Parallel Courses II
Problem
You are given an integer n, which indicates that there are n courses labeled from 1 to n. You are also given an array relations where
relations[i] = [prevCoursei, nextCoursei], representing a prerequisite relationship between course prevCoursei and course nextCoursei: course
prevCoursei has to be taken before course nextCoursei. Also, you are given the integer k.
In one semester, you can take at most k courses as long as you have taken all the prerequisites in the previous semesters for the courses you are taking.
Return theminimum number of semesters needed to take all courses. The testcases will be generated such that it is possible to take every course.
Examples
Example 1
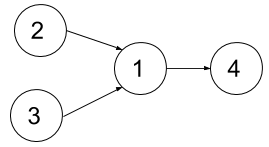
Input: n = 4, relations = [[2,1],[3,1],[1,4]], k = 2
Output: 3
Explanation: The figure above represents the given graph.
In the first semester, you can take courses 2 and 3.
In the second semester, you can take course 1.
In the third semester, you can take course 4.
Example 2
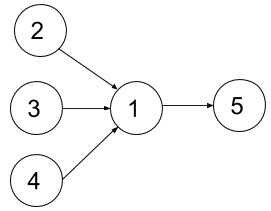
Input: n = 5, relations = [[2,1],[3,1],[4,1],[1,5]], k = 2
Output: 4
Explanation: The figure above represents the given graph.
In the first semester, you can only take courses 2 and 3 since you cannot take more than two per semester.
In the second semester, you can take course 4.
In the third semester, you can take course 1.
In the fourth semester, you can take course 5.
Constraints
1 <= n <= 151 <= k <= n0 <= relations.length <= n * (n-1) / 2relations[i].length == 21 <= prevCoursei, nextCoursei <= nprevCoursei != nextCoursei- All the pairs
[prevCoursei, nextCoursei]are unique. - The given graph is a directed acyclic graph.
Solution
Method 1 – Bitmask Dynamic Programming
Intuition
Since n is small (≤ 15), we can use bitmask DP to represent the set of courses taken. For each state, we try all subsets of available courses (up to k at a time) that can be taken in the next semester, and recursively compute the minimum number of semesters needed.
Approach
- For each course, build a bitmask of its prerequisites.
- Use a DP array where
dp[mask]is the minimum semesters needed to finish all courses inmask. - For each state, find all courses whose prerequisites are satisfied and not yet taken.
- Try all subsets of these available courses of size ≤ k, and update the DP for the new state.
- Use memoization to avoid recomputation.
- The answer is
dp[full_mask]where all courses are taken.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minNumberOfSemesters(int n, vector<vector<int>>& relations, int k) {
vector<int> pre(n, 0);
for (auto& r : relations) pre[r[1]-1] |= 1 << (r[0]-1);
vector<int> dp(1<<n, n+1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<n); ++mask) {
int avail = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if ((mask & (1<<i)) == 0 && (mask & pre[i]) == pre[i])
avail |= 1<<i;
for (int sub = avail; sub; sub = (sub-1)&avail) {
if (__builtin_popcount(sub) > k) continue;
dp[mask|sub] = min(dp[mask|sub], dp[mask]+1);
}
}
return dp[(1<<n)-1];
}
};
Go
func minNumberOfSemesters(n int, relations [][]int, k int) int {
pre := make([]int, n)
for _, r := range relations {
pre[r[1]-1] |= 1 << (r[0]-1)
}
dp := make([]int, 1<<n)
for i := range dp { dp[i] = n+1 }
dp[0] = 0
for mask := 0; mask < (1<<n); mask++ {
avail := 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if (mask&(1<<i)) == 0 && (mask&pre[i]) == pre[i] {
