Number Of Ways To Reconstruct A Tree
Problem
You are given an array pairs, where pairs[i] = [xi, yi], and:
- There are no duplicates.
xi < yi
Let ways be the number of rooted trees that satisfy the following conditions:
- The tree consists of nodes whose values appeared in
pairs. - A pair
[xi, yi]exists inpairsif and only ifxiis an ancestor ofyioryiis an ancestor ofxi. - Note: the tree does not have to be a binary tree.
Two ways are considered to be different if there is at least one node that has different parents in both ways.
Return:
0ifways == 01ifways == 12ifways > 1
A rooted tree is a tree that has a single root node, and all edges are oriented to be outgoing from the root.
An ancestor of a node is any node on the path from the root to that node (excluding the node itself). The root has no ancestors.
Examples
Example 1
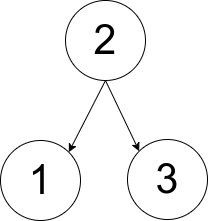
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3]]
Output: 1
Explanation: There is exactly one valid rooted tree, which is shown in the above figure.
Example 2
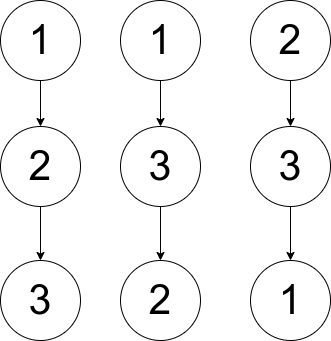
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3],[1,3]]
Output: 2
Explanation: There are multiple valid rooted trees. Three of them are shown in the above figures.
Example 3
Input: pairs = [[1,2],[2,3],[2,4],[1,5]]
Output: 0
Explanation: There are no valid rooted trees.
Constraints
1 <= pairs.length <= 10^51 <= xi < yi <= 500- The elements in
pairsare unique.
Solution
Method 1 – Graph Degree and Subset Checking
Intuition
We need to reconstruct a rooted tree from ancestor-descendant pairs. The root must be the node connected to all others. For each node, its parent must be the node with the smallest degree among its neighbors that contains all its neighbors as a subset. If multiple such parents exist, there are multiple ways. If any check fails, return 0.
Approach
- Build the adjacency list for all nodes.
- The root is the node with degree n-1 (connected to all others).
- For each node (except root), find the neighbor with the smallest degree that contains all its neighbors as a subset—this is its parent.
- If multiple such parents exist, set result to 2.
- If any node cannot find a valid parent, return 0.
- Return 1 if unique, 2 if multiple ways.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int checkWays(vector<vector<int>>& pairs) {
unordered_map<int, unordered_set<int>> g;
for (auto& p : pairs) {
g[p[0]].insert(p[1]);
g[p[1]].insert(p[0]);
}
int res = 1, n = g.size();
for (auto& [x, s] : g) {
if (s.size() == n-1) goto root_found;
}
return 0;
root_found:
for (auto& [x, s] : g) {
if (s.size() == n-1) continue;
int par = -1, min_deg = INT_MAX, cnt = 0;
for (int y : s) {
if (g[y].size() >= s.size() && g[y].size() < min_deg) {
bool ok = true;
for (int z : s) if (z != y && !g[y].count(z)) ok = false;
if (ok) {
min_deg = g[y].size();
par = y;
cnt = 1;
} else if (ok && g[y].size() == min_deg) cnt++;
}
}
if (par == -1) return 0;
if (cnt > 1) res = 2;
}
return res;
}
};
Go
func checkWays(pairs [][]int) int {
g := map[int]map[int]struct{}{}
for _, p := range pairs {
if g[p[0]] == nil { g[p[0]] = map[int]struct{}{} }
if g[p[1]] == nil { g[p[1]] = map[int]struct{}{} }
g[p[0]][p[1]] = struct{}{}
g[p[1]][p[0]] = struct{}{}
}
n := len(g)
rootFound := false
for _, s := range g {
if len(s) == n-1 { rootFound = true; break }
}
if !rootFound { return 0 }
res := 1
for x, s := range g {
if len(s) == n-1 { continue }
par, minDeg, cnt := -1, 1<<30, 0
for y := range s {
if len(g[y]) >= len(s) && len(g[y]) < minDeg {
ok := true
for z := range s {
if z != y {
if _, f := g[y][z]; !f { ok = false }
}
}
if ok {
minDeg = len(g[y])
par = y
cnt = 1
} else if ok && len(g[y]) == minDeg {
cnt++
}
}
}
if par == -1 { return 0 }
if cnt > 1 { res = 2 }
}
return res
}
Java
class Solution {
public int checkWays(int[][] pairs) {
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> g = new HashMap<>();
for (int[] p : pairs) {
