Pizza With 3n Slices
HardUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
There is a pizza with 3n slices of varying size, you and your friends will take slices of pizza as follows:
- You will pick any pizza slice.
- Your friend Alice will pick the next slice in the anti-clockwise direction of your pick.
- Your friend Bob will pick the next slice in the clockwise direction of your pick.
- Repeat until there are no more slices of pizzas.
Given an integer array slices that represent the sizes of the pizza slices in a clockwise direction, return the maximum possible sum of slice sizes that you can pick.
Examples
Example 1
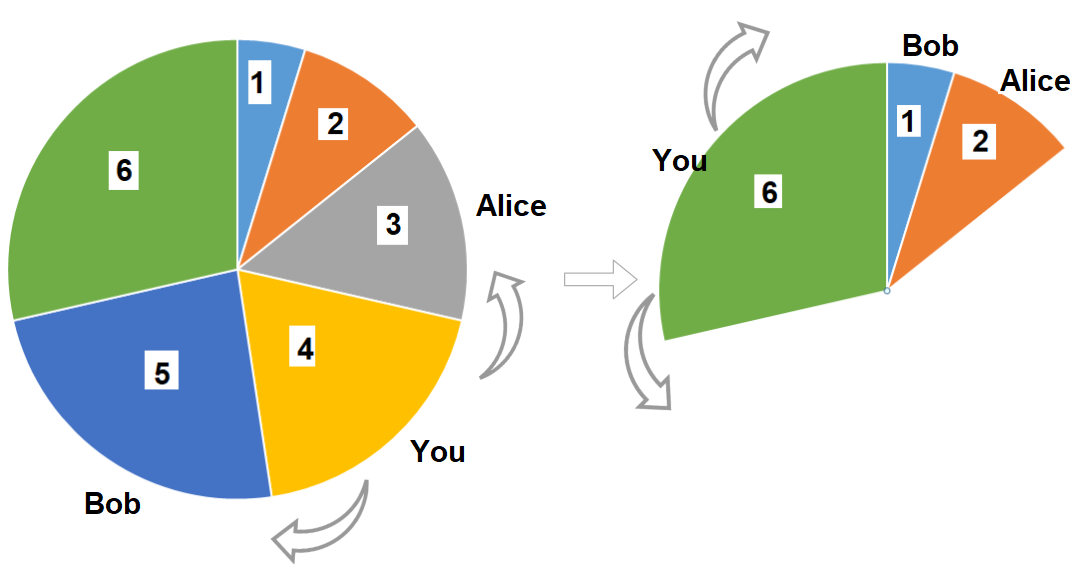
Input: slices = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: 10
Explanation: Pick pizza slice of size 4, Alice and Bob will pick slices with size 3 and 5 respectively. Then Pick slices with size 6, finally Alice and Bob will pick slice of size 2 and 1 respectively. Total = 4 + 6.
Example 2
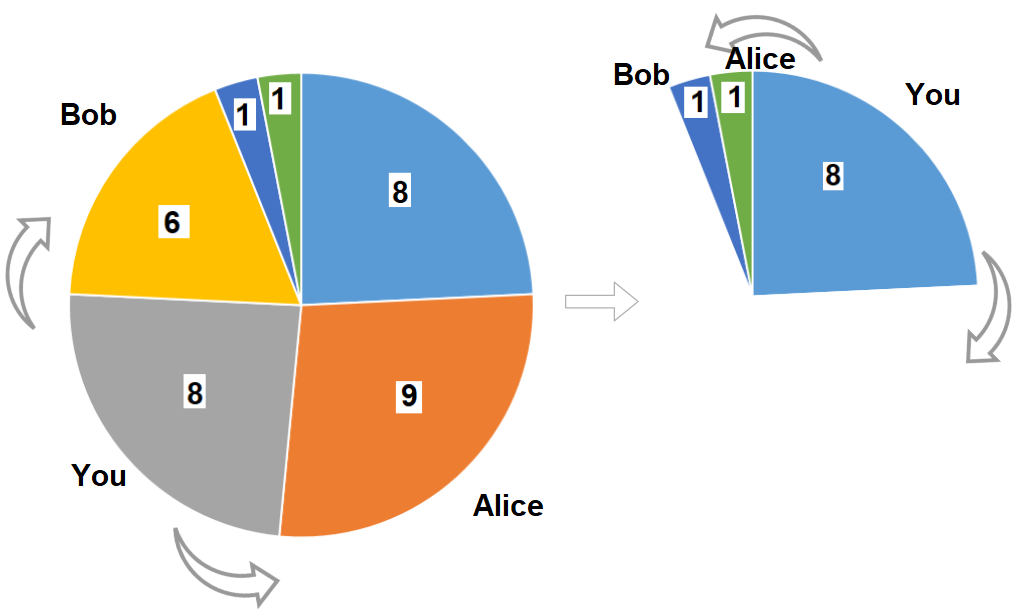
Input: slices = [8,9,8,6,1,1]
Output: 16
Explanation: Pick pizza slice of size 8 in each turn. If you pick slice with size 9 your partners will pick slices of size 8.
