Minimum Number of Visited Cells in a Grid
HardUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given a 0-indexed m x n integer matrix grid. Your initial position is at the top-left cell (0, 0).
Starting from the cell (i, j), you can move to one of the following cells:
- Cells
(i, k)withj < k <= grid[i][j] + j(rightward movement), or - Cells
(k, j)withi < k <= grid[i][j] + i(downward movement).
Return the minimum number of cells you need to visit to reach thebottom-right cell (m - 1, n - 1). If there is no valid path, return -1.
Examples
Example 1
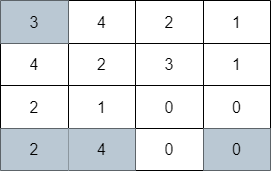
Input: grid = [[3,4,2,1],[4,2,3,1],[2,1,0,0],[2,4,0,0]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The image above shows one of the paths that visits exactly 4 cells.
Example 2
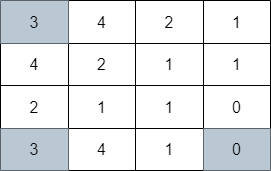
Input: grid = [[3,4,2,1],[4,2,1,1],[2,1,1,0],[3,4,1,0]]
Output: 3
Explanation: The image above shows one of the paths that visits exactly 3 cells.
Example 3
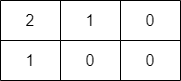
Input: grid = [[2,1,0],[1,0,0]]
Output: -1
Explanation: It can be proven that no path exists.
Constraints
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10^51 <= m * n <= 10^50 <= grid[i][j] < m * ngrid[m - 1][n - 1] == 0
Solution
Method 1 – BFS with Monotonic Queue
Intuition
We want the shortest path from (0,0) to (m-1,n-1) with allowed moves. BFS finds the minimum steps, but to avoid revisiting cells, we use monotonic queues to efficiently track reachable cells in each row and column.
Approach
- Use BFS starting from (0,0), tracking steps for each cell.
- For each cell, use two arrays of monotonic queues to track the next unvisited cell in the same row and column.
- For each move, push reachable cells into the queue and mark as visited.
- Stop when reaching (m-1,n-1) or queue is empty.
- Return the minimum steps or -1 if unreachable.
Code
C++
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int minVisitedCells(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<set<int>> row(m), col(n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
row[i].insert(j);
col[j].insert(i);
}
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({0, 0});
vector<vector<int>> dist(m, vector<int>(n, -1));
dist[0][0] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [i, j] = q.front(); q.pop();
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) return dist[i][j];
auto it = row[i].upper_bound(j);
while (it != row[i].end() && *it <= j + grid[i][j]) {
int nj = *it;
q.push({i, nj});
dist[i][nj] = dist[i][j] + 1;
row[i].erase(it++);
col[nj].erase(i);
}
auto it2 = col[j].upper_bound(i);
while (it2 != col[j].end() && *it2 <= i + grid[i][j]) {
int ni = *it2;
q.push({ni, j});
dist[ni][j] = dist[i][j] + 1;
col[j].erase(it2++);
row[ni].erase(j);
}
}
return -1;
}
};
Go
func minVisitedCells(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
row := make([]map[int]struct{}, m)
col := make([]map[int]struct{}, n)
for i := range row {
row[i] = make(map[int]struct{})
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
row[i][j] = struct{}{}
}
}
for j := range col {
col[j] = make(map[int]struct{})
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
col[j][i] = struct{}{}
}
}
type pair struct{ i, j int }
q := []pair{{0, 0}}
dist := make([][]int, m)
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range dist[i] {
dist[i][j] = -1
}
}
dist[0][0] = 1
for len(q) > 0 {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
i, j := p.i, p.j
if i == m-1 && j == n-1 {
return dist[i][j]
}
for nj := j + 1; nj <= j+grid[i][j] && nj < n; nj++ {
if _, ok := row[i][nj]; ok {
q = append(q, pair{i, nj})
dist[i][nj] = dist[i][j] + 1
delete(row[i], nj)
delete(col[nj], i)
}
}
for ni := i + 1; ni <= i+grid[i][j] && ni < m; ni++ {
if _, ok := col[j][ni]; ok {
q = append(q, pair{ni, j})
dist[ni][j] = dist[i][j] + 1
delete(col[j], ni)
delete(row[ni], j)
}
}
}
return -1
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int minVisitedCells(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
Set<Integer>[] row = new HashSet[m];
Set<Integer>[] col = new HashSet[n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
row[i] = new HashSet<>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) row[i].add(j);
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
col[j] = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) col[j].add(i);
}