g.computeIfAbsent(p[0], k -> new HashSet<>()).add(p[1]);
g.computeIfAbsent(p[1], k -> new HashSet<>()).add(p[0]);
}
int n = g.size(), res = 1;
boolean rootFound = false;
for (Set<Integer> s : g.values()) {
if (s.size() == n-1) { rootFound = true; break; }
}
if (!rootFound) return 0;
for (int x : g.keySet()) {
Set<Integer> s = g.get(x);
if (s.size() == n-1) continue;
int par = -1, minDeg = Integer.MAX_VALUE, cnt = 0;
for (int y : s) {
if (g.get(y).size() >= s.size() && g.get(y).size() < minDeg) {
boolean ok = true;
for (int z : s) if (z != y && !g.get(y).contains(z)) ok = false;
if (ok) {
minDeg = g.get(y).size();
par = y;
cnt = 1;
} else if (ok && g.get(y).size() == minDeg) cnt++;
}
}
if (par == -1) return 0;
if (cnt > 1) res = 2;
}
return res;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun checkWays(pairs: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val g = mutableMapOf<Int, MutableSet<Int>>()
for (p in pairs) {
g.computeIfAbsent(p[0]) { mutableSetOf() }.add(p[1])
g.computeIfAbsent(p[1]) { mutableSetOf() }.add(p[0])
}
val n = g.size
var res = 1
if (g.values.none { it.size == n-1 }) return 0
for ((x, s) in g) {
if (s.size == n-1) continue
var par = -1
var minDeg = Int.MAX_VALUE
var cnt = 0
for (y in s) {
if (g[y]!!.size >= s.size && g[y]!!.size < minDeg) {
var ok = true
for (z in s) if (z != y && !g[y]!!.contains(z)) ok = false
if (ok) {
minDeg = g[y]!!.size
par = y
cnt = 1
} else if (ok && g[y]!!.size == minDeg) cnt++
}
}
if (par == -1) return 0
if (cnt > 1) res = 2
}
return res
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def checkWays(self, pairs: list[list[int]]) -> int:
from collections import defaultdict
g: dict[int, set[int]] = defaultdict(set)
for x, y in pairs:
g[x].add(y)
g[y].add(x)
n = len(g)
if not any(len(s) == n-1 for s in g.values()):
return 0
res = 1
for x, s in g.items():
if len(s) == n-1:
continue
par, min_deg, cnt = -1, float('inf'), 0
for y in s:
if len(g[y]) >= len(s) and len(g[y]) < min_deg:
ok = all(z == y or z in g[y] for z in s)
if ok:
min_deg = len(g[y])
par = y
cnt = 1
elif ok and len(g[y]) == min_deg:
cnt += 1
if par == -1:
return 0
if cnt > 1:
res = 2
return res
Rust
use std::collections::{HashMap, HashSet};
impl Solution {
pub fn check_ways(pairs: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let mut g: HashMap<i32, HashSet<i32>> = HashMap::new();
for p in pairs.iter() {
g.entry(p[0]).or_default().insert(p[1]);
g.entry(p[1]).or_default().insert(p[0]);
}
let n = g.len();
if !g.values().any(|s| s.len() == n-1) { return 0; }
let mut res = 1;
for (x, s) in g.iter() {
if s.len() == n-1 { continue; }
let mut par = -1;
let mut min_deg = usize::MAX;
let mut cnt = 0;
for &y in s.iter() {
if g[&y].len() >= s.len() && g[&y].len() < min_deg {
let ok = s.iter().all(|&z| z == y || g[&y].contains(&z));
if ok {
min_deg = g[&y].len();
par = y;
cnt = 1;
} else if ok && g[&y].len() == min_deg {
cnt += 1;
}
}
}
if par == -1 { return 0; }
if cnt > 1 { res = 2; }
}
res
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
checkWays(pairs: number[][]): number {
const g: Record<number, Set<number>> = {}
for (const [x, y] of pairs) {
if (!g[x]) g[x] = new Set()
if (!g[y]) g[y] = new Set()
g[x].add(y)
g[y].add(x)
}
const n = Object.keys(g).length
if (!Object.values(g).some(s => s.size === n-1)) return 0
let res = 1
for (const x in g) {
const s = g[x]
if (s.size === n-1) continue
let par = -1, minDeg = Infinity, cnt = 0
for (const y of s) {
if (g[y].size >= s.size && g[y].size < minDeg) {
let ok = true
for (const z of s) if (z !== y && !g[y].has(z)) ok = false
if (ok) {
minDeg = g[y].size
par = y
cnt = 1
} else if (ok && g[y].size === minDeg) cnt++
}
}
if (par === -1) return 0
if (cnt > 1) res = 2
}
return res
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^2), where n is the number of unique nodes (since each node can have up to n neighbors and we check subsets). - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n^2), for the adjacency sets.