Rearrange array elements - first and second half in alternating order
EasyUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Problem
Given an array of integers of size 2n, write an algorithm to rearrange the array such that the first n elements and last n elements are set up in an alternating manner. For example, if n = 3 and the elements are [x1, x2, x3, y1, y2, y3], the result should be [x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3].
Examples
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Output: [1, 4, 2, 5, 3, 6]
Solution
Method 1 - Using Extra space
Here is the approach:
- Initialize an Output Array: Create an output array of the same size to store the rearranged elements.
- Rearrange Elements: Use a loop to copy elements from the input array to the output array in the alternating pattern:
- Copy the first
nelements (one by one) into even indices of the output array. - Copy the last
nelements (one by one) into odd indices of the output array.
- Copy the first
- Copy Back to Input Array (if needed).
Code
Java
public class Solution {
public void rearrangeArray(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length / 2;
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
// Copy elements in alternating fashion
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
result[2 * i] = nums[i]; // Copy from first half
result[2 * i + 1] = nums[i + n]; // Copy from second half
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2*n; i++) {
nums[i] = result[i];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution sol = new Solution();
int[] nums = {1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6};
sol.rearrangeArray(nums);
System.out.println("Rearranged array: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
// Expected output: 1 2 3 4 5 6
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def rearrangeArray(self, nums: List[int]):
n = len(nums) // 2
result = [0] * len(nums)
# Copy elements in alternating fashion
for i in range(n):
result[2 * i] = nums[i] # Copy from first half
result[2 * i + 1] = nums[i + n] # Copy from second half
