Number of Closed Islands
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Number of Closed Islands Problem
Problem
Given a 2D grid consists of 0s (land) and 1s (water). An island is a maximal 4-directionally connected group of 0s and a closed island is an island totally (all left, top, right, bottom) surrounded by 1s.
Return the number of closed islands.
Examples
Example 1:
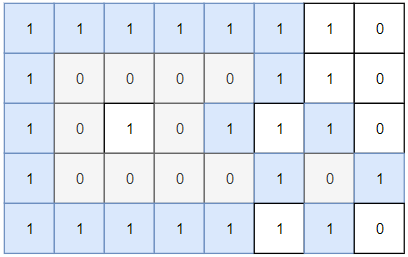
Input:
grid = [[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0],[1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0],[1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0],[1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0]]
Output:
2
Explanation:
Islands in gray are closed because they are completely surrounded by water (group of 1s).
Example 2:
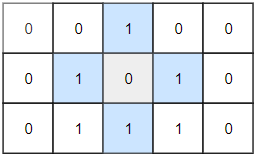
Input:
grid = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,1,0],[0,1,1,1,0]]
Output:
1
Example 3:
Input:
grid = [[1,1,1,1,1,1,1],
[1,0,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,0,1,1,1,0,1],
[1,0,1,0,1,0,1],
[1,0,1,1,1,0,1],
[1,0,0,0,0,0,1],
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1]]
Output:
2
Constraints:
1 <= grid.length, grid[0].length <= 1000 <= grid[i][j] <=1
Solution
Method 1 – BFS Flood Fill
Intuition
A closed island is a group of 0s completely surrounded by 1s (including the grid boundary). We can use BFS to flood fill all 0s connected to the boundary, then count the number of remaining closed islands by BFS.
Approach
- Flood fill all 0s connected to the boundary (turn them to 1) using BFS.
- For each cell inside the grid, if it is 0, start a BFS to mark all connected 0s as visited (turn to 1) and increment the count.
- Return the count of closed islands found.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int closedIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size(), ans = 0;
auto bfs = [&](int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({x, y});
grid[x][y] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [i, j] = q.front(); q.pop();
for (auto [dx, dy] : vector<pair<int,int>>{{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}) {
int ni = i + dx, nj = j + dy;
if (ni >= 0 && ni < m && nj >= 0 && nj < n && grid[ni][nj] == 0) {
grid[ni][nj] = 1;
q.push({ni, nj});
}
}
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) for (int j : {0, n-1}) if (grid[i][j] == 0) bfs(i, j);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) for (int i : {0, m-1}) if (grid[i][j] == 0) bfs(i, j);
for (int i = 1; i < m-1; ++i) for (int j = 1; j < n-1; ++j) if (grid[i][j] == 0) { bfs(i, j); ans++; }
return ans;
}
};
Go
func closedIsland(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs := [][2]int{{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}
var bfs func(int, int)
bfs = func(x, y int) {
q := [][2]int{{x, y}}
grid[x][y] = 1
for len(q) > 0 {
i, j := q[0][0], q[0][1]
q = q[1:]
for _, d := range dirs {
ni, nj := i+d[0], j+d[1]
if ni >= 0 && ni < m && nj >= 0 && nj < n && grid[ni][nj] == 0 {
grid[ni][nj] = 1
q = append(q, [2]int{ni, nj})
}
}
}
}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
if grid[i][0] == 0 { bfs(i, 0) }
if grid[i][n-1] == 0 { bfs(i, n-1) }
}
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if grid[0][j] == 0 { bfs(0, j) }
if grid[m-1][j] == 0 { bfs(m-1, j) }
}
ans := 0
for i := 1; i < m-1; i++ {
for j := 1; j < n-1; j++ {
if grid[i][j] == 0 {
bfs(i, j)
ans++
}
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int closedIsland(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length, ans = 0;
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
int[][] dirs = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
// Flood fill boundary
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) for (int j : new int[]{0, n-1}) if (grid[i][j] == 0) bfs(grid, i, j, dirs);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) for (int i : new int[]{0, m-1}) if (grid[i][j] == 0) bfs(grid, i, j, dirs);
// Count closed islands
for (int i = 1; i < m-1; i++) for (int j = 1; j < n-1; j++) if (grid[i][j] == 0) { bfs(grid, i, j, dirs); ans++; }
