Input: n = 3, ranges = [0,0,0,0]
Output: -1
Explanation: Even if you activate all the four taps you cannot water the whole garden.
Constraints
1 <= n <= 104ranges.length == n + 10 <= ranges[i] <= 100
Solution
Method 1 – Greedy Interval Covering
Intuition
This problem is similar to the Jump Game II or interval covering. For each tap, compute the interval it can water. Then, use a greedy approach to always open the tap that extends coverage the farthest among those starting before or at the current end.
Approach
- For each tap, compute its watering interval
[max(0, i - ranges[i]), min(n, i + ranges[i])]. - For each position, keep track of the farthest right it can be watered by any tap starting at or before that position.
- Use a greedy scan: at each step, open the tap that extends coverage the farthest.
- If at any point coverage cannot be extended, return -1.
- Continue until coverage reaches or exceeds n.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minTaps(int n, vector<int>& ranges) {
vector<int> maxReach(n+1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
int l = max(0, i - ranges[i]), r = min(n, i + ranges[i]);
maxReach[l] = max(maxReach[l], r);
}
int ans = 0, end = 0, far = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
if (i > far) return -1;
if (i > end) {
ans++;
end = far;
}
far = max(far, maxReach[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func minTaps(n int, ranges []int) int {
maxReach := make([]int, n+1)
for i := 0; i <= n; i++ {
l, r := max(0, i-ranges[i]), min(n, i+ranges[i])
if maxReach[l] < r {
maxReach[l] = r
}
}
ans, end, far := 0, 0, 0
for i := 0; i <= n; i++ {
if i > far { return -1 }
if i > end {
ans++
end = far
}
if maxReach[i] > far {
far = maxReach[i]
}
}
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a }; return b }
func min(a, b int) int { if a < b { return a }; return b }
Java
class Solution {
public int minTaps(int n, int[] ranges) {
int[] maxReach = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
int l = Math.max(0, i - ranges[i]), r = Math.min(n, i + ranges[i]);
maxReach[l] = Math.max(maxReach[l], r);
}
int ans = 0, end = 0, far = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (i > far) return -1;
if (i > end) {
ans++;
end = far;
}
far = Math.max(far, maxReach[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minTaps(n: Int, ranges: IntArray): Int {
val maxReach = IntArray(n+1)
for (i in 0..n) {
val l = maxOf(0, i - ranges[i])
val r = minOf(n, i + ranges[i])
maxReach[l] = maxOf(maxReach[l], r)
}
var ans = 0; var end = 0; var far = 0
for (i in 0..n) {
if (i > far) return -1
if (i > end) {
ans++
end = far
}
far = maxOf(far, maxReach[i])
}
return ans
}
}
Python
def minTaps(n: int, ranges: list[int]) -> int:
maxReach = [0]*(n+1)
for i in range(n+1):
l, r = max(0, i-ranges[i]), min(n, i+ranges[i])
maxReach[l] = max(maxReach[l], r)
ans = end = far = 0
for i in range(n+1):
if i > far:
return -1
if i > end:
ans += 1
end = far
far = max(far, maxReach[i])
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_taps(n: i32, ranges: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let n = n as usize;
let mut max_reach = vec![0; n+1];
for i in 0..=n {
let l = i.saturating_sub(ranges[i] as usize);
let r = (i + ranges[i] as usize).min(n);
max_reach[l] = max_reach[l].max(r);
}
let (mut ans, mut end, mut far) = (0, 0, 0);
for i in 0..=n {
if i > far { return -1; }
if i > end {
ans += 1;
end = far;
}
far = far.max(max_reach[i]);
}
ans as i32
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minTaps(n: number, ranges: number[]): number {
const maxReach = Array(n+1).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
const l = Math.max(0, i - ranges[i]), r = Math.min(n, i + ranges[i]);
maxReach[l] = Math.max(maxReach[l], r);
}
let ans = 0, end = 0, far = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (i > far) return -1;
if (i > end) {
ans++;
end = far;
}
far = Math.max(far, maxReach[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), since we process each tap and scan the garden. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the maxReach array.