Minimum Runes to Add to Cast Spell
Problem
Alice has just graduated from wizard school, and wishes to cast a magic spell to celebrate. The magic spell contains certain focus points where magic needs to be concentrated, and some of these focus points contain magic crystals which serve as the spell's energy source. Focus points can be linked through directed runes, which channel magic flow from one focus point to another.
You are given a integer n denoting the number of focus points and an array of integers crystals where crystals[i] indicates a focus point which holds a magic crystal. You are also given two integer arrays flowFrom and flowTo, which represent the existing directed runes. The ith rune allows magic to freely flow from focus point flowFrom[i] to focus point flowTo[i].
You need to find the number of directed runes Alice must add to her spell, such that each focus point either:
- Contains a magic crystal.
- Receives magic flow from another focus point.
Return the minimum number of directed runes that she should add.
Examples
Example 1
Input: n = 6, crystals = [0], flowFrom = [0,1,2,3], flowTo = [1,2,3,0]
Output: 2
Explanation:
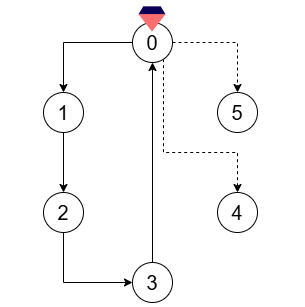
Add two directed runes:
- From focus point 0 to focus point 4.
- From focus point 0 to focus point 5.
Example 2
Input: n = 7, crystals = [3,5], flowFrom = [0,1,2,3,5], flowTo = [1,2,0,4,6]
Output: 1
Explanation:
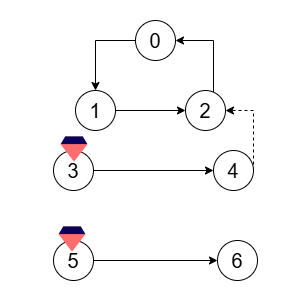
Add a directed rune from focus point 4 to focus point 2.
Constraints
2 <= n <= 10^51 <= crystals.length <= n0 <= crystals[i] <= n - 11 <= flowFrom.length == flowTo.length <= min(2 * 10^5, (n * (n - 1)) / 2)0 <= flowFrom[i], flowTo[i] <= n - 1flowFrom[i] != flowTo[i]- All pre-existing directed runes are distinct.
Solution
Method 1 – BFS + DFS for Strongly Connected Components
Intuition
We want every node to either have a crystal or be reachable from a crystal. BFS from crystals marks all reachable nodes. For the rest, we use DFS to find nodes that need new runes, processing in reverse topological order to minimize additions.
Approach
- Build the directed graph from
flowFromandflowTo. - Mark all crystal nodes and BFS from them to mark all reachable nodes.
- For each unvisited node, run DFS to build a post-order sequence.
- Process nodes in reverse post-order: for each node still unvisited, add a rune, BFS from it, and count the addition.
- Return the total number of runes added.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minRunesToAdd(int n, vector<int>& crystals, vector<int>& flowFrom, vector<int>& flowTo) {
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (int i = 0; i < flowFrom.size(); ++i) {
g[flowFrom[i]].push_back(flowTo[i]);
}
vector<int> vis(n, 0), seq;
queue<int> q;
for (int i : crystals) {
vis[i] = 1;
q.push(i);
}
auto bfs = [&](queue<int>& q) {
while (!q.empty()) {
int a = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (vis[b] == 1) continue;
vis[b] = 1;
q.push(b);
}
}
};
bfs(q);
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int a) {
vis[a] = 2;
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (vis[b] > 0) continue;
dfs(b);
}
seq.push_back(a);
};
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (vis[i] == 0) dfs(i);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = seq.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
int a = seq[i];
if (vis[a] == 2) {
vis[a] = 1;
queue<int> nq;
nq.push(a);
bfs(nq);
++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func minRunesToAdd(n int, crystals []int, flowFrom []int, flowTo []int) int {
g := make([][]int, n)
for i := range flowFrom {
g[flowFrom[i]] = append(g[flowFrom[i]], flowTo[i])
}
vis := make([]int, n)
seq := []int{}
q := []int{}
for _, i := range crystals {
vis[i] = 1
q = append(q, i)
}
bfs := func(q []int) {
for len(q) > 0 {
a := q[0]
q = q[1:]
for _, b := range g[a] {
if vis[b] == 1 {
continue
}
vis[b] = 1
q = append(q, b)
}
}
}
bfs(q)
var dfs func(int)
dfs = func(a int) {
vis[a] = 2
for _, b := range g[a] {
if vis[b] > 0 {
continue
}
dfs(b)
}
seq = append(seq, a)
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if vis[i] == 0 {
dfs(i)
}
}
ans := 0
for i := len(seq) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
a := seq[i]
if vis[a] == 2 {
vis[a] = 1
nq := []int{a}
bfs(nq)
ans++
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
private int[] vis;
private List<Integer>[] g;
private List<Integer> seq = new ArrayList<>();
public int minRunesToAdd(int n, int[] crystals, int[] flowFrom, int[] flowTo) {
g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 0; i < flowFrom.length; ++i) {
g[flowFrom[i]].add(flowTo[i]);
}
