Redundant Connection II
Problem
In this problem, a rooted tree is a directed graph such that, there is exactly one node (the root) for which all other nodes are descendants of this node, plus every node has exactly one parent, except for the root node which has no parents.
The given input is a directed graph that started as a rooted tree with n
nodes (with distinct values from 1 to n), with one additional directed edge added. The added edge has two different vertices chosen from 1 to n, and was not an edge that already existed.
The resulting graph is given as a 2D-array of edges. Each element of edges
is a pair [ui, vi] that represents a directed edge connecting nodes ui
and vi, where ui is a parent of child vi.
Return an edge that can be removed so that the resulting graph is a rooted tree of n nodes. If there are multiple answers, return the answer that occurs last in the given 2D-array.
Examples
Example 1
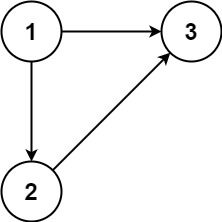
Input: edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: [2,3]
Example 2
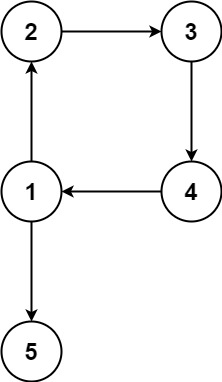
Input: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,1],[1,5]]
Output: [4,1]
Constraints
n == edges.length3 <= n <= 1000edges[i].length == 21 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi
Solution
Method 1 – Union-Find with Parent Tracking
Intuition
There are two possible issues: a node with two parents, or a cycle. If a node has two parents, removing either incoming edge may fix the tree. If not, the problem is a cycle. We use union-find to detect cycles and track parents to find nodes with two parents.
Approach
- For each edge, track the parent of each node. If a node has two parents, record both edges.
- Try removing the second edge (the later one). If the resulting graph is a tree (no cycle), return it. Otherwise, return the first edge.
- If no node has two parents, use union-find to find the edge that creates a cycle.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findRedundantDirectedConnection(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = edges.size();
vector<int> parent(n+1), candA, candB;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) parent[i] = i;
vector<int> par(n+1, 0);
for (auto& e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
if (par[v] == 0) par[v] = u;
else { candA = {par[v], v}; candB = e; e[1] = 0; }
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) parent[i] = i;
for (auto& e : edges) {
if (e[1] == 0) continue;
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
int pu = find(parent, u);
if (pu == v) return candA.empty() ? e : candA;
parent[v] = pu;
}
return candB;
}
int find(vector<int>& p, int x) { return p[x] == x ? x : p[x] = find(p, p[x]); }
};
Go
func findRedundantDirectedConnection(edges [][]int) []int {
n := len(edges)
parent := make([]int, n+1)
for i := range parent { parent[i] = i }
par := make([]int, n+1)
var candA, candB []int
for _, e := range edges {
u, v := e[0], e[1]
if par[v] == 0 {
par[v] = u
} else {
candA = []int{par[v], v}
candB = []int{u, v}
e[1] = 0
}
}
for i := range parent { parent[i] = i }
for _, e := range edges {
if e[1] == 0 { continue }
u, v := e[0], e[1]
pu := find(parent, u)
if pu == v {
if len(candA) == 0 { return e }
return candA
}
parent[v] = pu
}
return candB
}
func find(p []int, x int) int { if p[x] != x { p[x] = find(p, p[x]) }; return p[x] }
Java
class Solution {
public int[] findRedundantDirectedConnection(int[][] edges) {
int n = edges.length;
int[] parent = new int[n+1];
int[] par = new int[n+1];
int[] candA = null, candB = null;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) parent[i] = i;
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
if (par[v] == 0) par[v] = u;
else { candA = new int[]{par[v], v}; candB = e; e[1] = 0; }
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) parent[i] = i;
for (int[] e : edges) {
if (e[1] == 0) continue;
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
int pu = find(parent, u);
if (pu == v) return candA == null ? e : candA;
parent[v] = pu;
}
return candB;
}
int find(int[] p, int x) { return p[x] == x ? x : (p[x] = find(p, p[x])); }
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun findRedundantDirectedConnection(edges: Array<IntArray>): IntArray {
val n = edges.size
val parent = IntArray(n+1) { it }
val par = IntArray(n+1)
var candA: IntArray? = null
var candB: IntArray? = null
for (e in edges) {
val u = e[0]; val v = e[1]
if (par[v] == 0) par[v] = u
else { candA = intArrayOf(par[v], v); candB = e; e[1] = 0 }
}
for (i in 1..n) parent[i] = i
for (e in edges) {
if (e[1] == 0) continue
val u = e[0]; val v = e[1]
val pu = find(parent, u)
if (pu == v) return candA ?: e
parent[v] = pu
}
return candB!!
}
fun find(p: IntArray, x: Int): Int = if (p[x] == x) x else { p[x] = find(p, p[x]); p[x] }
}
Python
class Solution:
def findRedundantDirectedConnection(self, edges: list[list[int]]) -> list[int]:
n = len(edges)
parent = list(range(n+1))
par = [0] * (n+1)
candA = candB = None
for u, v in edges:
if par[v] == 0:
par[v] = u
else:
candA = [par[v], v]
candB = [u, v]
# Mark this edge as removed
v = 0
def find(p, x):
if p[x] != x:
p[x] = find(p, p[x])
return p[x]
for i in range(1, n+1):
parent[i] = i
for e in edges:
if e[1] == 0:
continue
u, v = e
pu = find(parent, u)
if pu == v:
return candA if candA else e
parent[v] = pu
return candB
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn find_redundant_directed_connection(edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = edges.len();
let mut parent: Vec<i32> = (0..=n as i32).collect();
let mut par = vec![0; n+1];
let mut cand_a = None;
let mut cand_b = None;
let mut edges = edges.clone();
for e in edges.iter_mut() {
let u = e[0] as usize;
let v = e[1] as usize;
if par[v] == 0 {
par[v] = u as i32;
} else {
cand_a = Some(vec![par[v], v as i32]);
cand_b = Some(vec![u as i32, v as i32]);
e[1] = 0;
}
}
for i in 1..=n { parent[i] = i as i32; }
for e in edges.iter() {
if e[1] == 0 { continue; }
let u = e[0] as usize;
let v = e[1] as usize;
let pu = find(&mut parent, u as i32);
if pu == v as i32 {
return cand_a.clone().unwrap_or_else(|| vec![e[0], e[1]]);
}
parent[v] = pu;
}
cand_b.unwrap()
}
}
fn find(p: &mut Vec<i32>, x: i32) -> i32 {
if p[x as usize] != x {
p[x as usize] = find(p, p[x as usize]);
}
p[x as usize]
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
findRedundantDirectedConnection(edges: number[][]): number[] {
const n = edges.length;
const parent = Array(n+1).fill(0).map((_,i)=>i);
const par = Array(n+1).fill(0);
let candA: number[]|null = null, candB: number[]|null = null;
for (const e of edges) {
const [u, v] = e;
if (par[v] === 0) par[v] = u;
else { candA = [par[v], v]; candB = [u, v]; e[1] = 0; }
}
for (let i = 1; i <= n; ++i) parent[i] = i;
for (const e of edges) {
if (e[1] === 0) continue;
const [u, v] = e;
let pu = find(parent, u);
if (pu === v) return candA ?? e;
parent[v] = pu;
}
return candB!;
}
}
function find(p: number[], x: number): number {
if (p[x] !== x) p[x] = find(p, p[x]);
return p[x];
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is the number of edges, since each edge is processed a constant number of times. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for parent and helper arrays.