Partition Array Into Two Arrays to Minimize Sum Difference
HardUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given an integer array nums of 2 * n integers. You need to
partition nums into two arrays of length n to minimize the absolute
difference of the sums of the arrays. To partition nums, put each
element of nums into one of the two arrays.
Return theminimum possible absolute difference.
Examples
Example 1:
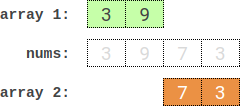
Input: nums = [3,9,7,3]
Output: 2
Explanation: One optimal partition is: [3,9] and [7,3].
The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((3 + 9) - (7 + 3)) = 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-36,36]
Output: 72
Explanation: One optimal partition is: [-36] and [36].
The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((-36) - (36)) = 72.
Example 3:
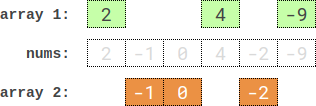
Input: nums = [2,-1,0,4,-2,-9]
Output: 0
Explanation: One optimal partition is: [2,4,-9] and [-1,0,-2].
The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((2 + 4 + -9) - (-1 + 0 + -2)) = 0.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 15nums.length == 2 * n-107 <= nums[i] <= 107
Solution
Method 1 – Meet in the Middle + Subset Sums
Intuition
The problem is a variant of the partition problem. Since n ≤ 15, we can split the array into two halves and enumerate all subset sums for each half, then use binary search to find the closest sum pair that balances the two halves.
Approach
- Split nums into left and right halves of size n.
- For each half, generate all possible subset sums for picking k elements (k = 0..n).
- For each possible split (k elements from left, n-k from right), try all combinations and use binary search to minimize the absolute difference.
- Return the minimum difference found.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minimumDifference(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size() / 2;
vector<int> left(nums.begin(), nums.begin()+n), right(nums.begin()+n, nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> lsum(n+1), rsum(n+1);
function<void(const vector<int>&, vector<vector<int>>&)> gen = [&](const vector<int>& arr, vector<vector<int>>& sums) {
int m = arr.size();
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<m); ++mask) {
int cnt = __builtin_popcount(mask), s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) if (mask & (1<<i)) s += arr[i];
sums[cnt].push_back(s);
}
};
gen(left, lsum); gen(right, rsum);
for (int k = 0; k <= n; ++k) sort(rsum[k].begin(), rsum[k].end());
int res = INT_MAX, total = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);
for (int k = 0; k <= n; ++k) {
for (int a : lsum[k]) {
int btarget = (total/2) - a;
auto& rv = rsum[n-k];
auto it = lower_bound(rv.begin(), rv.end(), btarget);
for (int d = -1; d <= 0; ++d) {
auto jt = it + d;
if (jt >= rv.begin() && jt < rv.end()) {
int b = *jt;
int sum1 = a + b, sum2 = total - sum1;
res = min(res, abs(sum1 - sum2));
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
Go
import "sort"
func minimumDifference(nums []int) int {
n := len(nums)/2
left, right := nums[:n], nums[n:]
lsum := make([][]int, n+1)
rsum := make([][]int, n+1)
for mask := 0; mask < 1<<n; mask++ {
lc, rc, ls, rs := 0, 0, 0, 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if mask&(1<<i) > 0 { lc++; ls += left[i] }
if mask&(1<<i) > 0 { rc++; rs += right[i] }
}
lsum[lc] = append(lsum[lc], ls)
rsum[rc] = append(rsum[rc], rs)
}
for k := 0; k <= n; k++ { sort.Ints(rsum[k]) }
res, total := 1<<31-1, 0
for _, v := range nums { total += v }
for k := 0; k <= n; k++ {
for _, a := range lsum[k] {
btarget := total/2 - a
rv := rsum[n-k]
i := sort.SearchInts(rv, btarget)
for d := -1; d <= 0; d++ {
j := i + d
if j >= 0 && j < len(rv) {
b := rv[j]
sum1 := a + b
sum2 := total - sum1
if abs(sum1-sum2) < res { res = abs(sum1-sum2) }
}
}
}
}
return res
}
func abs(x int) int { if x < 0 { return -x }; return x }
Java
class Solution {
public int minimumDifference(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length / 2;
int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, n), right = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, n, 2*n);
List<List<Integer>> lsum = new ArrayList<>(), rsum = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { lsum.add(new ArrayList<>()); rsum.add(new ArrayList<>()); }
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1<<n); mask++) {
int lc = 0, rc = 0, ls = 0, rs = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if ((mask & (1<<i)) > 0) { lc++; ls += left[i]; }
