Reschedule Meetings for Maximum Free Time I
Problem
You are given an integer eventTime denoting the duration of an event, where the event occurs from time t = 0 to time t = eventTime.
You are also given two integer arrays startTime and endTime, each of length n. These represent the start and end time of n non-overlapping meetings, where the ith meeting occurs during the time [startTime[i], endTime[i]].
You can reschedule at most k meetings by moving their start time while maintaining the same duration , to maximize the longest continuous period of free time during the event.
The relative order of all the meetings should stay the same and they should remain non-overlapping.
Return the maximum amount of free time possible after rearranging the meetings.
Note that the meetings can not be rescheduled to a time outside the event.
Examples
Example 1
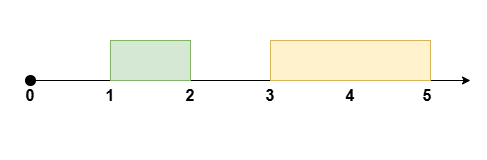
Input: eventTime = 5, k = 1, startTime = [1,3], endTime = [2,5]
Output: 2
Explanation:
Reschedule the meeting at `[1, 2]` to `[2, 3]`, leaving no meetings during the time `[0, 2]`.
Example 2
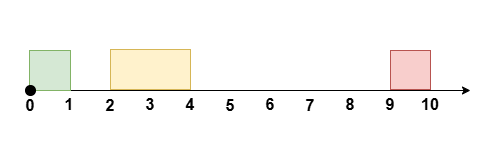
Input: eventTime = 10, k = 1, startTime = [0,2,9], endTime = [1,4,10]
Output: 6
Explanation:
Reschedule the meeting at `[2, 4]` to `[1, 3]`, leaving no meetings during the time `[3, 9]`.
Example 3
Input: eventTime = 5, k = 2, startTime = [0,1,2,3,4], endTime =
[1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 0
Explanation:
There is no time during the event not occupied by meetings.
Constraints
1 <= eventTime <= 10^9n == startTime.length == endTime.length2 <= n <= 10^51 <= k <= n0 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= eventTimeendTime[i] <= startTime[i + 1]whereilies in the range[0, n - 2].
Solution
Method 1 – Sliding Window on Gaps
Intuition
The free time is the gap between meetings. By rescheduling up to k meetings, we can "merge" up to k gaps, maximizing the largest continuous free time. This is a classic sliding window of size n-k+1 over the gaps.
Approach
- Compute all gaps between meetings, including before the first and after the last meeting.
- The answer is the maximum sum of any (k+1) consecutive gaps (i.e., after merging k gaps).
Code
C++
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int maxFreeTime(int eventTime, int k, vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime) {
int n = startTime.size();
vector<int> gaps(n + 1);
gaps[0] = startTime[0] - 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
gaps[i] = startTime[i] - endTime[i - 1];
}
gaps[n] = eventTime - endTime[n - 1];
int window = k + 1;
int curr = 0, maxSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < window; ++i) curr += gaps[i];
maxSum = curr;
for (int i = window; i < gaps.size(); ++i) {
curr += gaps[i] - gaps[i - window];
maxSum = max(maxSum, curr);
}
return maxSum;
}
};
Go
func maxFreeTime(eventTime int, k int, startTime []int, endTime []int) int {
n := len(startTime)
gaps := make([]int, n+1)
gaps[0] = startTime[0] - 0
for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
gaps[i] = startTime[i] - endTime[i-1]
}
gaps[n] = eventTime - endTime[n-1]
window := k + 1
curr, maxSum := 0, 0
for i := 0; i < window; i++ {
curr += gaps[i]
}
maxSum = curr
for i := window; i < len(gaps); i++ {
curr += gaps[i] - gaps[i-window]
if curr > maxSum {
maxSum = curr
}
}
return maxSum
}
Java
class Solution {
public int maxFreeTime(int eventTime, int k, int[] startTime, int[] endTime) {
int n = startTime.length;
int[] gaps = new int[n + 1];
// Before first meeting
gaps[0] = startTime[0] - 0;
// Between meetings
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
gaps[i] = startTime[i] - endTime[i - 1];
}
// After last meeting
gaps[n] = eventTime - endTime[n - 1];
int window = k + 1;
int curr = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < window; i++) curr += gaps[i];
int maxSum = curr;
for (int i = window; i < gaps.length; i++) {
curr += gaps[i] - gaps[i - window];
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, curr);
}
return maxSum;
}
}
Kotlin
fun maxFreeTime(eventTime: Int, k: Int, startTime: IntArray, endTime: IntArray): Int {
val n = startTime.size
val gaps = IntArray(n + 1)
gaps[0] = startTime[0] - 0
for (i in 1 until n) {
gaps[i] = startTime[i] - endTime[i - 1]
}
gaps[n] = eventTime - endTime[n - 1]
val window = k + 1
var curr = 0
for (i in 0 until window) curr += gaps[i]
var maxSum = curr
for (i in window until gaps.size) {
curr += gaps[i] - gaps[i - window]
maxSum = maxOf(maxSum, curr)
}
return maxSum
}
Python
def maxFreeTime(eventTime, k, startTime, endTime):
n = len(startTime)
# Compute all gaps
gaps = []
# Before first meeting
gaps.append(startTime[0] - 0)
# Between meetings
for i in range(1, n):
gaps.append(startTime[i] - endTime[i-1])
# After last meeting
gaps.append(eventTime - endTime[-1])
# Sliding window of size k+1
window = k + 1
max_sum = curr = sum(gaps[:window])
for i in range(window, len(gaps)):
curr += gaps[i] - gaps[i-window]
max_sum = max(max_sum, curr)
return max_sum
Rust
pub fn max_free_time(event_time: i32, k: i32, start_time: Vec<i32>, end_time: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let n = start_time.len();
let mut gaps = vec![0; n + 1];
gaps[0] = start_time[0];
for i in 1..n {
gaps[i] = start_time[i] - end_time[i - 1];
}
gaps[n] = event_time - end_time[n - 1];
let window = (k + 1) as usize;
let mut curr: i32 = gaps[..window].iter().sum();
let mut max_sum = curr;
for i in window..gaps.len() {
curr += gaps[i] - gaps[i - window];
if curr > max_sum {
max_sum = curr;
}
}
max_sum
}
TypeScript
function maxFreeTime(eventTime: number, k: number, startTime: number[], endTime: number[]): number {
const n = startTime.length;
const gaps: number[] = new Array(n + 1);
gaps[0] = startTime[0] - 0;
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
gaps[i] = startTime[i] - endTime[i - 1];
}
gaps[n] = eventTime - endTime[n - 1];
const window = k + 1;
let curr = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < window; i++) curr += gaps[i];
let maxSum = curr;
for (let i = window; i < gaps.length; i++) {
curr += gaps[i] - gaps[i - window];
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, curr);
}
return maxSum;
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n)— One pass to compute gaps, one pass for sliding window. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)— For the gaps array.