Number of Spaces Cleaning Robot Cleaned
Problem
A room is represented by a 0-indexed 2D binary matrix room where a 0
represents an empty space and a 1 represents a space with an object.
The top left corner of the room will be empty in all test cases.
A cleaning robot starts at the top left corner of the room and is facing right. The robot will continue heading straight until it reaches the edge of the room or it hits an object, after which it will turn 90 degrees clockwise and repeat this process. The starting space and all spaces that the robot visits are cleaned by it.
Return the number ofclean spaces in the room if the robot runs indefinitely.
Examples
Example 1:
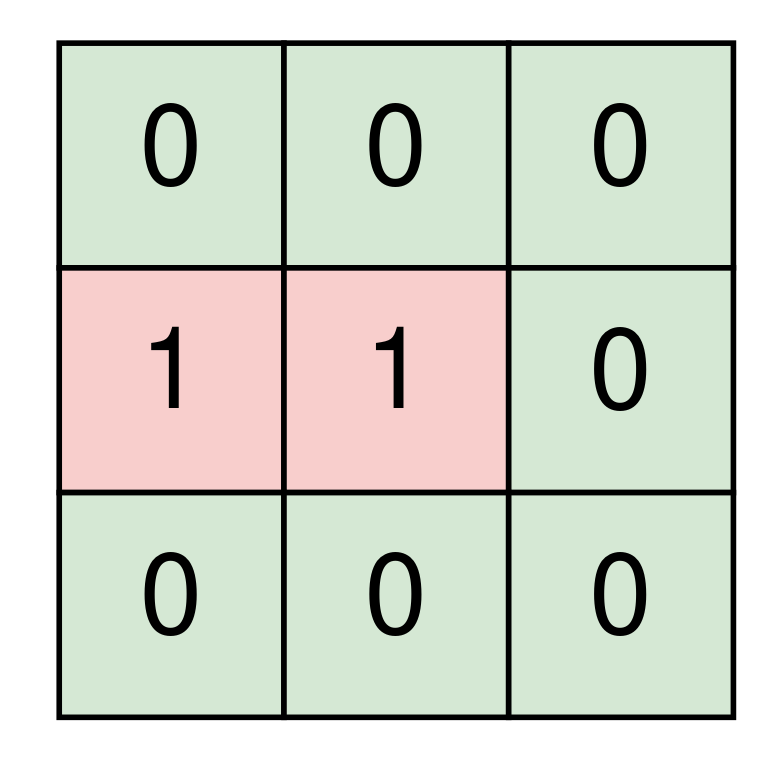
Input: room = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: 7
Explanation:
1. The robot cleans the spaces at (0, 0), (0, 1), and (0, 2).
2. The robot is at the edge of the room, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces down.
3. The robot cleans the spaces at (1, 2), and (2, 2).
4. The robot is at the edge of the room, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces left.
5. The robot cleans the spaces at (2, 1), and (2, 0).
6. The robot has cleaned all 7 empty spaces, so return 7.
Example 2:
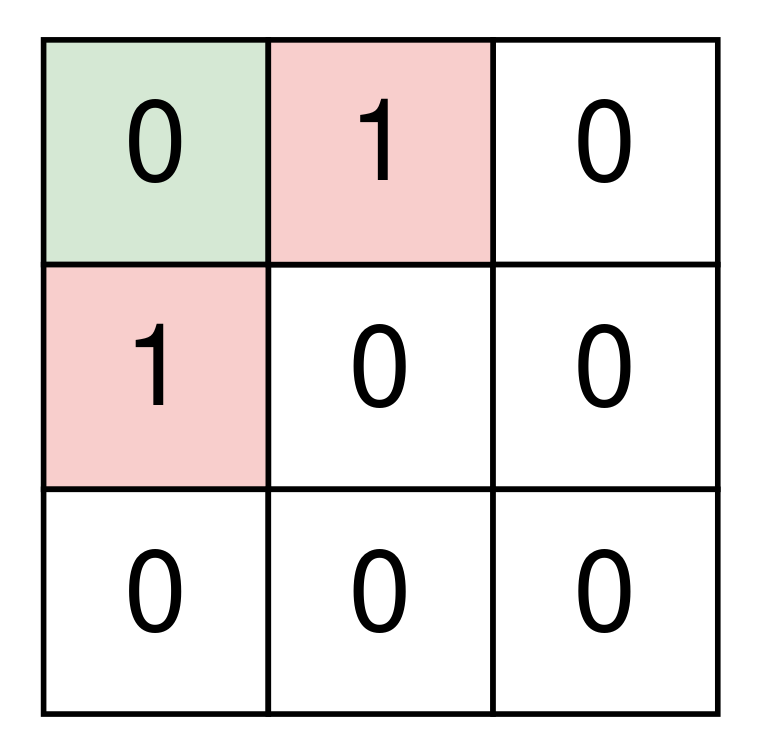
Input: room = [[0,1,0],[1,0,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: 1
Explanation:
1. The robot cleans the space at (0, 0).
2. The robot hits an object, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces down.
3. The robot hits an object, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces left.
4. The robot is at the edge of the room, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces up.
5. The robot is at the edge of the room, so it turns 90 degrees clockwise and now faces right.
6. The robot is back at its starting position.
7. The robot has cleaned 1 space, so return 1.
Example 3:
Input: room = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: 8
Constraints:
m == room.lengthn == room[r].length1 <= m, n <= 300room[r][c]is either0or1.room[0][0] == 0
Solution
Method 1 – Simulation with Visited Set
Intuition
The robot moves in a deterministic way: it goes straight until it can't, then turns right. It may revisit the same state (position and direction), causing a loop. We simulate the robot's movement, marking each cleaned cell, and stop if the robot returns to a previously visited (position, direction) state. The answer is the number of unique cleaned cells.
