Permutations of Array 2 - Array has duplicates
MediumUpdated: Sep 29, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a collection of numbers, nums, that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations in any order.
Examples
Example 1
Input: nums = [3,2,3]
Output: 3
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output:
[[1,1,2],
[1,2,1],
[2,1,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
Solution
Method 1 - Backtracking with frequency map
This is similar to [Permutations of Array 1](permutations-of-array-1). But the normal decision tree will not work.
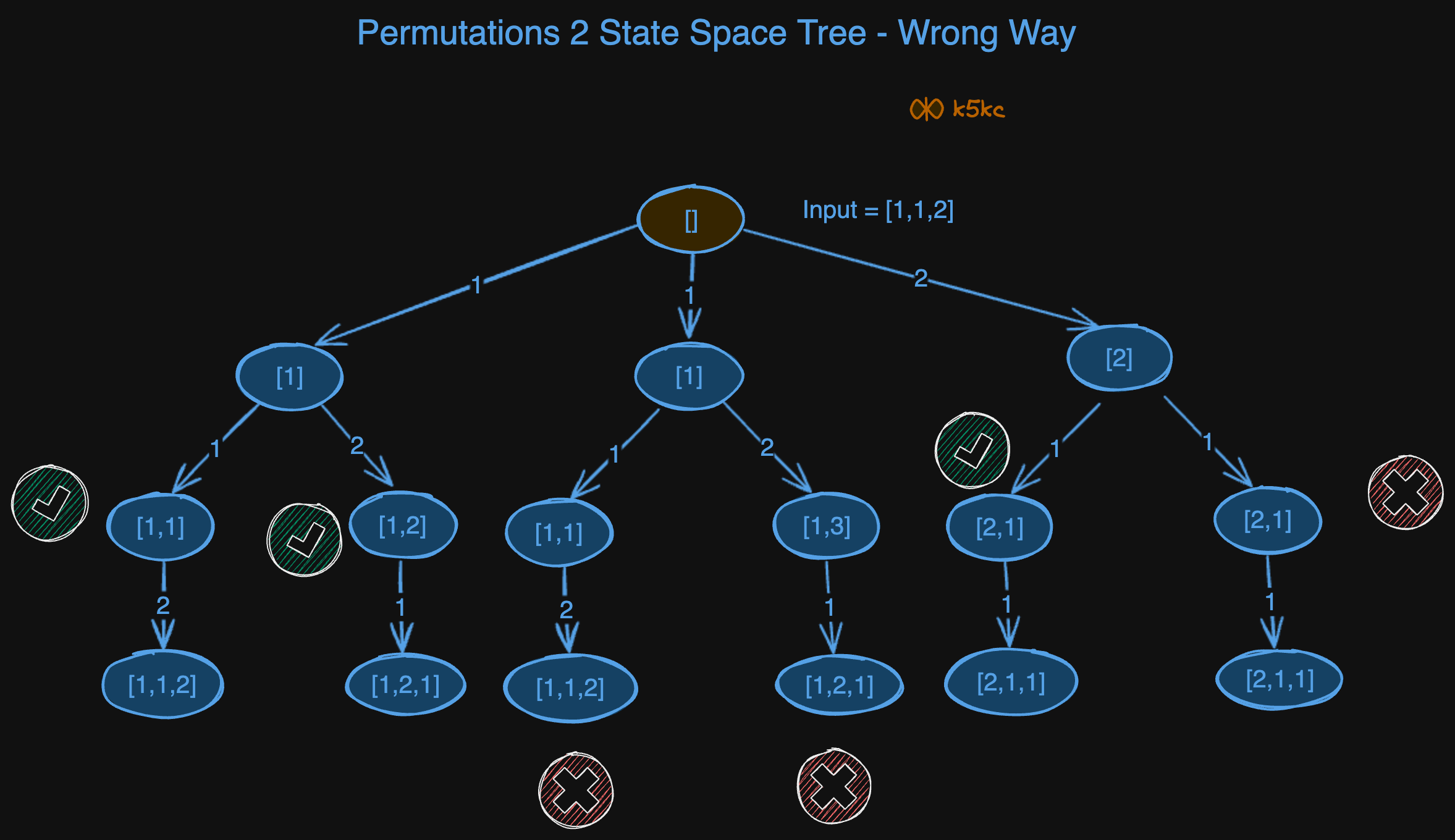
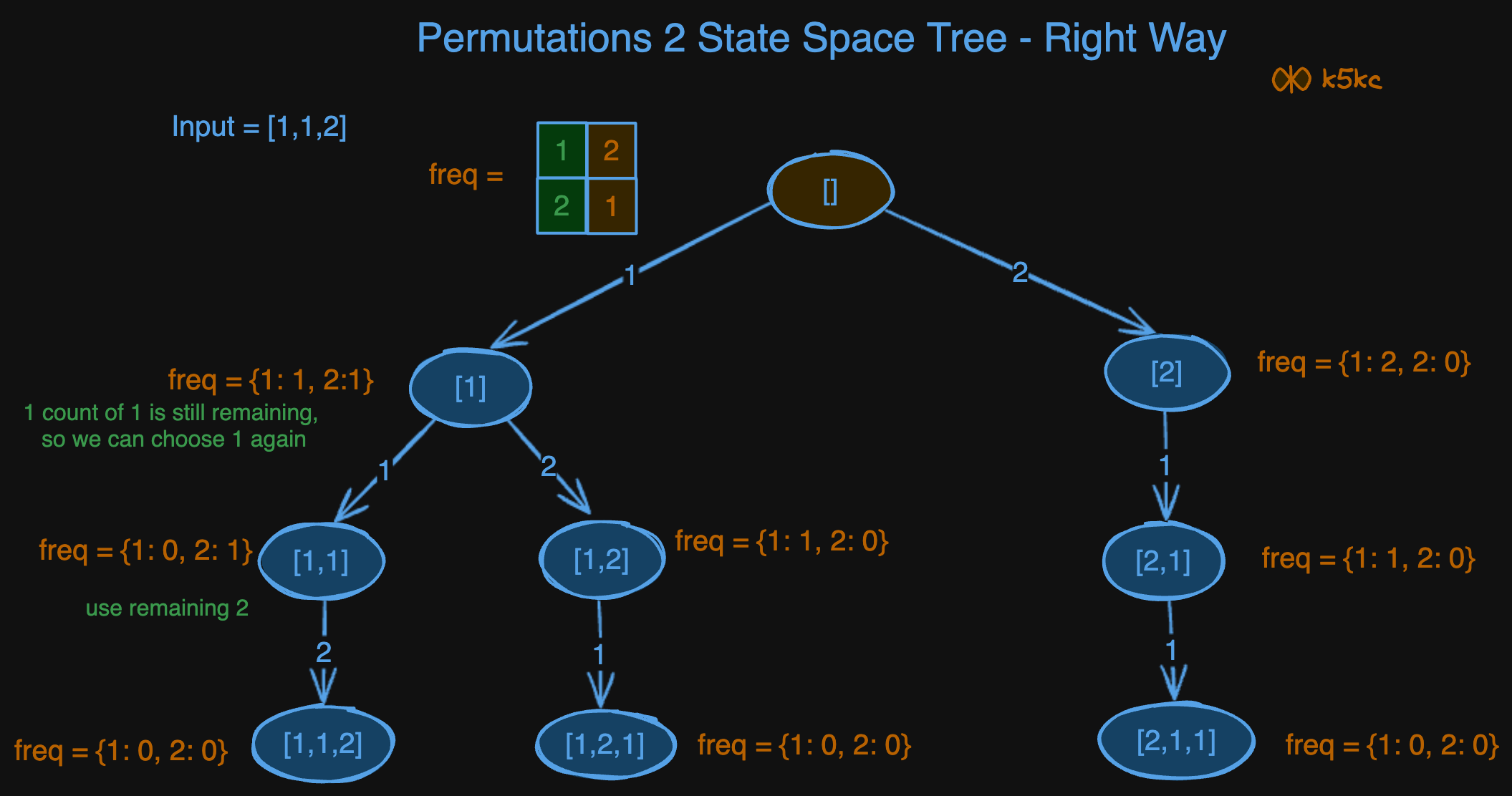
So, instead of array, we can use hashmap of frequency. This is our frequency map:
freq<num,count> = {1: 1, 2:1}
Now, decision tree will have 2 keys - [1, 2]. On the left side, we choose one 1 and one 2.
Final decision tree:
Code
Java
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> subAns = new ArrayList<>();
// frequency map
Map<Integer, Long> countMap = Arrays.stream(nums).boxed().
collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Integer::intValue, Collectors.counting()));
dfs(nums.length, countMap, subAns, ans);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(int numsLength, Map<Integer, Long> countMap, List<Integer> subAns, List<List<Integer>> ans) {
if (subAns.size() == numsLength) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(subAns));
return;
}
for(int num: countMap.keySet()){
if(countMap.get(num) > 0){
subAns.add(num);
countMap.put(num, countMap.get(num)-1);
dfs(numsLength, countMap, subAns, ans);
// undo
countMap.put(num, countMap.get(num)+1);
subAns.remove(subAns.size()-1);
}
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n*2^n) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)assuming recursion stack
Method 2 - Backtracking with visited array and sorting
Code
Java
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums, new boolean[nums.length]);
return list;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> tempList, int[] nums, boolean[] used) {
if (tempList.size() == nums.length) {
list.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i<nums.length; i++) {
if (used[i] || i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
tempList.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(list, tempList, nums, used);
used[i] = false;
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - 1);
}
}