Number of Ships in a Rectangle
Problem
(This problem is aninteractive problem.)
Each ship is located at an integer point on the sea represented by a cartesian plane, and each integer point may contain at most 1 ship.
You have a function Sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft) which takes two points as arguments and returns true If there is at least one ship in the rectangle represented by the two points, including on the boundary.
Given two points: the top right and bottom left corners of a rectangle, return the number of ships present in that rectangle. It is guaranteed that there are at most 10 ships in that rectangle.
Submissions making more than 400 calls to hasShips will be judged Wrong Answer. Also, any solutions that attempt to circumvent the judge will result in disqualification.
Examples
Example 1:
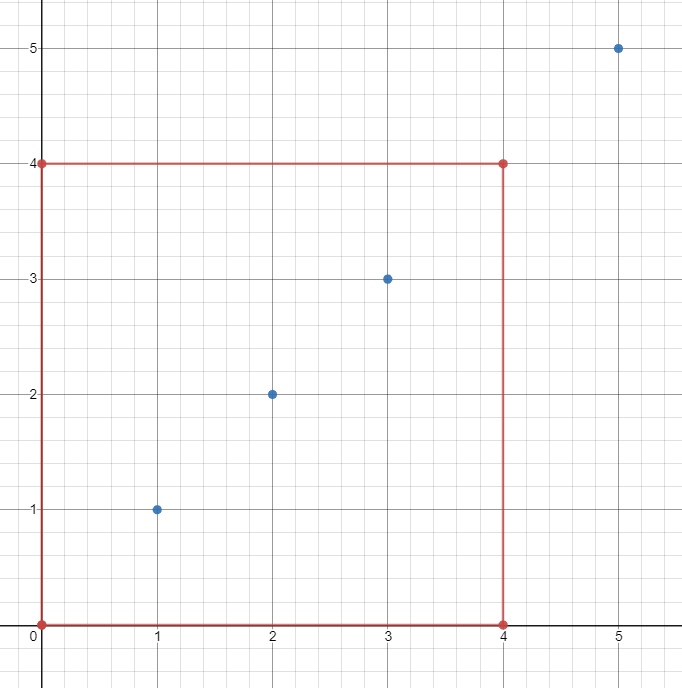
Input: ships = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3],[5,5]], topRight = [4,4], bottomLeft = [0,0]
Output: 3
Explanation: From [0,0] to [4,4] we can count 3 ships within the range.
Example 2:
Input: ans = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]], topRight = [1000,1000], bottomLeft = [0,0]
Output: 3
Constraints:
- On the input
shipsis only given to initialize the map internally. You must solve this problem "blindfolded". In other words, you must find the answer using the givenhasShipsAPI, without knowing theshipsposition. 0 <= bottomLeft[0] <= topRight[0] <= 10000 <= bottomLeft[1] <= topRight[1] <= 1000topRight != bottomLeft
Solution
Method 1 – Divide and Conquer (Quad Tree)
Intuition
Since the number of ships is small and the area is large, we use divide and conquer. We recursively split the rectangle into four smaller rectangles and use the hasShips API to prune empty regions. If a region is a single point and has a ship, we count it. This minimizes the number of API calls.
Approach
- If
hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft)is false, return 0. - If
topRight == bottomLeft, return 1 (there is a ship at this point). - Otherwise, split the rectangle into four smaller rectangles by dividing both x and y in half.
- Recursively count ships in each subrectangle and sum the results.
- Return the total count.
Code
C++
// This is the Sea's API interface.