Approach
- Use a set to track visited (row, col, direction) states to detect cycles.
- Use a set to track cleaned (row, col) cells.
- Start at (0,0) facing right (direction 0: right, 1: down, 2: left, 3: up).
- At each step:
- Mark the current cell as cleaned.
- Try to move forward; if blocked or out of bounds, turn right.
- If the (row, col, direction) is seen before, break (cycle detected).
- Return the number of unique cleaned cells.
Code
C++
#include <vector>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int numberOfCleanRooms(vector<vector<int>>& room) {
int m = room.size(), n = room[0].size();
set<tuple<int,int,int>> vis;
set<pair<int,int>> cleaned;
int dirs[4][2] = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
int r = 0, c = 0, d = 0;
while (!vis.count({r,c,d})) {
vis.insert({r,c,d});
cleaned.insert({r,c});
int nr = r + dirs[d][0], nc = c + dirs[d][1];
if (nr<0||nr>=m||nc<0||nc>=n||room[nr][nc]==1) d = (d+1)%4;
else { r = nr; c = nc; }
}
return cleaned.size();
}
};
Go
func numberOfCleanRooms(room [][]int) int {
m, n := len(room), len(room[0])
dirs := [][2]int{{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}
vis := make(map[[3]int]bool)
cleaned := make(map[[2]int]bool)
r, c, d := 0, 0, 0
for !vis[[3]int{r,c,d}] {
vis[[3]int{r,c,d}] = true
cleaned[[2]int{r,c}] = true
nr, nc := r+dirs[d][0], c+dirs[d][1]
if nr<0||nr>=m||nc<0||nc>=n||room[nr][nc]==1 {
d = (d+1)%4
} else {
r, c = nr, nc
}
}
return len(cleaned)
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int numberOfCleanRooms(int[][] room) {
int m = room.length, n = room[0].length;
Set<String> vis = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> cleaned = new HashSet<>();
int[][] dirs = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
int r = 0, c = 0, d = 0;
while (vis.add(r+","+c+","+d)) {
cleaned.add(r+","+c);
int nr = r+dirs[d][0], nc = c+dirs[d][1];
if (nr<0||nr>=m||nc<0||nc>=n||room[nr][nc]==1) d = (d+1)%4;
else { r = nr; c = nc; }
}
return cleaned.size();
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun numberOfCleanRooms(room: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = room.size
val n = room[0].size
val dirs = arrayOf(intArrayOf(0,1), intArrayOf(1,0), intArrayOf(0,-1), intArrayOf(-1,0))
val vis = mutableSetOf<Triple<Int,Int,Int>>()
val cleaned = mutableSetOf<Pair<Int,Int>>()
var r = 0; var c = 0; var d = 0
while (vis.add(Triple(r,c,d))) {
cleaned.add(Pair(r,c))
val nr = r+dirs[d][0]; val nc = c+dirs[d][1]
if (nr<0||nr>=m||nc<0||nc>=n||room[nr][nc]==1) d = (d+1)%4
else { r = nr; c = nc }
}
return cleaned.size
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def numberOfCleanRooms(self, room: list[list[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(room), len(room[0])
dirs = [(0,1),(1,0),(0,-1),(-1,0)]
vis = set()
cleaned = set()
r = c = d = 0
while (r,c,d) not in vis:
vis.add((r,c,d))
cleaned.add((r,c))
nr, nc = r+dirs[d][0], c+dirs[d][1]
if nr<0 or nr>=m or nc<0 or nc>=n or room[nr][nc]==1:
d = (d+1)%4
else:
r, c = nr, nc
return len(cleaned)
Rust
use std::collections::HashSet;
impl Solution {
pub fn number_of_clean_rooms(room: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = room.len();
let n = room[0].len();
let dirs = [(0,1),(1,0),(0,-1),(-1,0)];
let mut vis = HashSet::new();
let mut cleaned = HashSet::new();
let (mut r, mut c, mut d) = (0,0,0);
while vis.insert((r,c,d)) {
cleaned.insert((r,c));
let (nr, nc) = (r+dirs[d].0, c+dirs[d].1);
if nr<0||nr>=m||nc<0||nc>=n||room[nr][nc]==1 {
d = (d+1)%4;
} else {
r = nr; c = nc;
}
}
cleaned.len() as i32
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
numberOfCleanRooms(room: number[][]): number {
const m = room.length, n = room[0].length;
const dirs = [[0,1],[1,0],[0,-1],[-1,0]];
const vis = new Set<string>();
const cleaned = new Set<string>();
let r = 0, c = 0, d = 0;
while (!vis.has(`${r},${c},${d}`)) {
vis.add(`${r},${c},${d}`);
cleaned.add(`${r},${c}`);
const nr = r+dirs[d][0], nc = c+dirs[d][1];
if (nr<0||nr>=m||nc<0||nc>=n||room[nr][nc]===1) d = (d+1)%4;
else { r = nr; c = nc; }
}
return cleaned.size;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m*n), wheremandnare the dimensions of the room. Each state (row, col, dir) is visited at most once, and there are at most4*m*nstates. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m*n), for the visited and cleaned sets.