Minimum Time Visiting All Points
EasyUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
On a 2D plane, there are n points with integer coordinates points[i] = [xi, yi]. Return _theminimum time in seconds to visit all the points in the order given by _points.
You can move according to these rules:
- In
1second, you can either: - move vertically by one unit,
- move horizontally by one unit, or
- move diagonally
sqrt(2)units (in other words, move one unit vertically then one unit horizontally in1second).- You have to visit the points in the same order as they appear in the array.
- You are allowed to pass through points that appear later in the order, but these do not count as visits.
Examples
Example 1
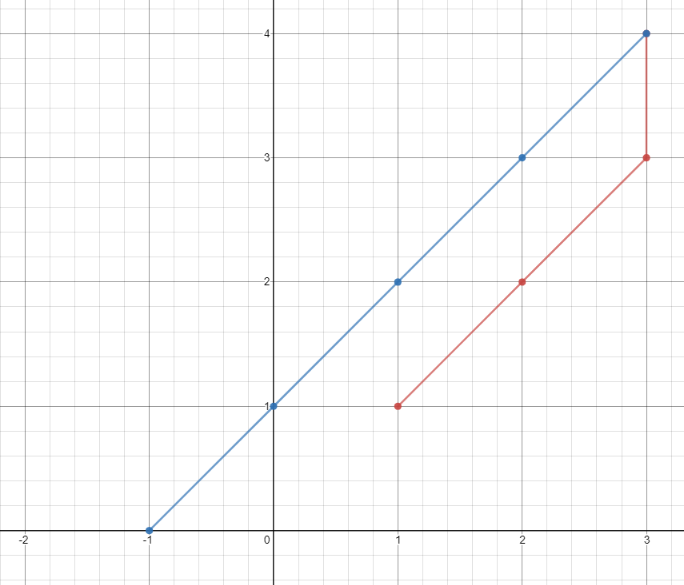
Input: points = [[1,1],[3,4],[-1,0]]
Output: 7
Explanation: One optimal path is **[1,1]** -> [2,2] -> [3,3] -> **[3,4]** -> [2,3] -> [1,2] -> [0,1] -> **[-1,0]**
Time from [1,1] to [3,4] = 3 seconds
Time from [3,4] to [-1,0] = 4 seconds
Total time = 7 seconds
Example 2
Input: points = [[3,2],[-2,2]]
Output: 5
Constraints
points.length == n1 <= n <= 100points[i].length == 2-1000 <= points[i][0], points[i][1] <= 1000
Solution
Method 1 – Greedy Manhattan/Diagonal Moves
Intuition
To minimize time, always move diagonally as much as possible, since a diagonal move covers both axes in one second. The minimum time between two points is the maximum of the differences in x and y coordinates.
Approach
- Iterate through each consecutive pair of points.
- For each pair, compute
dx = abs(x2 - x1)anddy = abs(y2 - y1). - Add
max(dx, dy)to the total time. - Return the total time.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minTimeToVisitAllPoints(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < points.size(); ++i) {
int dx = abs(points[i][0] - points[i-1][0]);
int dy = abs(points[i][1] - points[i-1][1]);
ans += max(dx, dy);
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func MinTimeToVisitAllPoints(points [][]int) int {
ans := 0
for i := 1; i < len(points); i++ {
dx := abs(points[i][0] - points[i-1][0])
dy := abs(points[i][1] - points[i-1][1])
if dx > dy {
ans += dx
} else {
ans += dy
}
}
return ans
}
func abs(x int) int { if x < 0 { return -x } else { return x } }
Java
class Solution {
public int minTimeToVisitAllPoints(int[][] points) {
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
int dx = Math.abs(points[i][0] - points[i-1][0]);
int dy = Math.abs(points[i][1] - points[i-1][1]);
ans += Math.max(dx, dy);
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minTimeToVisitAllPoints(points: Array<IntArray>): Int {
var ans = 0
for (i in 1 until points.size) {
val dx = kotlin.math.abs(points[i][0] - points[i-1][0])
val dy = kotlin.math.abs(points[i][1] - points[i-1][1])
ans += maxOf(dx, dy)
}
return ans
}
}
Python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def minTimeToVisitAllPoints(self, points: List[List[int]]) -> int:
ans = 0
for i in range(1, len(points)):
dx = abs(points[i][0] - points[i-1][0])
dy = abs(points[i][1] - points[i-1][1])
ans += max(dx, dy)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_time_to_visit_all_points(points: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let mut ans = 0;
for i in 1..points.len() {
let dx = (points[i][0] - points[i-1][0]).abs();
let dy = (points[i][1] - points[i-1][1]).abs();
ans += dx.max(dy);
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minTimeToVisitAllPoints(points: number[][]): number {
let ans = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
const dx = Math.abs(points[i][0] - points[i-1][0]);
const dy = Math.abs(points[i][1] - points[i-1][1]);
ans += Math.max(dx, dy);
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n)— We scan the points once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)— Only a few variables are used for computation.