for i in range(2 * n):
nums[i] = result[i]
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the auxiliary array.
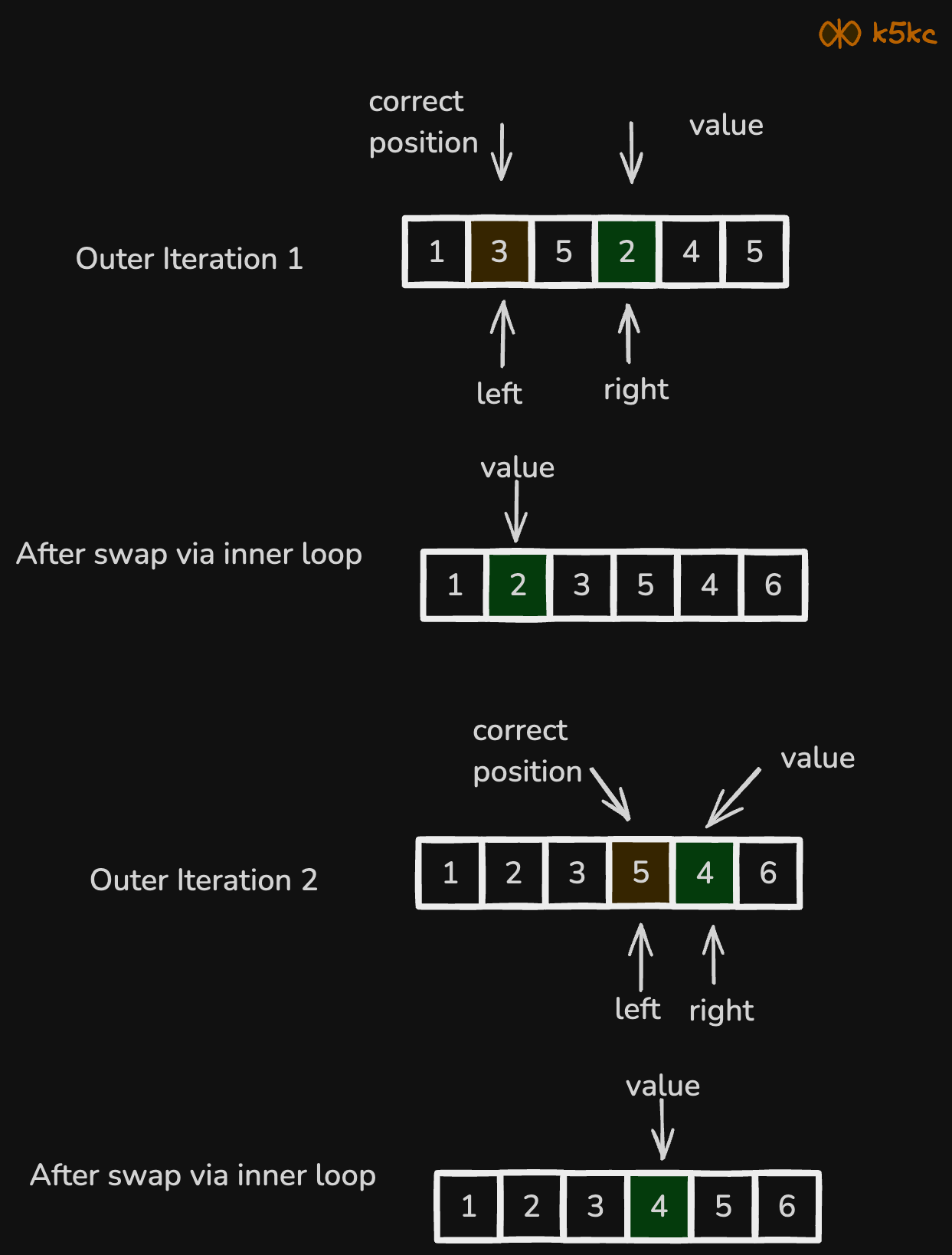
Method 2 - Naive - Shifting 1 by 1
Here is the approach:
- Shifting Elements:
- One by one, shift elements from the second half of the array to their correct positions in the left half.
- Use two pointers to keep track of elements to be swapped.
- In-place Swapping:
- Perform necessary swaps to achieve the desired rearrangement without using extra space.
Here is the visualization of how the logic will continue:
Code
Java
public class Solution {
public void rearrangeArray(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length / 2; // Calculate n from array length
int start = 0;
int end = nums.length - 1;
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
while (start < n && mid < end) {
int leftIndex = start + 1;
int rightIndex = mid + 1;
while (leftIndex < rightIndex) {
swap(nums, rightIndex, rightIndex - 1);
rightIndex--;
}
start += 2;
mid += 1;
}
// Print the rearranged array
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
System.out.print(nums[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int m, int n) {
int temp = nums[m];
nums[m] = nums[n];
nums[n] = temp;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def rearrangeArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
n = len(nums) // 2 # Calculate n from array length
start = 0
end = len(nums) - 1
mid = start + (end - start) // 2
while start < n and mid < end:
left_index = start + 1
right_index = mid + 1
while left_index < right_index:
self.swap(nums, right_index, right_index - 1)
right_index -= 1
start += 2
mid += 1
# Print the rearranged array
for i in range(len(nums)):
print(nums[i], end=" ")
print()
def swap(self, nums: List[int], m: int, n: int) -> None:
nums[m], nums[n] = nums[n], nums[m]
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^2), due to shifting elements in nested loops. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1), as the solution performs operations in place without extra space.