// class Sea {
// public:
// bool hasShips(vector<int> topRight, vector<int> bottomLeft);
// };
class Solution {
public:
int countShips(Sea sea, vector<int> topRight, vector<int> bottomLeft) {
if (!sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft)) return 0;
if (topRight == bottomLeft) return 1;
int midx = (topRight[0] + bottomLeft[0]) / 2;
int midy = (topRight[1] + bottomLeft[1]) / 2;
int ans = 0;
// bottomLeft
vector<int> bl = bottomLeft, tr = {midx, midy};
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1])
ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl);
// bottomRight
bl = {midx+1, bottomLeft[1]}, tr = {topRight[0], midy};
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1])
ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl);
// topLeft
bl = {bottomLeft[0], midy+1}, tr = {midx, topRight[1]};
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1])
ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl);
// topRight
bl = {midx+1, midy+1}, tr = topRight;
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1])
ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl);
return ans;
}
};
Go
// type Sea interface {
// HasShips(topRight, bottomLeft []int) bool
// }
func countShips(sea Sea, topRight, bottomLeft []int) int {
if !sea.HasShips(topRight, bottomLeft) {
return 0
}
if topRight[0] == bottomLeft[0] && topRight[1] == bottomLeft[1] {
return 1
}
midx := (topRight[0] + bottomLeft[0]) / 2
midy := (topRight[1] + bottomLeft[1]) / 2
ans := 0
// bottomLeft
bl, tr := []int{bottomLeft[0], bottomLeft[1]}, []int{midx, midy}
if bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1] {
ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl)
}
// bottomRight
bl, tr = []int{midx+1, bottomLeft[1]}, []int{topRight[0], midy}
if bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1] {
ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl)
}
// topLeft
bl, tr = []int{bottomLeft[0], midy+1}, []int{midx, topRight[1]}
if bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1] {
ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl)
}
// topRight
bl, tr = []int{midx+1, midy+1}, topRight
if bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1] {
ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl)
}
return ans
}
Java
// This is Sea's API interface.
// interface Sea {
// boolean hasShips(int[] topRight, int[] bottomLeft);
// }
class Solution {
public int countShips(Sea sea, int[] topRight, int[] bottomLeft) {
if (!sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft)) return 0;
if (topRight[0] == bottomLeft[0] && topRight[1] == bottomLeft[1]) return 1;
int midx = (topRight[0] + bottomLeft[0]) / 2;
int midy = (topRight[1] + bottomLeft[1]) / 2;
int ans = 0;
int[] bl, tr;
// bottomLeft
bl = new int[]{bottomLeft[0], bottomLeft[1]}; tr = new int[]{midx, midy};
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl);
// bottomRight
bl = new int[]{midx+1, bottomLeft[1]}; tr = new int[]{topRight[0], midy};
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl);
// topLeft
bl = new int[]{bottomLeft[0], midy+1}; tr = new int[]{midx, topRight[1]};
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl);
// topRight
bl = new int[]{midx+1, midy+1}; tr = new int[]{topRight[0], topRight[1]};
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl);
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
// interface Sea {
// fun hasShips(topRight: IntArray, bottomLeft: IntArray): Boolean
// }
class Solution {
fun countShips(sea: Sea, topRight: IntArray, bottomLeft: IntArray): Int {
if (!sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft)) return 0
if (topRight[0] == bottomLeft[0] && topRight[1] == bottomLeft[1]) return 1
val midx = (topRight[0] + bottomLeft[0]) / 2
val midy = (topRight[1] + bottomLeft[1]) / 2
var ans = 0
var bl: IntArray; var tr: IntArray
bl = intArrayOf(bottomLeft[0], bottomLeft[1]); tr = intArrayOf(midx, midy)
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl)
bl = intArrayOf(midx+1, bottomLeft[1]); tr = intArrayOf(topRight[0], midy)
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl)
bl = intArrayOf(bottomLeft[0], midy+1); tr = intArrayOf(midx, topRight[1])
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl)
bl = intArrayOf(midx+1, midy+1); tr = intArrayOf(topRight[0], topRight[1])
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += countShips(sea, tr, bl)
