Queens That Can Attack the King
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
On a 0-indexed 8 x 8 chessboard, there can be multiple black queens and one white king.
You are given a 2D integer array queens where queens[i] = [xQueeni, yQueeni] represents the position of the ith black queen on the chessboard.
You are also given an integer array king of length 2 where king = [xKing, yKing] represents the position of the white king.
Return the coordinates of the black queens that can directly attack the king. You may return the answer in any order.
Examples
Example 1
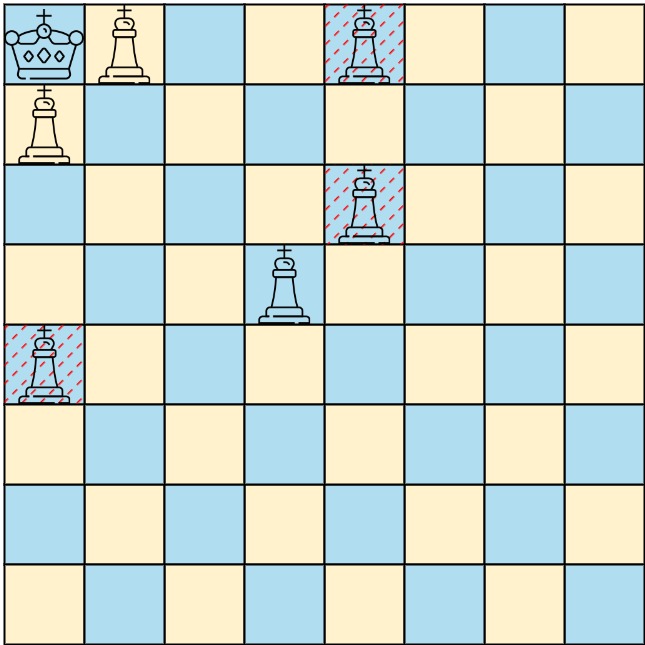
Input: queens = [[0,1],[1,0],[4,0],[0,4],[3,3],[2,4]], king = [0,0]
Output: [[0,1],[1,0],[3,3]]
Explanation: The diagram above shows the three queens that can directly attack the king and the three queens that cannot attack the king (i.e., marked with red dashes).
Example 2
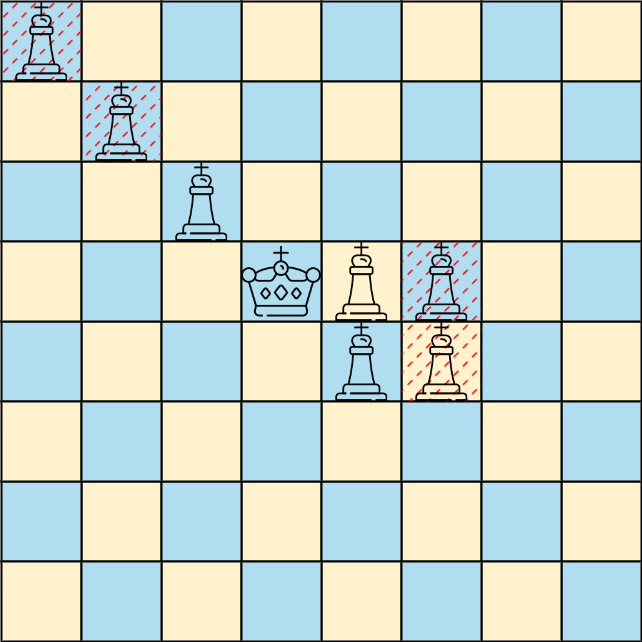
Input: queens = [[0,0],[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[3,5],[4,4],[4,5]], king = [3,3]
Output: [[2,2],[3,4],[4,4]]
Explanation: The diagram above shows the three queens that can directly attack the king and the three queens that cannot attack the king (i.e., marked with red dashes).
Constraints
1 <= queens.length < 64queens[i].length == king.length == 20 <= xQueeni, yQueeni, xKing, yKing < 8- All the given positions are unique.
Similar Problems
[Determine if a Chess King is in Check](determine-if-a-chess-king-is-in-check)
Solution
Method 1 – Directional Search
Intuition
For each of the 8 directions a queen can attack, move step by step from the king's position and stop at the first queen encountered. This ensures only the closest queen in each direction is considered.
Approach
- Store all queen positions in a set for O(1) lookup.
- For each of the 8 directions, move from the king's position until out of bounds or a queen is found.