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(new int[]{0, 0});
int[][] dist = new int[m][n];
for (int[] d : dist) Arrays.fill(d, -1);
dist[0][0] = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int i = p[0], j = p[1];
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) return dist[i][j];
for (int nj = j + 1; nj <= j + grid[i][j] && nj < n; nj++) {
if (row[i].contains(nj)) {
q.add(new int[]{i, nj});
dist[i][nj] = dist[i][j] + 1;
row[i].remove(nj);
col[nj].remove(i);
}
}
for (int ni = i + 1; ni <= i + grid[i][j] && ni < m; ni++) {
if (col[j].contains(ni)) {
q.add(new int[]{ni, j});
dist[ni][j] = dist[i][j] + 1;
col[j].remove(ni);
row[ni].remove(j);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
Kotlin
import java.util.LinkedList
class Solution {
fun minVisitedCells(grid: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = grid.size
val n = grid[0].size
val row = Array(m) { mutableSetOf<Int>() }
val col = Array(n) { mutableSetOf<Int>() }
for (i in 0 until m) for (j in 0 until n) row[i].add(j)
for (j in 0 until n) for (i in 0 until m) col[j].add(i)
val q = LinkedList<Pair<Int, Int>>()
q.add(0 to 0)
val dist = Array(m) { IntArray(n) { -1 } }
dist[0][0] = 1
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val (i, j) = q.poll()
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) return dist[i][j]
for (nj in j + 1..(j + grid[i][j]).coerceAtMost(n - 1)) {
if (row[i].remove(nj)) {
q.add(i to nj)
dist[i][nj] = dist[i][j] + 1
col[nj].remove(i)
}
}
for (ni in i + 1..(i + grid[i][j]).coerceAtMost(m - 1)) {
if (col[j].remove(ni)) {
q.add(ni to j)
dist[ni][j] = dist[i][j] + 1
row[ni].remove(j)
}
}
}
return -1
}
}
Python
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def minVisitedCells(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
row = [set(range(n)) for _ in range(m)]
col = [set(range(m)) for _ in range(n)]
q = deque([(0, 0)])
dist = [[-1] * n for _ in range(m)]
dist[0][0] = 1
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
if i == m - 1 and j == n - 1:
return dist[i][j]
for nj in range(j + 1, min(j + grid[i][j] + 1, n)):
if nj in row[i]:
q.append((i, nj))
dist[i][nj] = dist[i][j] + 1
row[i].remove(nj)
col[nj].remove(i)
for ni in range(i + 1, min(i + grid[i][j] + 1, m)):
if ni in col[j]:
q.append((ni, j))
dist[ni][j] = dist[i][j] + 1
col[j].remove(ni)
row[ni].remove(j)
return -1
Rust
use std::collections::{VecDeque, HashSet};
impl Solution {
pub fn min_visited_cells(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut row: Vec<HashSet<usize>> = vec![HashSet::new(); m];
let mut col: Vec<HashSet<usize>> = vec![HashSet::new(); n];
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
row[i].insert(j);
col[j].insert(i);
}
}
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
q.push_back((0, 0));
let mut dist = vec![vec![-1; n]; m];
dist[0][0] = 1;
while let Some((i, j)) = q.pop_front() {
if i == m - 1 && j == n - 1 {
return dist[i][j];
}
for nj in (j + 1)..=(j + grid[i][j] as usize).min(n - 1) {
if row[i].remove(&nj) {
q.push_back((i, nj));
dist[i][nj] = dist[i][j] + 1;
col[nj].remove(&i);
}
}
for ni in (i + 1)..=(i + grid[i][j] as usize).min(m - 1) {
if col[j].remove(&ni) {
q.push_back((ni, j));
dist[ni][j] = dist[i][j] + 1;
row[ni].remove(&j);
}
}
}
-1
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minVisitedCells(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
const row: Set<number>[] = Array.from({length: m}, () => new Set<number>());
const col: Set<number>[] = Array.from({length: n}, () => new Set<number>());
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) row[i].add(j);
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) col[j].add(i);
const dist: number[][] = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(-1));
dist[0][0] = 1;
let q: [number, number][] = [[0, 0]];
while (q.length) {
const [i, j] = q.shift()!;
if (i === m - 1 && j === n - 1) return dist[i][j];
for (let nj = j + 1; nj <= Math.min(j + grid[i][j], n - 1); ++nj) {
if (row[i].has(nj)) {
q.push([i, nj]);
dist[i][nj] = dist[i][j] + 1;
row[i].delete(nj);
col[nj].delete(i);
}
}
for (let ni = i + 1; ni <= Math.min(i + grid[i][j], m - 1); ++ni) {
if (col[j].has(ni)) {
q.push([ni, j]);
dist[ni][j] = dist[i][j] + 1;
col[j].delete(ni);
row[ni].delete(j);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n)— Each cell is visited at most once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m * n)— For visited sets and distance array.