avail |= 1 << i
}
}
for sub := avail; sub > 0; sub = (sub-1)&avail {
if bits.OnesCount(uint(sub)) > k { continue }
if dp[mask|sub] > dp[mask]+1 {
dp[mask|sub] = dp[mask]+1
}
}
}
return dp[(1<<n)-1]
}
Java
class Solution {
public int minNumberOfSemesters(int n, int[][] relations, int k) {
int[] pre = new int[n];
for (int[] r : relations) pre[r[1]-1] |= 1 << (r[0]-1);
int[] dp = new int[1<<n];
Arrays.fill(dp, n+1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<n); mask++) {
int avail = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if ((mask & (1<<i)) == 0 && (mask & pre[i]) == pre[i])
avail |= 1<<i;
for (int sub = avail; sub > 0; sub = (sub-1)&avail) {
if (Integer.bitCount(sub) > k) continue;
dp[mask|sub] = Math.min(dp[mask|sub], dp[mask]+1);
}
}
return dp[(1<<n)-1];
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minNumberOfSemesters(n: Int, relations: Array<IntArray>, k: Int): Int {
val pre = IntArray(n)
for (r in relations) pre[r[1]-1] = pre[r[1]-1] or (1 shl (r[0]-1))
val dp = IntArray(1 shl n) { n+1 }
dp[0] = 0
for (mask in 0 until (1 shl n)) {
var avail = 0
for (i in 0 until n)
if ((mask and (1 shl i)) == 0 && (mask and pre[i]) == pre[i])
avail = avail or (1 shl i)
var sub = avail
while (sub > 0) {
if (Integer.bitCount(sub) <= k)
dp[mask or sub] = minOf(dp[mask or sub], dp[mask]+1)
sub = (sub-1) and avail
}
}
return dp[(1 shl n)-1]
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minNumberOfSemesters(self, n: int, relations: list[list[int]], k: int) -> int:
pre = [0] * n
for u, v in relations:
pre[v-1] |= 1 << (u-1)
dp = [n+1] * (1<<n)
dp[0] = 0
for mask in range(1<<n):
avail = 0
for i in range(n):
if not (mask & (1<<i)) and (mask & pre[i]) == pre[i]:
avail |= 1<<i
sub = avail
while sub:
if bin(sub).count('1') <= k:
dp[mask|sub] = min(dp[mask|sub], dp[mask]+1)
sub = (sub-1)&avail
return dp[(1<<n)-1]
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_number_of_semesters(n: i32, relations: Vec<Vec<i32>>, k: i32) -> i32 {
let n = n as usize;
let k = k as usize;
let mut pre = vec![0; n];
for r in relations.iter() {
pre[r[1] as usize - 1] |= 1 << (r[0] as usize - 1);
}
let mut dp = vec![n+1; 1<<n];
dp[0] = 0;
for mask in 0..(1<<n) {
let mut avail = 0;
for i in 0..n {
if (mask & (1<<i)) == 0 && (mask & pre[i]) == pre[i] {
avail |= 1<<i;
}
}
let mut sub = avail;
while sub > 0 {
if sub.count_ones() as usize <= k {
dp[mask|sub] = dp[mask|sub].min(dp[mask]+1);
}
sub = (sub-1)&avail;
}
}
dp[(1<<n)-1]
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minNumberOfSemesters(n: number, relations: number[][], k: number): number {
const pre: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
for (const [u, v] of relations) pre[v-1] |= 1 << (u-1);
const dp: number[] = Array(1<<n).fill(n+1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (let mask = 0; mask < (1<<n); mask++) {
let avail = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
if ((mask & (1<<i)) === 0 && (mask & pre[i]) === pre[i])
avail |= 1<<i;
for (let sub = avail; sub > 0; sub = (sub-1)&avail) {
if (sub.toString(2).split('1').length-1 > k) continue;
dp[mask|sub] = Math.min(dp[mask|sub], dp[mask]+1);
}
}
return dp[(1<<n)-1];
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n * 2^n + 2^n * C(n, k)), where n is the number of courses. For each state, we try all subsets of available courses (up to k at a time). - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(2^n), for the DP array.