return ans
}
}
Python
# This is Sea's API interface.
# class Sea:
# def hasShips(self, topRight: List[int], bottomLeft: List[int]) -> bool:
class Solution:
def countShips(self, sea: 'Sea', topRight: list[int], bottomLeft: list[int]) -> int:
if not sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft):
return 0
if topRight == bottomLeft:
return 1
midx = (topRight[0] + bottomLeft[0]) // 2
midy = (topRight[1] + bottomLeft[1]) // 2
ans = 0
# bottomLeft
bl, tr = [bottomLeft[0], bottomLeft[1]], [midx, midy]
if bl[0] <= tr[0] and bl[1] <= tr[1]:
ans += self.countShips(sea, tr, bl)
# bottomRight
bl, tr = [midx+1, bottomLeft[1]], [topRight[0], midy]
if bl[0] <= tr[0] and bl[1] <= tr[1]:
ans += self.countShips(sea, tr, bl)
# topLeft
bl, tr = [bottomLeft[0], midy+1], [midx, topRight[1]]
if bl[0] <= tr[0] and bl[1] <= tr[1]:
ans += self.countShips(sea, tr, bl)
# topRight
bl, tr = [midx+1, midy+1], [topRight[0], topRight[1]]
if bl[0] <= tr[0] and bl[1] <= tr[1]:
ans += self.countShips(sea, tr, bl)
return ans
Rust
// This is Sea's API interface.
// struct Sea;
// impl Sea {
// fn has_ships(&self, top_right: Vec<i32>, bottom_left: Vec<i32>) -> bool;
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn count_ships(sea: &Sea, top_right: Vec<i32>, bottom_left: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
if !sea.has_ships(top_right.clone(), bottom_left.clone()) { return 0; }
if top_right == bottom_left { return 1; }
let midx = (top_right[0] + bottom_left[0]) / 2;
let midy = (top_right[1] + bottom_left[1]) / 2;
let mut ans = 0;
let mut bl; let mut tr;
bl = vec![bottom_left[0], bottom_left[1]]; tr = vec![midx, midy];
if bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1] { ans += Solution::count_ships(sea, tr.clone(), bl.clone()); }
bl = vec![midx+1, bottom_left[1]]; tr = vec![top_right[0], midy];
if bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1] { ans += Solution::count_ships(sea, tr.clone(), bl.clone()); }
bl = vec![bottom_left[0], midy+1]; tr = vec![midx, top_right[1]];
if bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1] { ans += Solution::count_ships(sea, tr.clone(), bl.clone()); }
bl = vec![midx+1, midy+1]; tr = vec![top_right[0], top_right[1]];
if bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1] { ans += Solution::count_ships(sea, tr.clone(), bl.clone()); }
ans
}
}
TypeScript
// interface Sea {
// hasShips(topRight: number[], bottomLeft: number[]): boolean;
// }
class Solution {
countShips(sea: Sea, topRight: number[], bottomLeft: number[]): number {
if (!sea.hasShips(topRight, bottomLeft)) return 0;
if (topRight[0] === bottomLeft[0] && topRight[1] === bottomLeft[1]) return 1;
const midx = Math.floor((topRight[0] + bottomLeft[0]) / 2);
const midy = Math.floor((topRight[1] + bottomLeft[1]) / 2);
let ans = 0;
let bl: number[], tr: number[];
bl = [bottomLeft[0], bottomLeft[1]]; tr = [midx, midy];
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += this.countShips(sea, tr, bl);
bl = [midx+1, bottomLeft[1]]; tr = [topRight[0], midy];
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += this.countShips(sea, tr, bl);
bl = [bottomLeft[0], midy+1]; tr = [midx, topRight[1]];
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += this.countShips(sea, tr, bl);
bl = [midx+1, midy+1]; tr = [topRight[0], topRight[1]];
if (bl[0] <= tr[0] && bl[1] <= tr[1]) ans += this.countShips(sea, tr, bl);
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(s log A), wheresis the number of ships andAis the area of the rectangle. Each ship is found inO(log A)recursive calls. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(log A), for the recursion stack.