Minimum Path Cost in a Grid
Problem
You are given a 0-indexed m x n integer matrix grid consisting of
distinct integers from 0 to m * n - 1. You can move in this matrix from a cell to any other cell in the next row. That is, if you are in cell
(x, y) such that x < m - 1, you can move to any of the cells (x + 1, 0),
(x + 1, 1), ..., (x + 1, n - 1). Note that it is not possible to move from cells in the last row.
Each possible move has a cost given by a 0-indexed 2D array moveCost of size (m * n) x n, where moveCost[i][j] is the cost of moving from a cell with value i to a cell in column j of the next row. The cost of moving from cells in the last row of grid can be ignored.
The cost of a path in grid is the sum of all values of cells visited plus the sum of costs of all the moves made. Return theminimum cost of a path that starts from any cell in the first row and ends at any cell in the last row.
Examples
Example 1
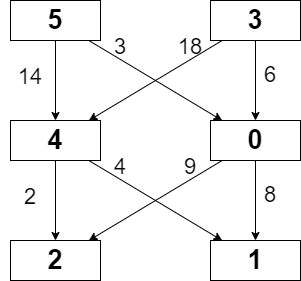
Input: grid = [[5,3],[4,0],[2,1]], moveCost = [[9,8],[1,5],[10,12],[18,6],[2,4],[14,3]]
Output: 17
Explanation: The path with the minimum possible cost is the path 5 -> 0 -> 1.
- The sum of the values of cells visited is 5 + 0 + 1 = 6.
- The cost of moving from 5 to 0 is 3.
- The cost of moving from 0 to 1 is 8.
So the total cost of the path is 6 + 3 + 8 = 17.
Example 2
Input: grid = [[5,1,2],[4,0,3]], moveCost = [[12,10,15],[20,23,8],[21,7,1],[8,1,13],[9,10,25],[5,3,2]]
Output: 6
Explanation: The path with the minimum possible cost is the path 2 -> 3.
- The sum of the values of cells visited is 2 + 3 = 5.
- The cost of moving from 2 to 3 is 1.
So the total cost of this path is 5 + 1 = 6.
Constraints
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 50gridconsists of distinct integers from0tom * n - 1.moveCost.length == m * nmoveCost[i].length == n1 <= moveCost[i][j] <= 100
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming (DP)
Intuition
For each cell, keep track of the minimum cost to reach it from the first row. For each move, add the cell value and the move cost. Use DP to propagate costs row by row.
Approach
- Initialize DP for the first row: cost is just the cell value.
- For each subsequent row, for each cell, try all possible previous cells in the row above, and update the minimum cost using moveCost.
- The answer is the minimum cost in the last row.
Code
C++
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
class Solution {
public:
int minPathCost(std::vector<std::vector<int>>& grid, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& moveCost) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
std::vector<std::vector<int>> dp(m, std::vector<int>(n, 1e9));
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) dp[0][j] = grid[0][j];
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
int prev = grid[i-1][k];
dp[i][j] = std::min(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][k] + moveCost[prev][j] + grid[i][j]);
}
}
}
return *std::min_element(dp[m-1].begin(), dp[m-1].end());
}
};
Go
func minPathCost(grid [][]int, moveCost [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
dp := make([][]int, m)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range dp[i] { dp[i][j] = 1<<30 }
}
for j := 0; j < n; j++ { dp[0][j] = grid[0][j] }
for i := 1; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
for k := 0; k < n; k++ {
prev := grid[i-1][k]
cost := dp[i-1][k] + moveCost[prev][j] + grid[i][j]
if cost < dp[i][j] { dp[i][j] = cost }
}
}
}
res := dp[m-1][0]
for j := 1; j < n; j++ {
if dp[m-1][j] < res { res = dp[m-1][j] }
}
return res
}
Java
class Solution {
public int minPathCost(int[][] grid, int[][] moveCost) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
for (int[] row : dp) Arrays.fill(row, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) dp[0][j] = grid[0][j];
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
int prev = grid[i-1][k];
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][k] + moveCost[prev][j] + grid[i][j]);
}
}
}
int res = dp[m-1][0];
for (int j = 1; j < n; ++j) res = Math.min(res, dp[m-1][j]);
return res;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minPathCost(grid: Array<IntArray>, moveCost: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = grid.size
val n = grid[0].size
val dp = Array(m) { IntArray(n) { Int.MAX_VALUE } }
for (j in 0 until n) dp[0][j] = grid[0][j]
for (i in 1 until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
for (k in 0 until n) {
val prev = grid[i-1][k]
dp[i][j] = minOf(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][k] + moveCost[prev][j] + grid[i][j])
}
}
}
return dp[m-1].minOrNull()!!
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minPathCost(self, grid: list[list[int]], moveCost: list[list[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dp = [[float('inf')]*n for _ in range(m)]
for j in range(n): dp[0][j] = grid[0][j]
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(n):
for k in range(n):
prev = grid[i-1][k]
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][k] + moveCost[prev][j] + grid[i][j])
return min(dp[m-1])
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_path_cost(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>, move_cost: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut dp = vec![vec![i32::MAX; n]; m];
for j in 0..n { dp[0][j] = grid[0][j]; }
for i in 1..m {
for j in 0..n {
for k in 0..n {
let prev = grid[i-1][k] as usize;
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j].min(dp[i-1][k] + move_cost[prev][j] + grid[i][j]);
}
}
}
*dp[m-1].iter().min().unwrap()
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minPathCost(grid: number[][], moveCost: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
const dp = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(Infinity));
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) dp[0][j] = grid[0][j];
for (let i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (let k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
const prev = grid[i-1][k];
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][k] + moveCost[prev][j] + grid[i][j]);
}
}
}
return Math.min(...dp[m-1]);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n^2)— For each cell, try all previous cells. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m * n)— DP table.