Constraints
3 * n == slices.length1 <= slices.length <= 5001 <= slices[i] <= 1000
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming with Circular Array
Intuition
Since the pizza is circular and you must pick n slices out of 3n, with no two picked slices adjacent, this is a variation of the "House Robber II" problem. We use dynamic programming to maximize the sum, considering two cases: exclude the first slice or exclude the last slice, to avoid picking both ends.
Approach
- Let n = slices.length / 3.
- Define a helper DP function to pick k slices from a linear array with no two adjacent.
- Run the DP for slices[0..n3-2] (exclude last) and slices[1..n3-1] (exclude first).
- Return the maximum of the two results.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxSizeSlices(vector<int>& slices) {
int n = slices.size() / 3;
auto dp = [&](vector<int>& arr) {
int m = arr.size();
vector<vector<int>> f(m+1, vector<int>(n+1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int k = 1; k <= n; ++k) {
f[i][k] = max(f[i-1][k], f[i-2][k-1] + arr[i-1]);
}
}
return f[m][n];
};
vector<int> a(slices.begin(), slices.end()-1), b(slices.begin()+1, slices.end());
return max(dp(a), dp(b));
}
};
Go
func maxSizeSlices(slices []int) int {
n := len(slices) / 3
dp := func(arr []int) int {
m := len(arr)
f := make([][]int, m+1)
for i := range f {
f[i] = make([]int, n+1)
}
for i := 1; i <= m; i++ {
for k := 1; k <= n; k++ {
f[i][k] = max(f[i-1][k], f[max(0,i-2)][k-1]+arr[i-1])
}
}
return f[m][n]
}
a := slices[:len(slices)-1]
b := slices[1:]
return max(dp(a), dp(b))
}
func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a }; return b }
Java
class Solution {
public int maxSizeSlices(int[] slices) {
int n = slices.length / 3;
return Math.max(dp(slices, 0, slices.length-2, n), dp(slices, 1, slices.length-1, n));
}
int dp(int[] arr, int l, int r, int k) {
int m = r-l+1;
int[][] f = new int[m+1][k+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i-1][j], f[Math.max(0,i-2)][j-1]+arr[l+i-1]);
}
}
return f[m][k];
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maxSizeSlices(slices: IntArray): Int {
val n = slices.size / 3
fun dp(arr: IntArray): Int {
val m = arr.size
val f = Array(m+1) { IntArray(n+1) }
for (i in 1..m) {
for (k in 1..n) {
f[i][k] = maxOf(f[i-1][k], f[maxOf(0,i-2)][k-1]+arr[i-1])
}
}
return f[m][n]
}
val a = slices.sliceArray(0 until slices.size-1)
val b = slices.sliceArray(1 until slices.size)
return maxOf(dp(a), dp(b))
}
}
Python
def maxSizeSlices(slices: list[int]) -> int:
def dp(arr: list[int], k: int) -> int:
m = len(arr)
f = [[0]*(k+1) for _ in range(m+1)]
for i in range(1, m+1):
for j in range(1, k+1):
f[i][j] = max(f[i-1][j], f[max(0,i-2)][j-1]+arr[i-1])
return f[m][k]
n = len(slices)//3
return max(dp(slices[:-1], n), dp(slices[1:], n))
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn max_size_slices(slices: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
fn dp(arr: &[i32], k: usize) -> i32 {
let m = arr.len();
let mut f = vec![vec![0; k+1]; m+1];
for i in 1..=m {
for j in 1..=k {
f[i][j] = f[i-1][j].max(f[i.saturating_sub(2)][j-1]+arr[i-1]);
}
}
f[m][k]
}
let n = slices.len()/3;
dp(&slices[..slices.len()-1], n).max(dp(&slices[1..], n))
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
maxSizeSlices(slices: number[]): number {
const n = slices.length / 3;
function dp(arr: number[]): number {
const m = arr.length;
const f: number[][] = Array.from({length: m+1}, () => Array(n+1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (let k = 1; k <= n; k++) {
f[i][k] = Math.max(f[i-1][k], f[Math.max(0,i-2)][k-1]+arr[i-1]);
}
}
return f[m][n];
}
const a = slices.slice(0, slices.length-1);
const b = slices.slice(1);
return Math.max(dp(a), dp(b));
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^2), where n is the number of slices. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n^2), for the DP table.