if ((mask & (1<<i)) > 0) { rc++; rs += right[i]; }
}
lsum.get(lc).add(ls);
rsum.get(rc).add(rs);
}
for (int k = 0; k <= n; k++) Collections.sort(rsum.get(k));
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE, total = 0;
for (int v : nums) total += v;
for (int k = 0; k <= n; k++) {
for (int a : lsum.get(k)) {
int btarget = total/2 - a;
List<Integer> rv = rsum.get(n-k);
int i = Collections.binarySearch(rv, btarget);
if (i < 0) i = -i-1;
for (int d = -1; d <= 0; d++) {
int j = i + d;
if (j >= 0 && j < rv.size()) {
int b = rv.get(j);
int sum1 = a + b, sum2 = total - sum1;
res = Math.min(res, Math.abs(sum1 - sum2));
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minimumDifference(nums: IntArray): Int {
val n = nums.size / 2
val left = nums.sliceArray(0 until n)
val right = nums.sliceArray(n until 2*n)
val lsum = Array(n+1) { mutableListOf<Int>() }
val rsum = Array(n+1) { mutableListOf<Int>() }
for (mask in 0 until (1 shl n)) {
var lc = 0; var rc = 0; var ls = 0; var rs = 0
for (i in 0 until n) {
if ((mask and (1 shl i)) > 0) { lc++; ls += left[i] }
if ((mask and (1 shl i)) > 0) { rc++; rs += right[i] }
}
lsum[lc].add(ls)
rsum[rc].add(rs)
}
for (k in 0..n) rsum[k].sort()
var res = Int.MAX_VALUE
val total = nums.sum()
for (k in 0..n) {
for (a in lsum[k]) {
val btarget = total/2 - a
val rv = rsum[n-k]
val i = rv.binarySearch(btarget).let { if (it < 0) -it-1 else it }
for (d in -1..0) {
val j = i + d
if (j in rv.indices) {
val b = rv[j]
val sum1 = a + b
val sum2 = total - sum1
res = minOf(res, kotlin.math.abs(sum1-sum2))
}
}
}
}
return res
}
}
Python
from bisect import bisect_left
class Solution:
def minimumDifference(self, nums: list[int]) -> int:
n = len(nums)//2
left, right = nums[:n], nums[n:]
lsum = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
rsum = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
for mask in range(1<<n):
lc = rc = ls = rs = 0
for i in range(n):
if mask & (1<<i):
lc += 1; ls += left[i]
rc += 1; rs += right[i]
lsum[lc].append(ls)
rsum[rc].append(rs)
for k in range(n+1): rsum[k].sort()
res = float('inf')
total = sum(nums)
for k in range(n+1):
for a in lsum[k]:
btarget = total//2 - a
rv = rsum[n-k]
i = bisect_left(rv, btarget)
for d in [-1, 0]:
j = i + d
if 0 <= j < len(rv):
b = rv[j]
sum1 = a + b
sum2 = total - sum1
res = min(res, abs(sum1-sum2))
return res
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn minimum_difference(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let n = nums.len()/2;
let (left, right) = (&nums[..n], &nums[n..]);
let mut lsum = vec![vec![]; n+1];
let mut rsum = vec![vec![]; n+1];
for mask in 0..(1<<n) {
let (mut lc, mut rc, mut ls, mut rs) = (0, 0, 0, 0);
for i in 0..n {
if (mask & (1<<i)) > 0 {
lc += 1; ls += left[i];
rc += 1; rs += right[i];
}
}
lsum[lc].push(ls);
rsum[rc].push(rs);
}
for k in 0..=n { rsum[k].sort(); }
let total: i32 = nums.iter().sum();
let mut res = i32::MAX;
for k in 0..=n {
for &a in &lsum[k] {
let btarget = total/2 - a;
let rv = &rsum[n-k];
let i = rv.binary_search(&btarget).unwrap_or_else(|x| x);
for d in [-1, 0] {
let j = i as isize + d;
if j >= 0 && (j as usize) < rv.len() {
let b = rv[j as usize];
let sum1 = a + b;
let sum2 = total - sum1;
res = res.min((sum1-sum2).abs());
}
}
}
}
res
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
minimumDifference(nums: number[]): number {
const n = nums.length/2;
const left = nums.slice(0, n), right = nums.slice(n);
const lsum: number[][] = Array.from({length: n+1}, () => []);
const rsum: number[][] = Array.from({length: n+1}, () => []);
for (let mask = 0; mask < (1<<n); mask++) {
let lc = 0, rc = 0, ls = 0, rs = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (mask & (1<<i)) { lc++; ls += left[i]; rc++; rs += right[i]; }
}
lsum[lc].push(ls);
rsum[rc].push(rs);
}
for (let k = 0; k <= n; k++) rsum[k].sort((a,b)=>a-b);
const total = nums.reduce((a,b)=>a+b,0);
let res = Infinity;
for (let k = 0; k <= n; k++) {
for (const a of lsum[k]) {
const btarget = Math.floor(total/2) - a;
const rv = rsum[n-k];
let i = rv.findIndex(x => x >= btarget);
if (i === -1) i = rv.length;
for (const d of [-1,0]) {
const j = i + d;
if (j >= 0 && j < rv.length) {
const b = rv[j];
const sum1 = a + b, sum2 = total - sum1;
res = Math.min(res, Math.abs(sum1-sum2));
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(2^n * n)wherenis half the array size (for subset generation and search). - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(2^n)for storing all subset sums.