Out of Boundary Paths
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Out of Boundary Paths Problem
Problem
There is an m x n grid with a ball. The ball is initially at the position [startRow, startColumn]. You are allowed to move the ball to one of the four adjacent cells in the grid (possibly out of the grid crossing the grid boundary). You can apply at most maxMove moves to the ball.
Given the five integers m, n, maxMove, startRow, startColumn, return the number of paths to move the ball out of the grid boundary. Since the answer can be very large, return it modulo 10^9 + 7.
Examples
Example 1:
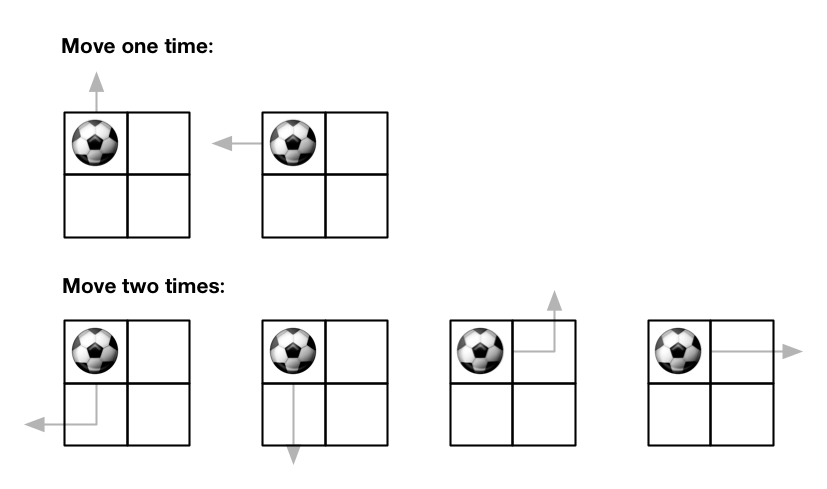
Input:
m = 2, n = 2, maxMove = 2, startRow = 0, startColumn = 0
Output:
6
Example 2:
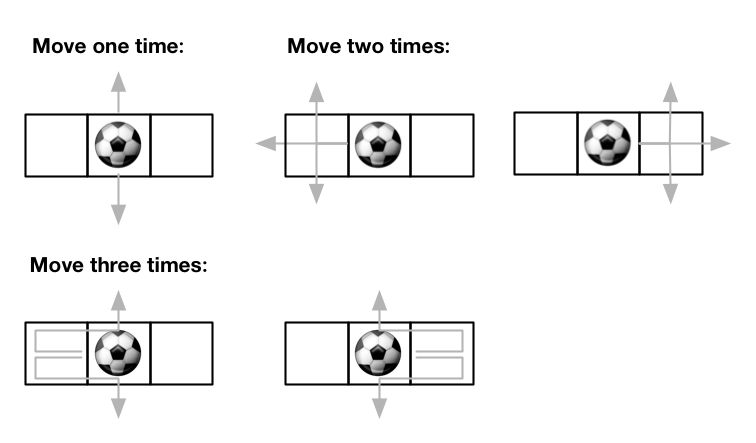
Input:
m = 1, n = 3, maxMove = 3, startRow = 0, startColumn = 1
Output:
12
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming (Top-Down Memoization) 1
Intuition
We use dynamic programming to count the number of ways to move the ball out of the grid. For each position and move count, we recursively try all four directions, and use memoization to avoid recomputation.
Approach
- Define a recursive function
dp(move, row, col)that returns the number of ways to move the ball out of the grid from position(row, col)withmovemoves left. - If the ball is out of bounds, return 1.
- If no moves left, return 0.
- Use memoization to cache results for each
(move, row, col). - Try all four directions (up, down, left, right) and sum the results.
