Path Crossing
EasyUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a string path, where path[i] = 'N', 'S', 'E' or 'W', each representing moving one unit north, south, east, or west, respectively. You start at the origin (0, 0) on a 2D plane and walk on the path specified by
path.
Return true if the path crosses itself at any point, that is, if at any time you are on a location you have previously visited. Return false
otherwise.
Examples
Example 1
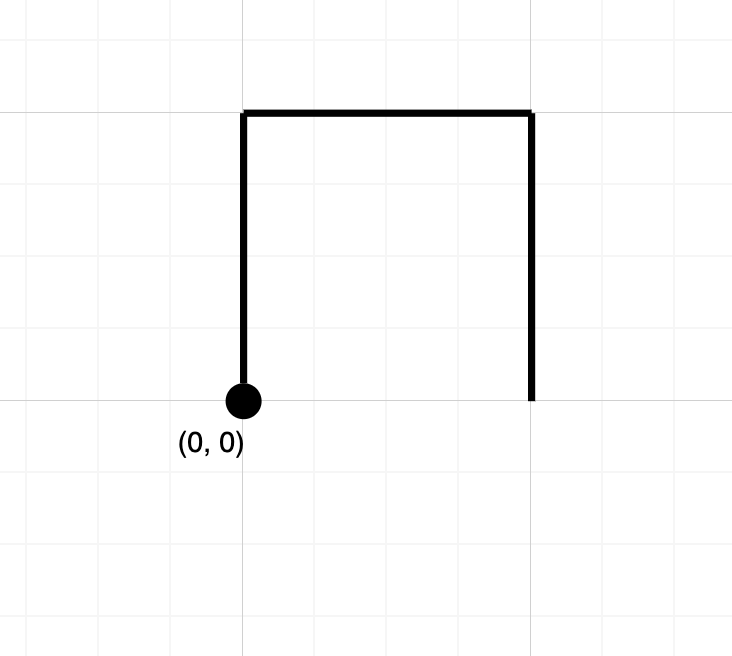
Input: path = "NES"
Output: false
Explanation: Notice that the path doesn't cross any point more than once.
Example 2
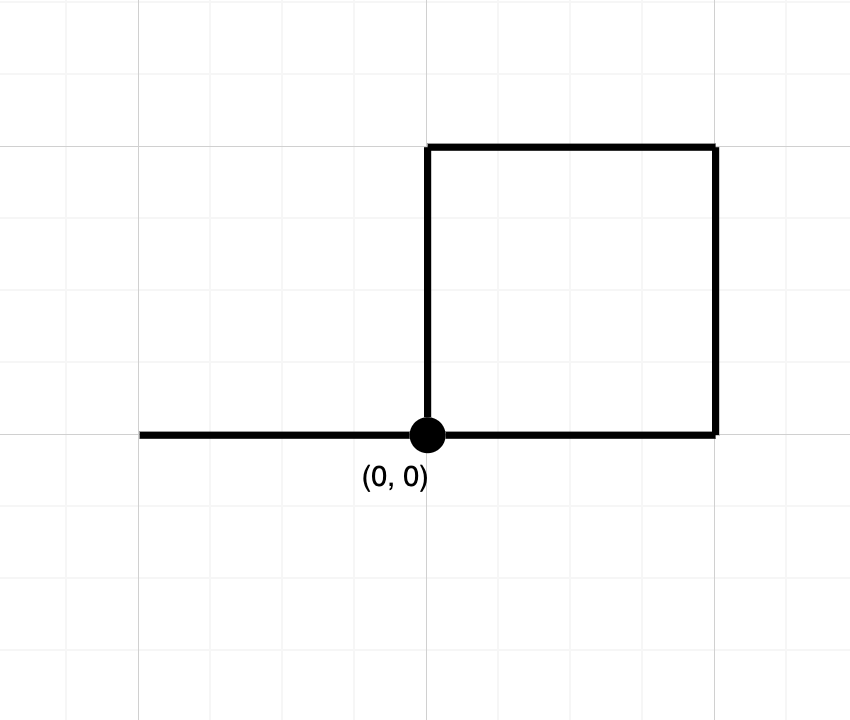
Input: path = "NESWW"
Output: true
Explanation: Notice that the path visits the origin twice.
Constraints
1 <= path.length <= 10^4path[i]is either'N','S','E', or'W'.
Solution
Method 1 - Hash Set for Visited Positions
Intuition
We simulate the walk on the 2D grid, keeping track of all visited positions in a set. If we ever visit a position we've already seen, the path crosses itself.
Approach
- Start at (0, 0) and add it to a set.
- For each character in
path, move in the corresponding direction and check if the new position is already in the set. - If yes, return true. If we finish the path without revisiting any position, return false.
Code
C++
#include <unordered_set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
bool isPathCrossing(string path) {
unordered_set<long long> seen;
int x = 0, y = 0;
seen.insert(0);
for (char c : path) {
if (c == 'N') ++y;
else if (c == 'S') --y;
else if (c == 'E') ++x;
else if (c == 'W') --x;
long long key = ((long long)x << 32) | (y & 0xffffffffLL);
if (seen.count(key)) return true;
seen.insert(key);
}
return false;
}
Go
func isPathCrossing(path string) bool {
seen := map[[2]int]bool{}
x, y := 0, 0
seen[[2]int{x, y}] = true
for _, c := range path {
switch c {
case 'N': y++
case 'S': y--
case 'E': x++
case 'W': x--
}
pos := [2]int{x, y}
if seen[pos] { return true }
seen[pos] = true
}
return false
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public boolean isPathCrossing(String path) {
Set<String> seen = new HashSet<>();
int x = 0, y = 0;
seen.add("0,0");
for (char c : path.toCharArray()) {
if (c == 'N') y++;
else if (c == 'S') y--;
else if (c == 'E') x++;
else if (c == 'W') x--;
String key = x + "," + y;
if (seen.contains(key)) return true;
seen.add(key);
}
return false;
}
}
Kotlin
fun isPathCrossing(path: String): Boolean {
val seen = mutableSetOf<Pair<Int, Int>>()
var x = 0; var y = 0
seen.add(0 to 0)
for (c in path) {
when (c) {
'N' -> y++
'S' -> y--
'E' -> x++
'W' -> x--
}
val pos = x to y
if (!seen.add(pos)) return true
}
return false
}
Python
def isPathCrossing(path: str) -> bool:
seen = set()
x = y = 0
seen.add((0, 0))
for c in path:
if c == 'N': y += 1
elif c == 'S': y -= 1
elif c == 'E': x += 1
elif c == 'W': x -= 1
if (x, y) in seen:
return True
seen.add((x, y))
return False
Rust
use std::collections::HashSet;
pub fn is_path_crossing(path: String) -> bool {
let mut seen = HashSet::new();
let (mut x, mut y) = (0, 0);
seen.insert((x, y));
for c in path.chars() {
match c {
'N' => y += 1,
'S' => y -= 1,
'E' => x += 1,
'W' => x -= 1,
_ => {}
}
if !seen.insert((x, y)) { return true; }
}
false
}
TypeScript
function isPathCrossing(path: string): boolean {
const seen = new Set<string>();
let x = 0, y = 0;
seen.add('0,0');
for (const c of path) {
if (c === 'N') y++;
else if (c === 'S') y--;
else if (c === 'E') x++;
else if (c === 'W') x--;
const key = `${x},${y}`;
if (seen.has(key)) return true;
seen.add(key);
}
return false;
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), wherenis the length of the path. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)for the set of visited positions.