Modify the Matrix
EasyUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a 0-indexed m x n integer matrix matrix, create a new
0-indexed matrix called answer. Make answer equal to matrix, then replace each element with the value -1 with the maximum element in its respective column.
Return the matrix answer.
Examples
Example 1
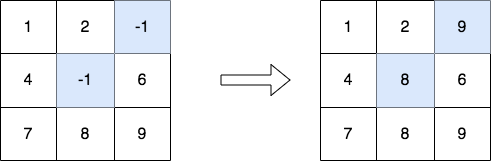
Input: matrix = [[1,2,-1],[4,-1,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [[1,2,9],[4,8,6],[7,8,9]]
Explanation: The diagram above shows the elements that are changed (in blue).
- We replace the value in the cell [1][1] with the maximum value in the column 1, that is 8.
- We replace the value in the cell [0][2] with the maximum value in the column 2, that is 9.
Example 2
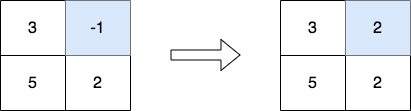
Input: matrix = [[3,-1],[5,2]]
Output: [[3,2],[5,2]]
Explanation: The diagram above shows the elements that are changed (in blue).
Constraints
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length2 <= m, n <= 50-1 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100- The input is generated such that each column contains at least one non-negative integer.
Solution
Method 1 – Column Maximum Replacement
Intuition
The key idea is to replace every -1 in the matrix with the maximum value of its column. Since each column is guaranteed to have at least one non-negative value, we can safely compute the maximum for each column and use it for replacement.
Approach
- Iterate through each column and find its maximum value (ignoring -1).
- Create a copy of the original matrix to avoid modifying it in place.
- For each cell, if its value is -1, replace it with the column's maximum value.
- Return the modified matrix.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> modifiedMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
vector<int> colMax(n, INT_MIN);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
if (matrix[i][j] != -1) colMax[j] = max(colMax[j], matrix[i][j]);
}
}
vector<vector<int>> ans = matrix;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (ans[i][j] == -1) ans[i][j] = colMax[j];
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func ModifiedMatrix(matrix [][]int) [][]int {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
colMax := make([]int, n)
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
colMax[j] = -1 << 31
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
if matrix[i][j] != -1 && matrix[i][j] > colMax[j] {
colMax[j] = matrix[i][j]
}
}
}
ans := make([][]int, m)
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
ans[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if matrix[i][j] == -1 {
ans[i][j] = colMax[j]
} else {
ans[i][j] = matrix[i][j]
}
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int[][] modifiedMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int[] colMax = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(colMax, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (matrix[i][j] != -1) colMax[j] = Math.max(colMax[j], matrix[i][j]);
}
}
int[][] ans = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
ans[i][j] = matrix[i][j] == -1 ? colMax[j] : matrix[i][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun modifiedMatrix(matrix: Array<IntArray>): Array<IntArray> {
val m = matrix.size
val n = matrix[0].size
val colMax = IntArray(n) { Int.MIN_VALUE }
for (j in 0 until n) {
for (i in 0 until m) {
if (matrix[i][j] != -1) colMax[j] = maxOf(colMax[j], matrix[i][j])
}
}
val ans = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
for (i in 0 until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
ans[i][j] = if (matrix[i][j] == -1) colMax[j] else matrix[i][j]
}
}
return ans
}
}
Python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def modifiedMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
col_max = [float('-inf')] * n
for j in range(n):
for i in range(m):
if matrix[i][j] != -1:
col_max[j] = max(col_max[j], matrix[i][j])
ans = [row[:] for row in matrix]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if ans[i][j] == -1:
ans[i][j] = col_max[j]
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn modified_matrix(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let m = matrix.len();
let n = matrix[0].len();
let mut col_max = vec![i32::MIN; n];
for j in 0..n {
for i in 0..m {
if matrix[i][j] != -1 {
col_max[j] = col_max[j].max(matrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
let mut ans = matrix.clone();
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if ans[i][j] == -1 {
ans[i][j] = col_max[j];
}
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
modifiedMatrix(matrix: number[][]): number[][] {
const m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
const colMax = Array(n).fill(Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY);
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (matrix[i][j] !== -1) colMax[j] = Math.max(colMax[j], matrix[i][j]);
}
}
const ans = matrix.map(row => [...row]);
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (ans[i][j] === -1) ans[i][j] = colMax[j];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n)— We scan every element twice: once to compute column maximums, once to replace -1s. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m * n + n)— We use a copy of the matrix for the answer and an array for column maximums.