- If a queen is found, add its position to the result and stop searching in that direction.
- Return all found positions.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> queensAttacktheKing(vector<vector<int>>& queens, vector<int>& king) {
set<pair<int,int>> s;
for (auto& q : queens) s.insert({q[0], q[1]});
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<pair<int,int>> dirs = {{-1,-1},{-1,0},{-1,1},{0,-1},{0,1},{1,-1},{1,0},{1,1}};
for (auto& d : dirs) {
int x = king[0], y = king[1];
while (0 <= x+d.first && x+d.first < 8 && 0 <= y+d.second && y+d.second < 8) {
x += d.first; y += d.second;
if (s.count({x, y})) { ans.push_back({x, y}); break; }
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func queensAttacktheKing(queens [][]int, king []int) [][]int {
s := map[[2]int]bool{}
for _, q := range queens { s[[2]int{q[0], q[1]}] = true }
dirs := [8][2]int{{-1,-1},{-1,0},{-1,1},{0,-1},{0,1},{1,-1},{1,0},{1,1}}
ans := [][]int{}
for _, d := range dirs {
x, y := king[0], king[1]
for {
x, y = x+d[0], y+d[1]
if x < 0 || x >= 8 || y < 0 || y >= 8 { break }
if s[[2]int{x, y}] { ans = append(ans, []int{x, y}); break }
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> queensAttacktheKing(int[][] queens, int[] king) {
Set<String> s = new HashSet<>();
for (int[] q : queens) s.add(q[0] + "," + q[1]);
int[][] dirs = {{-1,-1},{-1,0},{-1,1},{0,-1},{0,1},{1,-1},{1,0},{1,1}};
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] d : dirs) {
int x = king[0], y = king[1];
while (x + d[0] >= 0 && x + d[0] < 8 && y + d[1] >= 0 && y + d[1] < 8) {
x += d[0]; y += d[1];
if (s.contains(x + "," + y)) { ans.add(Arrays.asList(x, y)); break; }
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun queensAttacktheKing(queens: Array<IntArray>, king: IntArray): List<List<Int>> {
val s = queens.map { it[0] to it[1] }.toSet()
val dirs = listOf(-1 to -1, -1 to 0, -1 to 1, 0 to -1, 0 to 1, 1 to -1, 1 to 0, 1 to 1)
val ans = mutableListOf<List<Int>>()
for ((dx, dy) in dirs) {
var x = king[0]; var y = king[1]
while (x+dx in 0..7 && y+dy in 0..7) {
x += dx; y += dy
if (x to y in s) { ans.add(listOf(x, y)); break }
}
}
return ans
}
}
Python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def queensAttacktheKing(self, queens: List[List[int]], king: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
s = set(map(tuple, queens))
ans = []
for dx, dy in [(-1,-1),(-1,0),(-1,1),(0,-1),(0,1),(1,-1),(1,0),(1,1)]:
x, y = king
while 0 <= x+dx < 8 and 0 <= y+dy < 8:
x += dx; y += dy
if (x, y) in s:
ans.append([x, y])
break
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn queens_attackthe_king(queens: Vec<Vec<i32>>, king: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let s: std::collections::HashSet<(i32, i32)> = queens.iter().map(|q| (q[0], q[1])).collect();
let dirs = [(-1,-1),(-1,0),(-1,1),(0,-1),(0,1),(1,-1),(1,0),(1,1)];
let mut ans = vec![];
for (dx, dy) in dirs {
let (mut x, mut y) = (king[0], king[1]);
while 0 <= x+dx && x+dx < 8 && 0 <= y+dy && y+dy < 8 {
x += dx; y += dy;
if s.contains(&(x, y)) { ans.push(vec![x, y]); break; }
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
queensAttacktheKing(queens: number[][], king: number[]): number[][] {
const s = new Set(queens.map(([x, y]) => `${x},${y}`));
const dirs = [[-1,-1],[-1,0],[-1,1],[0,-1],[0,1],[1,-1],[1,0],[1,1]];
const ans: number[][] = [];
for (const [dx, dy] of dirs) {
let [x, y] = king;
while (x+dx >= 0 && x+dx < 8 && y+dy >= 0 && y+dy < 8) {
x += dx; y += dy;
if (s.has(`${x},${y}`)) { ans.push([x, y]); break; }
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(Q), where Q is the number of queens. Each direction checks at most 8 cells, and there are 8 directions. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(Q), for storing the queen positions in a set.