- Start the recursion from the initial position and
maxMove.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
int findPaths(int m, int n, int maxMove, int startRow, int startColumn) {
vector<vector<vector<int>>> memo(maxMove+1, vector<vector<int>>(m, vector<int>(n, -1)));
function<int(int,int,int)> dp = [&](int move, int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n) return 1;
if (move == 0) return 0;
if (memo[move][r][c] != -1) return memo[move][r][c];
int ans = 0;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r-1, c)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r+1, c)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c-1)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c+1)) % MOD;
return memo[move][r][c] = ans;
};
return dp(maxMove, startRow, startColumn);
}
};
Go
func findPaths(m, n, maxMove, startRow, startColumn int) int {
MOD := int(1e9 + 7)
memo := make([][][]int, maxMove+1)
for i := range memo {
memo[i] = make([][]int, m)
for j := range memo[i] {
memo[i][j] = make([]int, n)
for k := range memo[i][j] {
memo[i][j][k] = -1
}
}
}
var dp func(move, r, c int) int
dp = func(move, r, c int) int {
if r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n {
return 1
}
if move == 0 {
return 0
}
if memo[move][r][c] != -1 {
return memo[move][r][c]
}
ans := 0
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r-1, c)) % MOD
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r+1, c)) % MOD
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c-1)) % MOD
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c+1)) % MOD
memo[move][r][c] = ans
return ans
}
return dp(maxMove, startRow, startColumn)
}
Java
class Solution {
int MOD = 1000000007;
Integer[][][] memo;
public int findPaths(int m, int n, int maxMove, int startRow, int startColumn) {
memo = new Integer[maxMove+1][m][n];
return dp(maxMove, startRow, startColumn, m, n);
}
int dp(int move, int r, int c, int m, int n) {
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n) return 1;
if (move == 0) return 0;
if (memo[move][r][c] != null) return memo[move][r][c];
int ans = 0;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r-1, c, m, n)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r+1, c, m, n)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c-1, m, n)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c+1, m, n)) % MOD;
return memo[move][r][c] = ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
val MOD = 1000000007
lateinit var memo: Array<Array<Array<Int?>>>
fun findPaths(m: Int, n: Int, maxMove: Int, startRow: Int, startColumn: Int): Int {
memo = Array(maxMove+1) { Array(m) { Array<Int?>(n) { null } } }
return dp(maxMove, startRow, startColumn, m, n)
}
fun dp(move: Int, r: Int, c: Int, m: Int, n: Int): Int {
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n) return 1
if (move == 0) return 0
memo[move][r][c]?.let { return it }
var ans = 0
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r-1, c, m, n)) % MOD
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r+1, c, m, n)) % MOD
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c-1, m, n)) % MOD
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c+1, m, n)) % MOD
memo[move][r][c] = ans
return ans
}
}
Python
def findPaths(m: int, n: int, maxMove: int, startRow: int, startColumn: int) -> int:
MOD = 10**9 + 7
from functools import lru_cache
@lru_cache(None)
def dp(move: int, r: int, c: int) -> int:
if r < 0 or r >= m or c < 0 or c >= n:
return 1
if move == 0:
return 0
ans = 0
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r-1, c)) % MOD
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r+1, c)) % MOD
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c-1)) % MOD
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c+1)) % MOD
return ans
return dp(maxMove, startRow, startColumn)
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn find_paths(m: i32, n: i32, max_move: i32, start_row: i32, start_column: i32) -> i32 {
const MOD: i32 = 1_000_000_007;
use std::collections::HashMap;
fn dp(move: i32, r: i32, c: i32, m: i32, n: i32, memo: &mut HashMap<(i32,i32,i32),i32>) -> i32 {
if r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n { return 1; }
if move == 0 { return 0; }
if let Some(&v) = memo.get(&(move,r,c)) { return v; }
let mut ans = 0;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r-1, c, m, n, memo)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r+1, c, m, n, memo)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c-1, m, n, memo)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c+1, m, n, memo)) % MOD;
memo.insert((move,r,c), ans);
ans
}
let mut memo = HashMap::new();
dp(max_move, start_row, start_column, m, n, &mut memo)
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
findPaths(m: number, n: number, maxMove: number, startRow: number, startColumn: number): number {
const MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const memo: number[][][] = Array.from({length: maxMove+1}, () => Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(-1)));
const dp = (move: number, r: number, c: number): number => {
if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n) return 1;
if (move === 0) return 0;
if (memo[move][r][c] !== -1) return memo[move][r][c];
let ans = 0;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r-1, c)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r+1, c)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c-1)) % MOD;
ans = (ans + dp(move-1, r, c+1)) % MOD;
memo[move][r][c] = ans;
return ans;
};
return dp(maxMove, startRow, startColumn);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(maxMove * m * n), since each state is computed once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(maxMove * m * n), for memoization table.