Nearest Exit from Entrance in Maze
Problem
You are given an m x n matrix maze (0-indexed) with empty cells (represented as '.') and walls (represented as '+'). You are also given the entrance of the maze, where entrance = [entrancerow, entrancecol]
denotes the row and column of the cell you are initially standing at.
In one step, you can move one cell up , down , left , or
right. You cannot step into a cell with a wall, and you cannot step outside the maze. Your goal is to find the nearest exit from the
entrance. An exit is defined as an empty cell that is at the
border of the maze. The entrance does not count as an exit.
Return _thenumber of steps in the shortest path from the _entrance to the nearest exit, or-1 if no such path exists.
Examples
Example 1
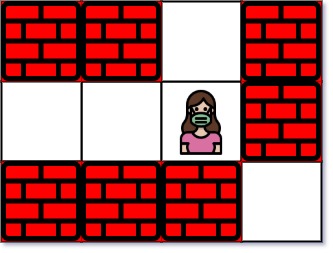
Input: maze = [["+","+",".","+"],[".",".",".","+"],["+","+","+","."]], entrance = [1,2]
Output: 1
Explanation: There are 3 exits in this maze at [1,0], [0,2], and [2,3].
Initially, you are at the entrance cell [1,2].
- You can reach [1,0] by moving 2 steps left.
- You can reach [0,2] by moving 1 step up.
It is impossible to reach [2,3] from the entrance.
Thus, the nearest exit is [0,2], which is 1 step away.
Example 2
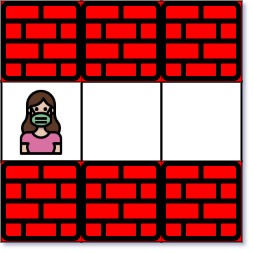
Input: maze = [["+","+","+"],[".",".","."],["+","+","+"]], entrance = [1,0]
Output: 2
Explanation: There is 1 exit in this maze at [1,2].
[1,0] does not count as an exit since it is the entrance cell.
Initially, you are at the entrance cell [1,0].
- You can reach [1,2] by moving 2 steps right.
Thus, the nearest exit is [1,2], which is 2 steps away.
Example 3

Input: maze = [[".","+"]], entrance = [0,0]
Output: -1
Explanation: There are no exits in this maze.
Constraints
maze.length == mmaze[i].length == n1 <= m, n <= 100maze[i][j]is either'.'or'+'.entrance.length == 20 <= entrancerow < m0 <= entrancecol < nentrancewill always be an empty cell.
Solution
Method 1 -
Intuition
This is a shortest path problem in a grid. Breadth-first search (BFS) is ideal for finding the minimum number of steps to the nearest exit.
Approach
Use BFS starting from the entrance. For each cell, check its neighbors. If a neighbor is an empty cell and on the border (but not the entrance), return the number of steps. Mark visited cells to avoid cycles.
Code
C++
int nearestExit(vector<vector<char>>& maze, vector<int>& entrance) {
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[0].size();
queue<pair<int,int>> q; q.push({entrance[0], entrance[1]});
vector<vector<int>> vis(m, vector<int>(n, 0));
vis[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = 1;
int steps = 0;
int dirs[4][2] = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
while (sz--) {
auto [x, y] = q.front(); q.pop();
for (auto& d : dirs) {
int nx = x + d[0], ny = y + d[1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n) continue;
if (maze[nx][ny] != '.' || vis[nx][ny]) continue;
if ((nx == 0 || ny == 0 || nx == m-1 || ny == n-1) && (nx != entrance[0] || ny != entrance[1]))
return steps+1;
vis[nx][ny] = 1; q.push({nx, ny});
}
}
steps++;
}
return -1;
}
Go
func nearestExit(maze [][]byte, entrance []int) int {
m, n := len(maze), len(maze[0])
vis := make([][]bool, m)
for i := range vis { vis[i] = make([]bool, n) }
dirs := [][]int{{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}}
q := [][]int{{entrance[0], entrance[1]}}
vis[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = true
steps := 0
for len(q) > 0 {
nq := [][]int{}
for _, p := range q {
x, y := p[0], p[1]
for _, d := range dirs {
nx, ny := x+d[0], y+d[1]
if nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n { continue }
if maze[nx][ny] != '.' || vis[nx][ny] { continue }
if (nx == 0 || ny == 0 || nx == m-1 || ny == n-1) && (nx != entrance[0] || ny != entrance[1]) {
return steps+1
}
vis[nx][ny] = true
nq = append(nq, []int{nx, ny})
}
}
q = nq
steps++
}
return -1
}
Java
public int nearestExit(char[][] maze, int[] entrance) {
int m = maze.length, n = maze[0].length;
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[m][n];
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[]{entrance[0], entrance[1]});