return ans;
}
void bfs(int[][] grid, int x, int y, int[][] dirs) {
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[]{x, y});
grid[x][y] = 1;
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = q.poll();
for (int[] d : dirs) {
int ni = cur[0] + d[0], nj = cur[1] + d[1];
if (ni >= 0 && ni < m && nj >= 0 && nj < n && grid[ni][nj] == 0) {
grid[ni][nj] = 1;
q.offer(new int[]{ni, nj});
}
}
}
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun closedIsland(grid: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = grid.size
val n = grid[0].size
val dirs = arrayOf(0 to 1, 1 to 0, 0 to -1, -1 to 0)
fun bfs(x: Int, y: Int) {
val q = ArrayDeque<Pair<Int, Int>>()
q.add(x to y)
grid[x][y] = 1
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val (i, j) = q.removeFirst()
for ((dx, dy) in dirs) {
val ni = i + dx
val nj = j + dy
if (ni in 0 until m && nj in 0 until n && grid[ni][nj] == 0) {
grid[ni][nj] = 1
q.add(ni to nj)
}
}
}
}
for (i in 0 until m) {
if (grid[i][0] == 0) bfs(i, 0)
if (grid[i][n-1] == 0) bfs(i, n-1)
}
for (j in 0 until n) {
if (grid[0][j] == 0) bfs(0, j)
if (grid[m-1][j] == 0) bfs(m-1, j)
}
var ans = 0
for (i in 1 until m-1) for (j in 1 until n-1) if (grid[i][j] == 0) { bfs(i, j); ans++ }
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def closedIsland(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> int:
from collections import deque
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs = [(0,1),(1,0),(0,-1),(-1,0)]
def bfs(x, y):
q = deque([(x, y)])
grid[x][y] = 1
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
for dx, dy in dirs:
ni, nj = i+dx, j+dy
if 0 <= ni < m and 0 <= nj < n and grid[ni][nj] == 0:
grid[ni][nj] = 1
q.append((ni, nj))
for i in range(m):
if grid[i][0] == 0: bfs(i, 0)
if grid[i][n-1] == 0: bfs(i, n-1)
for j in range(n):
if grid[0][j] == 0: bfs(0, j)
if grid[m-1][j] == 0: bfs(m-1, j)
ans = 0
for i in range(1, m-1):
for j in range(1, n-1):
if grid[i][j] == 0:
bfs(i, j)
ans += 1
return ans
Rust
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
pub fn closed_island(mut grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let dirs = [(0,1),(1,0),(0,-1),(-1,0)];
let mut bfs = |x: usize, y: usize, grid: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>| {
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
q.push_back((x, y));
grid[x][y] = 1;
while let Some((i, j)) = q.pop_front() {
for (dx, dy) in dirs.iter() {
let ni = i as i32 + dx;
let nj = j as i32 + dy;
if ni >= 0 && ni < m as i32 && nj >= 0 && nj < n as i32 && grid[ni as usize][nj as usize] == 0 {
grid[ni as usize][nj as usize] = 1;
q.push_back((ni as usize, nj as usize));
}
}
}
};
for i in 0..m {
if grid[i][0] == 0 { bfs(i, 0, &mut grid); }
if grid[i][n-1] == 0 { bfs(i, n-1, &mut grid); }
}
for j in 0..n {
if grid[0][j] == 0 { bfs(0, j, &mut grid); }
if grid[m-1][j] == 0 { bfs(m-1, j, &mut grid); }
}
let mut ans = 0;
for i in 1..m-1 {
for j in 1..n-1 {
if grid[i][j] == 0 {
bfs(i, j, &mut grid);
ans += 1;
}
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
closedIsland(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
const dirs = [[0,1],[1,0],[0,-1],[-1,0]];
const bfs = (x: number, y: number) => {
const q: [number, number][] = [[x, y]];
grid[x][y] = 1;
while (q.length) {
const [i, j] = q.shift()!;
for (const [dx, dy] of dirs) {
const ni = i + dx, nj = j + dy;
if (ni >= 0 && ni < m && nj >= 0 && nj < n && grid[ni][nj] === 0) {
grid[ni][nj] = 1;
q.push([ni, nj]);
}
}
}
};
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] === 0) bfs(i, 0);
if (grid[i][n-1] === 0) bfs(i, n-1);
}
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[0][j] === 0) bfs(0, j);
if (grid[m-1][j] === 0) bfs(m-1, j);
}
let ans = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < m-1; i++) for (let j = 1; j < n-1; j++) if (grid[i][j] === 0) { bfs(i, j); ans++; }
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n), since each cell is visited at most once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m * n), for the queue and visited marking