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
vis = new int[n];
for (int i : crystals) {
vis[i] = 1;
q.offer(i);
}
bfs(q);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (vis[i] == 0) {
dfs(i);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = seq.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
int a = seq.get(i);
if (vis[a] == 2) {
vis[a] = 1;
q.clear();
q.offer(a);
bfs(q);
++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
private void bfs(Deque<Integer> q) {
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int a = q.poll();
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (vis[b] == 1) {
continue;
}
vis[b] = 1;
q.offer(b);
}
}
}
private void dfs(int a) {
vis[a] = 2;
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (vis[b] > 0) {
continue;
}
dfs(b);
}
seq.add(a);
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
private lateinit var vis: IntArray
private lateinit var g: Array<MutableList<Int>>
private val seq = mutableListOf<Int>()
fun minRunesToAdd(n: Int, crystals: IntArray, flowFrom: IntArray, flowTo: IntArray): Int {
g = Array(n) { mutableListOf() }
for (i in flowFrom.indices) {
g[flowFrom[i]].add(flowTo[i])
}
vis = IntArray(n)
val q = ArrayDeque<Int>()
for (i in crystals) {
vis[i] = 1
q.add(i)
}
bfs(q)
for (i in 0 until n) {
if (vis[i] == 0) {
dfs(i)
}
}
var ans = 0
for (i in seq.size - 1 downTo 0) {
val a = seq[i]
if (vis[a] == 2) {
vis[a] = 1
val nq = ArrayDeque<Int>()
nq.add(a)
bfs(nq)
ans++
}
}
return ans
}
private fun bfs(q: ArrayDeque<Int>) {
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val a = q.removeFirst()
for (b in g[a]) {
if (vis[b] == 1) continue
vis[b] = 1
q.add(b)
}
}
}
private fun dfs(a: Int) {
vis[a] = 2
for (b in g[a]) {
if (vis[b] > 0) continue
dfs(b)
}
seq.add(a)
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minRunesToAdd(self, n: int, crystals: list[int], flowFrom: list[int], flowTo: list[int]) -> int:
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for a, b in zip(flowFrom, flowTo):
g[a].append(b)
vis = [0] * n
seq: list[int] = []
q: list[int] = []
for i in crystals:
vis[i] = 1
q.append(i)
def bfs(q: list[int]):
while q:
a = q.pop(0)
for b in g[a]:
if vis[b] == 1:
continue
vis[b] = 1
q.append(b)
bfs(q)
def dfs(a: int):
vis[a] = 2
for b in g[a]:
if vis[b] > 0:
continue
dfs(b)
seq.append(a)
for i in range(n):
if vis[i] == 0:
dfs(i)
ans = 0
for a in reversed(seq):
if vis[a] == 2:
vis[a] = 1
nq = [a]
bfs(nq)
ans += 1
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_runes_to_add(n: i32, crystals: Vec<i32>, flow_from: Vec<i32>, flow_to: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let n = n as usize;
let mut g = vec![vec![]; n];
for (&a, &b) in flow_from.iter().zip(flow_to.iter()) {
g[a as usize].push(b as usize);
}
let mut vis = vec![0; n];
let mut seq = Vec::new();
let mut q = Vec::new();
for &i in &crystals {
vis[i as usize] = 1;
q.push(i as usize);
}
let mut bfs = |q: &mut Vec<usize>| {
while let Some(a) = q.pop() {
for &b in &g[a] {
if vis[b] == 1 { continue; }
vis[b] = 1;
q.push(b);
}
}
};
bfs(&mut q);
fn dfs(a: usize, g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>, vis: &mut Vec<i32>, seq: &mut Vec<usize>) {
vis[a] = 2;
for &b in &g[a] {
if vis[b] > 0 { continue; }
dfs(b, g, vis, seq);
}
seq.push(a);
}
for i in 0..n {
if vis[i] == 0 {
dfs(i, &g, &mut vis, &mut seq);
}
}
let mut ans = 0;
for &a in seq.iter().rev() {
if vis[a] == 2 {
vis[a] = 1;
let mut nq = vec![a];
bfs(&mut nq);
ans += 1;
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minRunesToAdd(n: number, crystals: number[], flowFrom: number[], flowTo: number[]): number {
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (let i = 0; i < flowFrom.length; ++i) {
g[flowFrom[i]].push(flowTo[i]);
}
const vis: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
const seq: number[] = [];
let q: number[] = [];
for (const i of crystals) {
vis[i] = 1;
q.push(i);
}
const bfs = (q: number[]) => {
while (q.length) {
const a = q.shift()!;
for (const b of g[a]) {
if (vis[b] === 1) continue;
vis[b] = 1;
q.push(b);
}
}
};
bfs(q);
const dfs = (a: number) => {
vis[a] = 2;
for (const b of g[a]) {
if (vis[b] > 0) continue;
dfs(b);
}
seq.push(a);
};
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (vis[i] === 0) dfs(i);
}
let ans = 0;
for (let i = seq.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
const a = seq[i];
if (vis[a] === 2) {
vis[a] = 1;
bfs([a]);
++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n + m)— BFS and DFS each visit every node and edge once, where n is number of nodes and m is number of edges. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n + m)— Graph, visited array, and sequence all use linear space.