vis[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = true;
int steps = 0;
int[][] dirs = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int x = p[0], y = p[1];
for (int[] d : dirs) {
int nx = x + d[0], ny = y + d[1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n) continue;
if (maze[nx][ny] != '.' || vis[nx][ny]) continue;
if ((nx == 0 || ny == 0 || nx == m-1 || ny == n-1) && (nx != entrance[0] || ny != entrance[1]))
return steps+1;
vis[nx][ny] = true; q.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
}
}
steps++;
}
return -1;
}
Kotlin
fun nearestExit(maze: Array<CharArray>, entrance: IntArray): Int {
val m = maze.size; val n = maze[0].size
val vis = Array(m) { BooleanArray(n) }
val dirs = arrayOf(intArrayOf(0,1), intArrayOf(0,-1), intArrayOf(1,0), intArrayOf(-1,0))
val q = ArrayDeque<Pair<Int,Int>>()
q.add(Pair(entrance[0], entrance[1]))
vis[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = true
var steps = 0
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
repeat(q.size) {
val (x, y) = q.removeFirst()
for (d in dirs) {
val nx = x + d[0]; val ny = y + d[1]
if (nx !in 0 until m || ny !in 0 until n) continue
if (maze[nx][ny] != '.' || vis[nx][ny]) continue
if ((nx == 0 || ny == 0 || nx == m-1 || ny == n-1) && (nx != entrance[0] || ny != entrance[1]))
return steps+1
vis[nx][ny] = true; q.add(Pair(nx, ny))
}
}
steps++
}
return -1
}
Python
from collections import deque
def nearestExit(maze, entrance):
m, n = len(maze), len(maze[0])
vis = [[False]*n for _ in range(m)]
q = deque([(entrance[0], entrance[1])])
vis[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = True
steps = 0
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
x, y = q.popleft()
for dx, dy in ((0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0)):
nx, ny = x+dx, y+dy
if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and maze[nx][ny] == '.' and not vis[nx][ny]:
if (nx == 0 or ny == 0 or nx == m-1 or ny == n-1) and (nx != entrance[0] or ny != entrance[1]):
return steps+1
vis[nx][ny] = True
q.append((nx, ny))
steps += 1
return -1
Rust
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
pub fn nearest_exit(maze: Vec<Vec<char>>, entrance: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let m = maze.len(); let n = maze[0].len();
let mut vis = vec![vec![false; n]; m];
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
q.push_back((entrance[0] as usize, entrance[1] as usize));
vis[entrance[0] as usize][entrance[1] as usize] = true;
let dirs = [(0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0)];
let mut steps = 0;
while !q.is_empty() {
for _ in 0..q.len() {
let (x, y) = q.pop_front().unwrap();
for (dx, dy) in dirs.iter() {
let nx = x as i32 + dx; let ny = y as i32 + dy;
if nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m as i32 || ny >= n as i32 { continue; }
let nx = nx as usize; let ny = ny as usize;
if maze[nx][ny] != '.' || vis[nx][ny] { continue; }
if (nx == 0 || ny == 0 || nx == m-1 || ny == n-1) && (nx != entrance[0] as usize || ny != entrance[1] as usize) {
return steps+1;
}
vis[nx][ny] = true; q.push_back((nx, ny));
}
}
steps += 1;
}
-1
}
}
TypeScript
function nearestExit(maze: string[][], entrance: number[]): number {
const m = maze.length, n = maze[0].length;
const vis = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(false));
const q: [number, number][] = [[entrance[0], entrance[1]]];
vis[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = true;
let steps = 0;
while (q.length) {
const nq: [number, number][] = [];
for (const [x, y] of q) {
for (const [dx, dy] of [[0,1],[0,-1],[1,0],[-1,0]]) {
const nx = x + dx, ny = y + dy;
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n) continue;
if (maze[nx][ny] !== '.' || vis[nx][ny]) continue;
if ((nx === 0 || ny === 0 || nx === m-1 || ny === n-1) && (nx !== entrance[0] || ny !== entrance[1]))
return steps+1;
vis[nx][ny] = true; nq.push([nx, ny]);
}
}
q.length = 0; q.push(...nq);
steps++;
}
return -1;
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(mn)where m, n are maze dimensions. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(mn)for visited and queue.