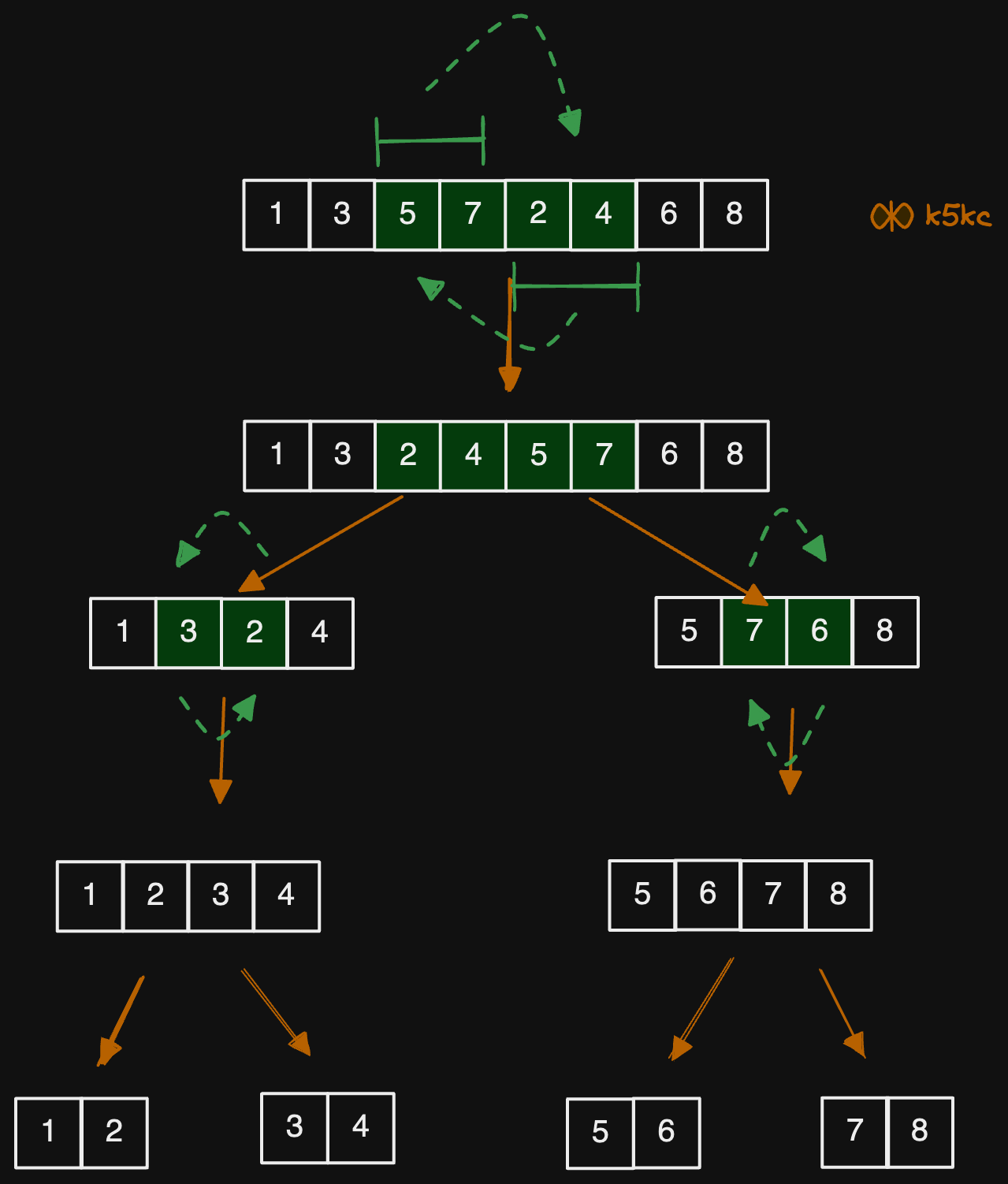
Method 3 - Divide and Conquer but for special case
This method only works if the total number of elements is a power of 2 (e.g., 2, 4, 8, 16, etc.).
Here is the approach
- For an array of length
2n, identify thenelements around the midpoint. - Swap
n/2elements to the left of the midpoint withn/2elements to the right of the midpoint. - Divide the array into two parts: the first
nelements and the lastnelements. - Recursively repeat steps 2 and 3 on both parts.
Code
Java
public class Solution {
public void rearrangeArray(int[] nums) {
rearrange(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private void rearrange(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
if (start >= end) return;
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
int x = 1 + (start + mid) / 2;
int y = mid + 1;
// Swap elements around the midpoint
for (int i = x, j = y; i <= mid; i++, j++) {
swap(nums, i, j);
}
// Recursively rearrange the two halves
rearrange(nums, start, mid);
rearrange(nums, mid + 1, end);
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int m, int n) {
int temp = nums[m];
nums[m] = nums[n];
nums[n] = temp;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def rearrangeArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
self.rearrange(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1)
def rearrange(self, nums: List[int], start: int, end: int) -> None:
if start >= end:
return
mid = start + (end - start) // 2
x = 1 + (start + mid) // 2
y = mid + 1
# Swap elements around the midpoint
for i, j in zip(range(x, mid + 1), range(y, y + (mid - x + 1))):
self.swap(nums, i, j)
# Recursively rearrange the two halves
self.rearrange(nums, start, mid)
self.rearrange(nums, mid + 1, end)
def swap(self, nums: List[int], m: int, n: int) -> None:
nums[m], nums[n] = nums[n], nums[m]
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n log n), due to the recursive division and swapping operations. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(log n), due to the recursion stack.